Part Browser
Use the Part Browser to create, organize and manage the CAE part structure/hierarchy.

By default, the following attributes are listed as columns.
Add or remove columns by right-clicking on a column and checking/unchecking the appropriate attribute.
- Entity
- List of the Model, Part Assemblies, Parts, and Components. By default the browser is displayed in Hierarchical View.
- Color
- Displays the Component and Part entity colors.
- UID
- Displays the Part Assembly and Part Unique IDs.
- Revision
- Displays the Major revision, Study revision, and Library Part revision.
- Representation
- Displays the in-session/loaded representation.
- Active
- Displays the Part entity active status.
For a full description of usage, refer to Manage Configurations.
- CID
- Displays the entity specific Component ID’s. At the Part level it displays IDs for owned components. At Component level it shows the ID of components.
- PID
- Displays the entity specific Property ID’s. At the Part level it displays IDs for referenced properties. At Component level it shows the ID of the referenced property.
- MID
- Displays the entity specific Material ID’s. At the Part level it displays IDs for referenced materials. At Component level it shows the ID of the referenced material.
- Material
- Displays the material name.
- Thickness
- Displays the entity specific thickness. At the Part level it displays the thicknesses of the referenced properties. At Component level it shows the thickness of the referenced property.
- PDM PID
- PDM Property ID metadata.
- PDM MID
- PDM Material ID metadata.
- PDM Material
- PDM Material name metadata.
- PDM Thickness
- PDM Thickness metadata.
- PDM MeshFlag
- PDM Mesh metadata (not case sensitive).
- PDM Variant Condition
- If populated, displays the part that is used as a variant in one or multiple part configurations. It is user editable in the Entity Editor.
- PDM Variant Scope
- Along with the Variant Condition attribute, displays which part configurations the part belongs to as a variant. It is user editable in the Entity Editor.
View Modes
Access different views to create and organize parts, and subsystem sets and configurations.

- Entity View: displays a single view in the browser for parts.
- Set View: splits the browser into two views: Entity View and Set View. In the Set View you can create, organize and manage part sets.
- Configuration View: splits the browser into three vertical views: Configuration, Set and Entity View. In the Configuration view you can create, organize and manage configurations.
- Configuration View, Split Left: splits the browser into three views: Configuration, Set and Entity View. In the Configuration view you can create, organize and manage part configurations.
Part View Modes
- Hierarchical Part View: displays all entities, including components, in a
hierarchical view.
Figure 4. 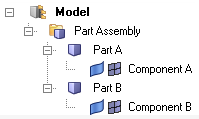
- Flat Part View: displays entities in a flat list. Part Assemblies and Parts
are grouped into their own collectors.
Figure 5. 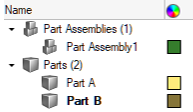
Entity Editor
Edit part and component attributes in the Entity Editor.
Edits can be made for a single part or component or multiple parts and components. If a component is selected, the Entity Editor displays component specific attributes.
The attributes available in the Entity Editor vary based on the entity type selected.
Part/Part Assembly
- General Data
- Displays attributes that are unique to the part or assembly, including part/assembly name, Unique ID (UID), color, and include file, and Revision data.
- Representations Data
- Displays attributes that are specific to a part representation, such as representation name, file location, property ID, material ID/name, and thickness. These attributes are non-editable at the part level.
- Position Data
- Displays the 4 x 3 transformation matrix of a part, namely its translation, rotation, and scaling. These attributes are non-editable in the Entity Editor, but updates as you move the part.
- Library Data
- Displays the Major, Study, and Library revisions of the representations. The comment saved along with the representation is displayed here.
- PDM Data
- Displays PDM attributes that were parsed as metadata during the BOM importation, such as PDM ID, PDM Revision, PDM Variant Condition and PDM Variant Scope. This information, namely the PDM PID, PDM MID, PDM Material and PDM Thickness, is used to generate the initial component, property, and material cards upon creation of the common representation. These attributes can be used to cross-reference common and discipline specific mesh representation attributes.
Part Set
- General Data
- Displays attributes that are unique to the part set, including part/assembly name and ID.
- Part Assemblies / Parts Data
- Displays the number of parts organized into the selected part set.
- Part Sets Data
- Displays the number part sets organized into the selected part set.
Configuration
- General Data
- Displays attributes that are unique to the configuration, including name, and ID.
- Parts Assemblies / Parts Data
- Displays the number of parts organized into the selected configuration.
- Configurations Data
- Displays the number of configurations organized into the selected configuration.
- Part Sets Data
- Displays the number part sets organized into the selected configuration.
- Active
- Indicates the active/inactive state of the selected configuration. This attribute is non-editable. To activate a configuration, enable the configuration’s associated checkbox in the Active column of the Configuration view.