DMI
Bulk Data Entry Defines matrix (real) data blocks for Aeroelastic Analysis.
The matrix is defined by a single header entry and one or more column entries. Only one header entry is required.
Format
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | (10) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DMI | NAME | “0” | FORM | TIN | TOUT | M | N |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | (10) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DMI | NAME | J | I1 | A(I1, J) | A(I1+1, J) | … | I2 | ||
| A(I2, J) | etc |
Example 1
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | (10) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DMI | W2GJ | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 1 | ||
| DMI | W2GJ | 1 | 2 | 0.0017 | THRU | 4 |
Example 2
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | (10) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DMI | W2GJ | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 1 | ||
| DMI | W2GJ | 1 | 2 | 0.0017 | 0.0113 | 0.0045 |
Example 3
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | (10) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DMI | W2GJ | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 1 | ||
| DMI | W2GJ | 1 | 2 | 0.0017 | |||||
| 3 | 0.0125 | ||||||||
| 4 | 0.0713 |
Definitions
| Field | Contents | SI Unit Example |
|---|---|---|
| NAME | Name of the matrix. 1
(One to eight alpha-numeric characters, the first of which must be alphabetic.) |
|
| FORM | Matrix form.
(Integer) |
|
| TIN | Matrix input type.
One entry is used per aerodynamic panel/element. The size of these matrices should be the number of aerodynamic elements in the model. (Integer) |
|
| TOUT | Matrix output type. This field is currently unused, but a positive integer needs to be specified. |
|
| M | Number of rows in
NAME. (Integer > 0) |
|
| N | Number of columns in
NAME. (Integer > 0) |
|
| “0” | Indicates the header line. | |
| J | Column number of
NAME. (Integer > 0) |
|
| I1, I2, etc. | Row number of
NAME, which indicates the beginning of a
group of non-zero elements in the column. (Integer > 0) |
|
| A(Ix, J) | Value of element in row
Ix and column J.
(Real) |
Comments
- The DMI Bulk Data
Entry is only supported for Aeroelastic Analysis. The following names are
supported and any other names are ignored.
- WKK or WTFACT: Defines a diagonal matrix for an aero element where each element has its own weighting coefficient. This is relevant for both response (trim) and stability (divergence and flutter) analysis. The aerodynamic loads are corrected by pre-multiplying the aerodynamic forces by a weighting matrix.
- FA2J: Defines initial pressure coefficients for a panel or initial line doublet strength for a body element in Static Aeroelastic Analysis. This is relevant only for response (trim) analysis.
- W2GJ: Defines
initial downwash for an aero element in Static Aeroelastic Analysis.
This is relevant only for response (trim) analysis.
An example use-case for DMI in aeroelasticity is when a curved wing needs to be modeled. Instead of designing a complex geometry, a W2GJ matrix with suitable downwash can be defined for panels along the wing, which can account for the gradual change in the angle of attack.
- If the aeroelastic model does not have any slender bodies
(CAERO2), the values in a DMI matrix are referenced
in the aeroelastic panels as follows.
- The entries of DMI must be a column vector of size equal the number of aeroelastic boxes across all boxes in a CAERO1 Bulk Data Entry.
- When multiple CAERO1 Bulk Data Entries are present, then the box number set of each CAERO1 is arranged in ascending order of the CAERO1 IDs.
- For example, consider CAERO1 #1000 and CAERO1 # 2000 which have four and six boxes respectively and a DMI Bulk Data Entry defining initial downwash matrix (W2GJ).
Figure 1. 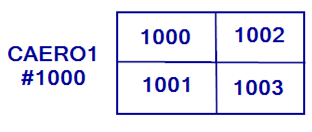
Figure 2. 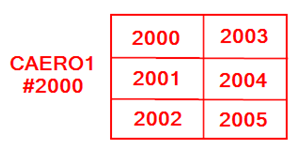
Then the values from the DMI Bulk Data Entry are applied as follows on the boxes.CAERO1 ID Box ID Initial Downwash 1000 1000 0.10 1001 0.20 1002 0.0 1003 0.40 2000 2000 0.30 2001 0.35 2002 0.50 2003 0.40 2004 0.60 2005 0.31 - If the aeroelastic model contains slender bodies
(CAERO2), the values corresponding to the bodies in
the DMI vector must be put behind those for the panels.
- The size of the column vector corresponding to the bodies is equal to the number of Z bodies and/or Y bodies plus two times the number of ZY bodies.
- When multiple CAERO2 entries are present, the element number set of each CAERO2 is arranged in ascending order of the CAERO2 IDs.
- Following the example of Figure 1 and Figure 2, assume that there are two additional bodies with one of them
being a ZY body (CAERO2 #3000) and the other
being a Z body (CAERO2 #4000).
Figure 3. 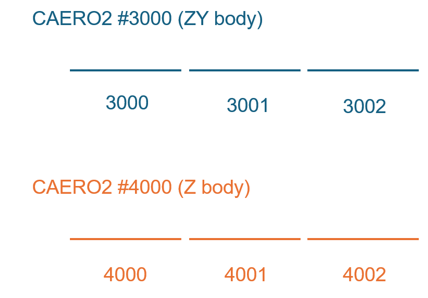
Then the complete set of values from the DMI entry are applied as follows:CAERO1 ID Box ID Initial Downwash 1000 1000 0.10 1001 0.20 1002 0.0 1003 0.40 2000 2000 0.30 2001 0.35 2002 0.50 2003 0.40 2004 0.60 2005 0.31 3000 3000(Y) 0.11 3000(Z) 0.12 3001(Y) 0.13 3001(Z) 0.21 3002(Y) 0.22 3002(Z) 0.23 4000 4000(Z) 0.31 4001(Z) 0.32 4002(Z) 0.33 - Only non-zero terms need be entered.
- Leading and trailing zeros in a column do not have to be entered. However, a blank field between non-zero fields on this entry is not equivalent to a zero. If a zero input is required, the appropriate type zero must be entered (0.0 or 0.0D0).
- If A(Ix, J) is
followed by THRU in the next field and an integer row number
Ix after the THRU, then A(lx, J)
will be repeated in each row through Ix. THRU must follow
an element value. For example, the entries for a real matrix FA2J would appear as:
(1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) (7) (8) (9) (10) DMI FA2J J I1 A(I1, J) I1 A(I2, J) DMI FA2J 1 2 1.0 THRU 10 12 2.0 These entries will cause the first column of the matrix FA2J to have a zero in row 1, the values 1.0 in rows 2 through 10, a zero in row 11, and 2.0 in row 12.
- Each column must be a single logical entry. The terms in each column must be specified in increasing row number order.
- I1 must be specified. I2, etc. are not required, if their matrix elements follow the preceding element in the next row of the matrix.
- The DMIG entry is more convenient for matrices with rows and columns that are referenced by grid or scalar point degrees-of-freedom.
- For more details, refer to the Aeroelastic Analysis in the User Guide.