CTPSTS
Bulk Data Entry Plane stress triangular element connection. Defines a plane stress triangular element in the x-z or x-y plane.
Format
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | (10) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTPSTS | EID | PID | G1 | G2 | G3 | G4 | G5 | G6 | |
| Theta |
Example
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | (10) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTPSTS | 111 | 2 | 31 | 74 | 75 | 32 | 51 | 52 | |
| 15.0 |
Definitions
| Field | Contents | SI Unit Example |
|---|---|---|
| EID | Unique element
identification number. No default (Integer > 0) |
|
| PID | A PPLANE entry identification
number. Default = EID (Integer > 0) |
|
| G1, G2, G3 | Identification numbers
of connected corner grid points. These fields are mandatory. No default (Integers > 0, all unique) |
|
| G4, G5, G6 | Identification numbers
of connected edge grid points. No default (Integers > 0 or blank) |
|
| Theta | Material orientation angle in
degrees. Default = 0.0 (Real) |
Comments
- Element identification numbers must be unique with respect to all other element identification numbers.
- The Grid ordering of
G1 through G6 is defined as:
Figure 1. 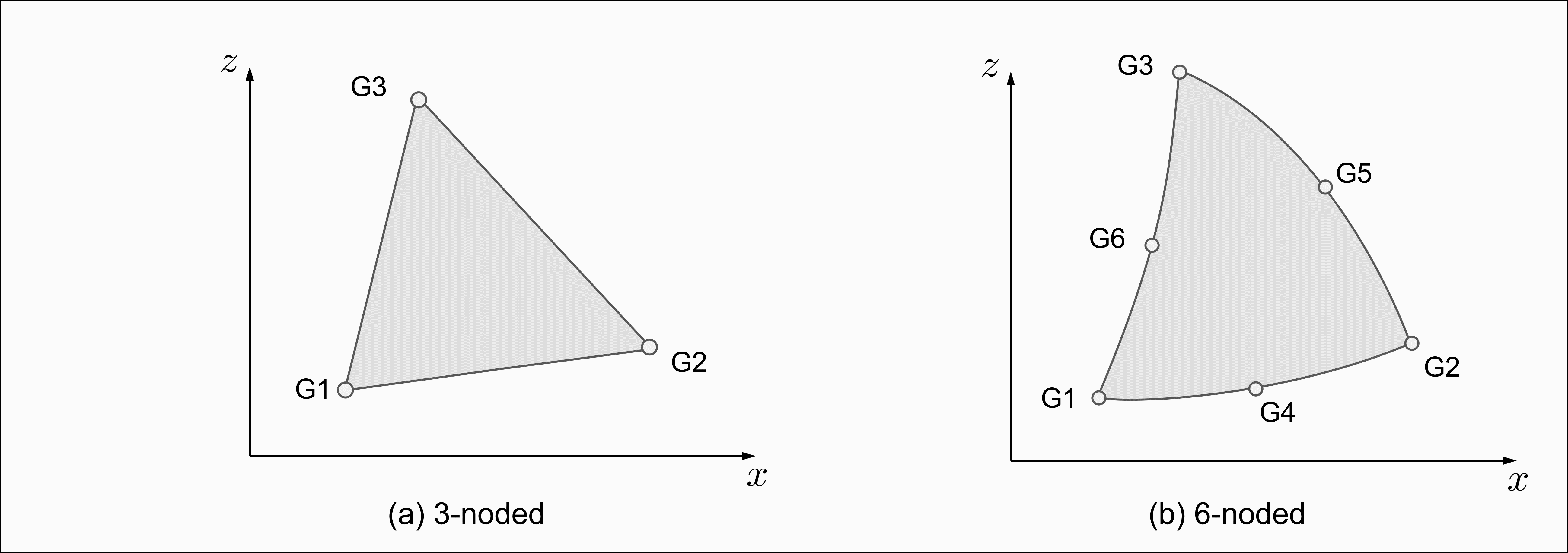
- The continuation is optional.
- The definition of the elemental coordinate system and material orientation angle theta is the same as defined for CTRIA3 and CTRIA6, depending on the number of nodes of CTPSTS elements.
- Plane stress analysis defined in x-y plane is supported, that is. the axis labels of “z” can be replaced by “y”. The out-of-plane normal direction defined by the corner node sequence with the right hand rule should point to the z direction if the element is in the x-y plane, or the -y direction if in the x-z plane.
- A concentrated load (for example,
a load specified by a FORCE entry) at a grid Gi of this
element is defined to distribute along the thickness, T, of the element. For
example, to apply a load of 200 N/m to a node Gi with the element thickness
being 0.05 m, the amount to be specified on the load entry should be
(200N/m) * 0.05m = 10N.
The default thickness of 1.0 is used if T is not specified on the PPLANE entry.
- Plane stress elements are
supported in:
- Linear static analysis
- Nonlinear Static analysis (Small and large displacement)
- Linear Transient Analysis
- Frequency Response Analysis
- Real and Complex Eigenvalue Analysis
These elements are currently not supported in:- Inertia Relief analysis
- Buckling analysis
- Heat transfer analysis
- Optimization