.cmode.csv file
This file is an output file generated during an Acoustic Complex Eigenvalue Analysis.
File Creation
This file is created when the PARAM, FCACSV Bulk Data Entry is set to -1 or 2 in an Acoustic Complex Eigenvalue Analysis.
File Contents
This file consists of four sections including Mass Fraction, Modal Assurance Criterion (MAC) – Structural, Modal Assurance Criterion (MAC) – Interface (Wet Surface), and Modal Assurance Criterion (MAC) – Fluid.
Mass Fraction
File Format
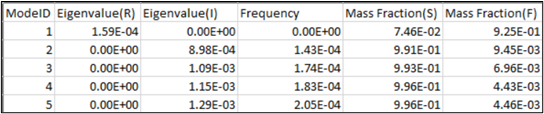
- Column
- Description
- Mode ID
- Complex mode ID
- Eigenvalue(R)
- Real part of eigenvalue
- Eigenvalue(I)
- Imaginary part of eigenvalue
- Frequency
- Frequency of modes
- Mass Fraction(S)
- Mass fraction (structural)
- Mass Fraction(F)
- Mass fraction (fluid)
Modal Assurance Criterion (MAC) – Structural
File Contents
Mapped Structural Modes:
A complex coupled mode corresponding to only structural grids is correlated with each
uncoupled structural mode. The mode with the highest MAC value is chosen for
printing under Mapped Mode ID shown in Figure 2. Corresponding frequency difference values are then calculated.
There is an extra column, MAC_Wet(S), which contains MAC values of the coupled mode
corresponding to wet structural grids versus uncoupled structural mode (this mode is
already identified via mapped mode ID).
- Coupled Mode ID
- ID of full eigenvector coupled mode (For example, mode Α1).
- Mapped Mode ID(S)
- ID of full eigenvector (EV) uncoupled structural mode.
- MAC(S)
- MAC values are calculated for: Coupled mode (Α1) EV corresponding to the only structural grids versus each full EV uncoupled structural mode (mode 1 to mode N, where N is the total number of uncoupled structural modes).
- MAC_Wet(S)
- MAC value is calculated for: Coupled mode (Α1) EV corresponding to only the wet surface structural grids versus uncoupled structural mode (identified in the Mapped Mode ID(S) field) corresponding to the wet surface structural grids.
File Format
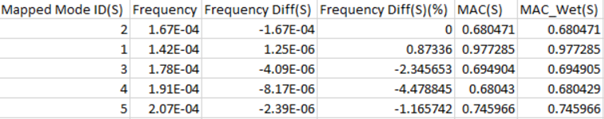
- Column
- Description
- Mapped Mode ID
- Mapped uncoupled structural mode ID
- Frequency
- Frequency of uncoupled structural mode
- Frequency Diff(S)
- Frequency Diff: Coupled mode – Uncoupled mode
- Frequency Diff(S) (%)
- Percentage of frequency difference
- MAC(S)
- Modal Assurance Criterion: Coupled modes (structural grids only) versus uncoupled full eigenvector structural modes (MAC)
- MAC_Wet(S)
- Model assurance criterion values for coupled modes versus structural
wetted modesImportant: These are modes of the wet surface structural grids for corresponding modes in the listed Mapped Mode ID(S) column.
Modal Assurance Criterion (MAC) –Interface (Wet Surface)
File Contents
Mapped Wetted Modes:
A coupled mode corresponding only to structural grids of the wet surface is
correlated with each uncoupled structural mode corresponding to the structural grids
of the wet surface. The one with highest MAC value is chosen for printing under
Mapped Mode ID shown in Figure 3. Corresponding frequency difference values are then
calculated.
- Coupled Mode ID
- ID of full eigenvector coupled mode (For example, mode Α1).
- Mapped Mode ID(WS)
- ID of uncoupled structural mode corresponding only to structural grids of the wet surface.
- MAC(WS)
- MAC values are calculated for: Coupled mode (Α1) corresponding only to structural grids of the wet surface versus each uncoupled structural mode corresponding only to structural grids of the wet surface (mode 1 to mode N, where N is the total number of uncoupled structural modes).
File Format
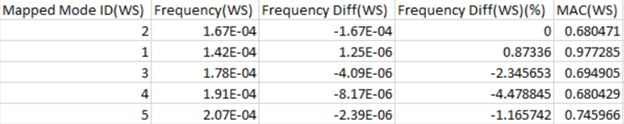
- Column
- Description
- Mapped Mode ID(WS)
- Mapped uncoupled mode ID corresponding to the wet surface
- Frequency(WS)
- Frequency of mode ID corresponding to the wet surface
- Frequency Diff(WS)
- Frequency Diff: Coupled mode corresponding to the wet surface – Uncoupled mode corresponding to the wet surface
- Frequency Diff(WS) (%)
- Percentage of frequency difference
- MAC(WS)
- Model assurance criterion values for uncoupled modes corresponding to wet surface versus coupled modes corresponding to the wetted surface
Modal Assurance Criterion (MAC) – Fluid
File Contents
Mapping Fluid Modes:
A coupled mode corresponding to only the fluid grids is correlated with each
uncoupled fluid mode and the one with highest MAC value is chosen for printing under
Mapped Mode ID, as shown in Figure 4. Corresponding frequency difference values are then
calculated.
- Coupled Mode ID
- ID of full eigenvector coupled mode (For example, mode Α1).
- Mapped Mode ID
- ID of full eigenvector (EV) uncoupled fluid mode.
- MAC(F)
- MAC values are calculated for: Coupled mode (Α1) EV corresponding to only the fluid grids versus each full EV uncoupled fluid mode (mode 1 to mode N, where N is the total number of uncoupled fluid modes).
File Format
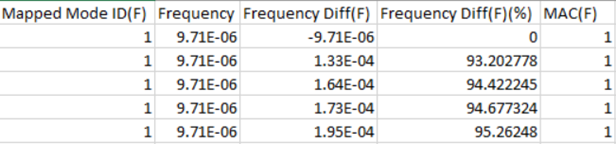
- Column
- Description
- Mapped Mode ID(F)
- Mapped uncoupled fluid mode ID
- Frequency
- Frequency of uncoupled fluid mode
- Frequency Diff(F)
- Frequency Diff: Coupled mode – Uncoupled mode
- Frequency Diff(F) (%)
- Percentage of frequency difference
- MAC(F)
- Model assurance criterion values for fluid modes versus coupled modes