3D Anisotropic Medium
This option specifies an anisotropic (3D) medium represented by a simple diagonal tensor, a nine element (full) tensor, complex tensor or a Polder tensor (for ferrites)
Diagonal tensor
Define the diagonal permittivity and permeability tensors by defining up to three dielectrics constituting the medium properties along the UU, VV and NN axes. If no linear dependencies exist between two axes, enter 0. A value of 0 indicates empty or zero. Use the text, Free space, to indicate the free space medium.
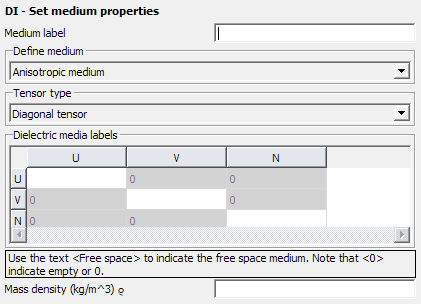
Figure 1. The DI - Set medium properties dialog, for Anisotropic medium, set to Diagonal tensor.
Full tensor
Define the permittivity and permeability tensors by defining up to nine dielectrics constituting the medium properties along the UU, UV, UN, VU, VV, VN, NU, NV and NN axes. If no linear dependencies exist between two axes, enter 0. A value of 0 indicates empty or zero. Use the text, Free space, to indicate the free space medium.
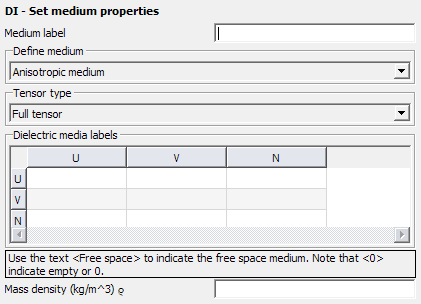
Figure 2. The DI - Set medium properties dialog, for Anisotropic medium, set to Full tensor.
Complex tensor
Define the permittivity and permeability tensors by using complex values. An entry in the tensor may be a complex number, pure real number or a pure imaginary number, but not 0.
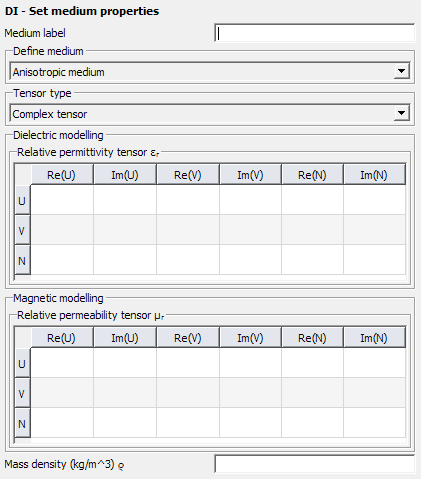
Figure 3. The DI - Set medium properties dialog, for Anisotropic medium, set to Complex tensor.
Polder tensor (ferrites)
Define a ferromagnetic material.
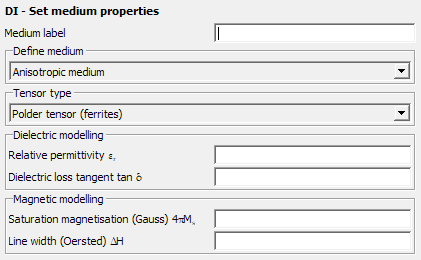
Figure 4. The DI - Set medium properties dialog, for Anisotropic medium, set to Polder tensor.
- Relative permittivity
- Relative permittivity of the medium.
- Dielectric loss tangent
- Dielectric loss tangent of the ferrite.
- Saturation magnetisation (Gauss)
- Saturation magnetisation of the ferrite.
- Line width (Oersted)
- Line width of the ferrite.