ID Management
Manage the IDs for the entities that you create, and define ID ranges for the entities in each Include file in order to avoid ID duplication across files.
Perform ID management in the ID Manager.
Once the ID ranges are defined for an Include file, any new entities created will be assigned an ID within the ID range following the new ID rules. Entities that are imported into the Include file will have the IDs that overflow after import automatically corrected by Move After Max option.
Aside from new entity creation and import, the ID Manager will not actively correct IDs in the model. If there are entity IDs that fall outside of the ID range, they will remain as overflow and must be corrected by renumbering in ID Manager.
FE entities in CAE models are labeled and tagged using IDs and names. IDs are used by the solvers during analysis and then passed on by the solver to the results. This process enables you to interpret the results and relate them to the FE model. In most cases, the IDs of the FE entities in a FE model must be unique for efficient identification. In large models it is essential to have a tool that manages a model's IDs consistently at the global level for ease of identification using IDs.
Manage IDs
Learn how to perform various ID management operations.
Create ID Ranges for New Entity Types
ID ranges can be defined for entity types that do not yet exist in the Main Model or in an Include file.
-
From the Assembly ribbon, click the ID
Manager tool.
Figure 1. 
The ID Manager opens. - Click on the Min or Max column of an Include file and enter the start or end value of the include's ID range.
- Alternatively, right-click on the Master Model or an Include file and select from the context menu.
- In the Create dialog, select an entity type and enter a Minimum ID and Maximum ID.
- Click OK.
Edit ID Ranges
Edit the minimum and maximum ID range of the Main Model, Include files, and entities.
-
From the Assembly ribbon, click the ID
Manager tool.
Figure 2. 
The ID Manager opens. - Click the Min and Max columns and enter new values.
Clear ID Ranges
-
From the Assembly ribbon, click the ID
Manager tool.
Figure 3. 
The ID Manager opens. -
Clear ID ranges in the following ways:
Option Description Clear all ID ranges Clear all defined ID ranges across all Include files in your model by right-clicking on the Main Model and selecting Clear All ID Ranges from the context menu. Clear selected ID ranges Clear ID ranges for a single Include file or entity by right-clicking on the Include file or entity and selecting Clear ID-Ranges from the context menu.
Review ID Overflow
-
From the Assembly ribbon, click the ID
Manager tool.
Figure 4. 
The ID Manager opens. - In the ID Manager, use the No. Overflow column to review the number of entities that do not fail inside the ID range of the include.
- Right-click on an entity and select to review the list of IDs that are outside of the designated range.
-
Review overflow IDs in the modeling window.
- Right-click on each entity to access additional display options from the context menu, such as Show, Hide, Isolate, or Isolate.
Renumber
-
From the Assembly ribbon, click the ID
Manager tool.
Figure 5. 
The ID Manager opens. - Right-click on an Include file or entity and select Renumber from the context menu.
Any IDs which fall outside of the ID range will be renumbered using the correction option assigned in the Correction Option column. If you right-click in whitespace, then this operation will be performed on all of the overflow IDs inside of the model.
If the ID Manager cannot correct all of the IDs, a warning message will be displayed and none of the overflow IDs within an Include file/entity folder will be corrected.
Compact Entities
All entities in an Include File will be renumbered starting from the minimum ID and will ensure there are no ID gaps.
-
From the Assembly ribbon, click the ID
Manager tool.
Figure 6. 
The ID Manager opens. -
Right-click on a Main Model, Include File, or entity and select
Compact Entities from the context menu.
Note: This option is only available if you have an ID range defined.
Lock/Unlock IDs
Lock IDs to prevent them from being changed by future ID management and renumbering operations, or unlock IDs so they can be changed.
-
Lock IDs.
-
Unlock IDs.
Reserve/Unreserve IDs
Reserve and unreserve available IDs for future use. After IDs are reserved, they cannot be occupied from renumbering operations or new entity creation.
When reserving IDs, if the IDs being reserved does not fall within the defined ID range, then those IDs will still be reserved but will be listed under the Main Model.
If you reserve IDs for an entity that supports ID pools, the reserved IDs will be applied to each ID pool. For example, the count for elements reserves in LS-DYNA includes reserves for each element pool available for the given ID range.
When an ID range is cleared, reserved IDs will be moved to the Main Model. If the ID range is re-entered, reserved IDs will be moved back to the entity it was originally reserved for. If you create an exclusion or delete an ID range at the entity level, the reserve range defined and the reserves defined within that range will be removed.
-
Reserve IDs.
-
Unreserve IDs.
Import/Export a CSV File of ID Management Rules
Import/export a .csv file of ID management rules.
-
From the Assembly ribbon, click the ID
Manager tool.
Figure 11. 
The ID Manager opens. -
Right-click and select Export CSV file.
A Save File dialog opens.
- Select a location in which to write the .csv file.
-
Click
 , and select a method.
Three different levels of detail are available for the export.
, and select a method.
Three different levels of detail are available for the export.- All entities: exports each row shown in ID Manager into the .csv.
- Entities with ID rules: exports only rows with ID ranges defined into the .csv.
- Includes and entities with ID rules: exports all include information regardless of if ID ranges have been defined and additionally each line has ID rules.
Note: If an entity contained in an include has the same ID rules as the include itself, for options 2 and 3 those entities will not be written into the .csv as the entities are taking the rule from the include itself. If the ID rules on the entity level are different to the include, they will be exported.
ID management data related to overflow, min/max occupied IDs, number of conflicts, number of reserves, and number of locks will be calculated while reading the .csv file.
When you are importing a .csv file, you will be notified if overlapped ID ranges are identified.
Create/Delete Included Files
-
From the Assembly ribbon, click the ID
Manager tool.
Figure 12. 
The ID Manager opens. -
Create or delete Include files.
Option Description Create From the right-click context menu, select . Delete - Right-click on an Include file and select Delete from the context menu.
- In the Delete Entity dialog, select Also delete children entities to delete the selected Include file(s) along with its child entities.
- Click OK.
Exclude Entities
Excluded entities will not be renumbered by ID Manager. The excluded column is off by default.
-
From the Assembly ribbon, click the ID
Manager tool.
Figure 13. 
The ID Manager opens. -
Exclude entities in the following ways:
- To exclude a specific entity, right-click on a Main Model, Include file,
or entity and select from the context menu.
If you right-click on a Main Model or Include file you must select a type of entity to exclude in the Exclude dialog.
- To exclude IDs of the same entity type across all Include files, right-click on an entity and select from the context menu.
- To exclude a specific entity, right-click on a Main Model, Include file,
or entity and select from the context menu.
Clear Exclusions
-
From the Assembly ribbon, click the ID
Manager tool.
Figure 14. 
The ID Manager opens. -
Clear exclusions in the following ways:
- To clear excluded IDs for a specific entity, right-click on one or more entities and select from the context menu.
- To clear excluded IDs of the same entity type across all Include files, right-click on an entity and select from the context menu.
Note: Multiple entities across Include files can be selected.
Correct Reserve Conflicts
-
From the Assembly ribbon, click the ID
Manager tool.
Figure 15. 
The ID Manager opens. -
Right-click on the entity folder that contains conflicts and select from the context menu.
Note: Nodes and element entities are isolated in the modeling window.
- In the panel area, use the selector or other extended entity selection options to select IDs to correct.
- Click proceed.
-
In the Correct Reserve Conflicts dialog, select a
correction method to resolve conflicts with.
- Choose Move Out to move the selected IDs out of reserve range and renumbers them using the max +1 rule, which is the maximum ID available plus 1. If the ID range is full, corrected IDs will be marked as overflow. The conflict icon will only be removed if you resolve all of the conflicts.
- Choose Lock to lock IDs in the reserve range and populates the Lock column. The conflict icon will display, and all of the IDs listed in the reserve range are locked.
- Click OK.
ID Manager Dialog
Overview of the ID Manager user interface.

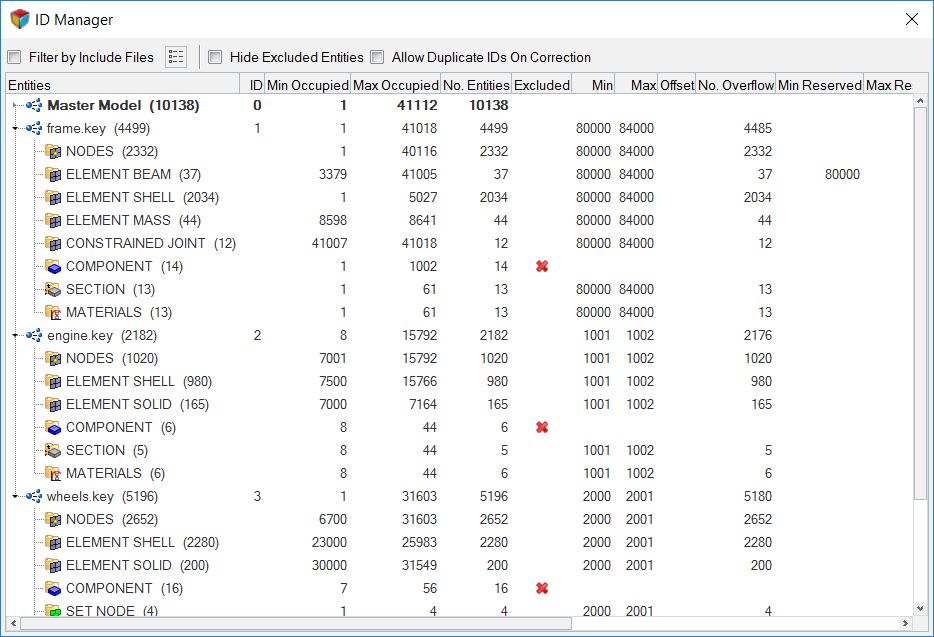
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Allow Duplicate IDs on Correction | When enabled, duplicate ID pool's for supported entities are permitted to have the same IDs. |
| Name | Displays the Main Model, Includes, and the child entity types within them. |
| Include | For entities, displays the ID of the include in which they are organized. |
| Min Occupied | Displays the minimum ID occupied by all of the entities in an Include file. For individual entities, it displays the corresponding minimum ID occupied in the Include file. |
| Max Occupied | Displays the maximum ID occupied by all of the entities in an Include file. For individual entities, it displays the corresponding maximum ID occupied in the Include file. |
| No. Entities | Displays the total number of entities in Include files and entity folders. |
| Min | Enter a minimum integer value for the ID range that does not overlap with any other range definitions in the model. |
| Max | Enter a maximum integer value for the ID range that does not overlap with any other range definitions in the model. |
| No. Overflow | Displays the number of IDs in an Include file or entity folder that are outside of the defined range. |
| No. Reserved | Displays the number of IDs reserved at the entity level. If an entity type supports ID pools, the #Reserved column will display the total number of reserves applied to each ID pool in that entity type. |
| No. Locks | Displays the number of IDs that have been locked from renumbering. |
| New ID | Determines where new IDs will be placed within the current Include file range.
If the ID Manager cannot find any free IDs using the After Max and Before Min options, then newly created entities will be assigned IDs using the Fill in Gaps option. If the ID Manager cannot find any free IDs within the defined ID range using any of the above options, then newly created entities will be assigned IDs beyond the Max ID occupied or the Max ID defined in the model, whichever one is being the highest. |
| Correction | Determines how duplicate IDs are renumbered to correct overflow.
Note: IDs that are locked or reserved in an Include file will not be
renumbered. |
| Advanced columns default off: | |
| ID | Displays the ID of the Include file. |
| Excluded | Displays an X icon ( ) when an entity is excluded from ID
management operations. ) when an entity is excluded from ID
management operations. |
| Offset | Displays the ID range offset for a solversubmodel. |
| Min Reserved | Minimum integer value for the reserve ID range. You can manually edit the Min
Reserved column as long as your modifications do not violate the Min and Max ID
range. When you reserve all IDs, the Min Reserved and Max Reserved columns are populated using the Min and Max ID range defined at the entity level. |
| Max Reserved | Maximum integer value for the reserve ID range. You can manually edit the Max
Reserved column as long as your modifications do not violate the Min and Max ID
range. When you reserve all IDs, the Min Reserved and Max Reserved columns are populated using the Min and Max ID range defined at the entity level. |
| Conflict | Displays a conflict icon ( |
| No. Conflicts | Displays the number of conflicts in a reserve range. |
| User Status | User defined status indicator which can be manually set to show the status of
reserve conflicts.
|
ID Manager Examples
Examples to provide you with a more in-depth understanding of the ID management functionality.
New ID
The example below explains how new components are assigned an ID after you have defined an ID range and established rules for ID management.
- After Max
- New components will be assigned IDs from 98, 99, and 100. Once the Max ID of 100 reached, any new component created will use the Fill in Gap option and be assigned IDs starting from 1.
- Before Min
- New components will be assigned IDs from 3, 2, and 1. Once the Min ID of 1 reached, any new component created will use the Fill in Gap option and be assigned IDs starting from 1.
- Fill in Gaps
- New components will be assigned available IDs starting from the Min ID of 1, 2, 3, 6, and so on.
ID Correction
The example below explains how the different correction options correct overflow IDs.
- None
- No correction is performed and the overflow IDs remain the same.
- Compact and Fit
- Compacts the IDs that are already occupied in the Include, and places the overflow
IDs into the range starting from the Min ID of the defined range. The overflow IDs
will be assigned the following new IDs:
IDs Before Correction IDs After Correction 4 10 5 11 20 -60 12 - 52 80 - 90 53 - 63 101 64 105 65 110 66 117 67 - Move After Max
- Places the IDs that overflow after the Max ID occupied in the defined range. The
overflow IDs will be assigned the following new IDs:
IDs Before Correction IDs After Correction 4 91 5 92 20 - 60 20 - 60 80 - 90 80 - 90 101 93 105 94 110 95 117 96 - Move Before Min
- Places the IDs that overflow before the Min ID occupied in the defined range. The
overflow IDs will be assigned the following new IDs:
IDs Before Correction IDs After Correction 4 19 5 18 20 - 60 20 - 60 80 - 90 80 - 90 101 17 105 16 110 15 117 14 - Insert in Gaps
- Places the IDs that overflow into the gaps in the defined range. The overflow IDs
will be assigned the following new IDs:
IDs Before Correction IDs After Correction 4 10 5 11 20 -60 20 - 60 80 - 90 80 - 90 101 12 105 13 110 14 117 15
Reserve ID
The following examples explain how to reserve IDs using the ID Manager.
An Include file contains components with the following IDs: 4, 5, 20 - 60, 80 - 90, 101, 105, 110, and 117. From the ID Manager, an ID range of 10 through 100 is defined for the Include file, resulting in six overflow components. To correct the overflow IDs, a correction option is selected.
By reserving all of the IDs within the range 1-100, the Number of ID reserves will be populated to 46, which is number of available IDs for the ID range 1-100 (available IDs include: 1-3, 6-19, 61-79 and 91-100).
If a reserve is applied to an entity that supports ID pools, the reserves will be applied to each ID pool of that entity. For example, consider a LS-DYNA model that has 10 ID pools for properties. If an ID range of 1-100 as defined, as in the above example with the same individual IDs for properties as opposed to components, the total count of reserves will be 460 (46 per pool and a total 10 pools).