Swept Sine
A Swept Sine event simulates a vehicle driving at a constant speed with a sinusoidal steering input of constant magnitude but increasing frequency applied.
Output Requests are included to measure the vehicle state variables, tire forces, and tire state variables. The Altair Driver steers the vehicle and maintains constant speed.
The Swept Sine event is supported by the Cars & Small Trucks and Heavy Trucks vehicle libraries. Automated output reports are available to plot the results.
The Swept Sine event follows the ISO +7401-2003 - Road vehicles — Lateral transient response test methods — Open-loop test methods.
Parameters
| Parameter Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Units | Describes the Length, Velocity, and Acceleration units.
|
| Velocity | The constant speed that the vehicle attempts to maintain during the event. |
| Steer amplitude | Amplitude of the steering input (degrees). |
| Frequency change rate | The rate of change of frequency (hz/sec) of the sine wave function applied to the steering wheel. |
| Minimum frequency | The minimum (initial) frequency sine wave that is applied to the steering wheel. |
| Maximum frequency | The maximum (final) frequency sine wave that can be applied to the steering wheel. |
| Start time | The start time of the sine wave. |
| End Time | End time of the simulation (calculated using the start time, the frequency rate, and the max and min frequencies). |
- Initial Static and Steering Ratio
-
Run initial static Enables the execution of the initial static simulation. Compute steering ratio Enables the automatic calculation of the steering ratio at the beginning of the event simulation. Turn this option off to use a different Steering ratio (default value of 16 is provided). - End Time Calculation
- The parameters defined above are also used to determine the total simulation time.
The total simulation time for each maneuver is specified in the Altair Drive File
(.adf) as shown below:
Figure 1. Maneuvers List Block for a Swept Sine Steering Event 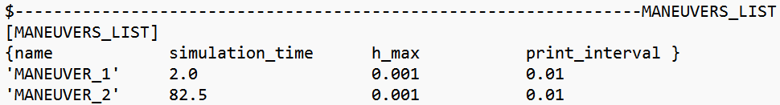
In a Swept Sine Steering event:.- MANEUVER_1 represents the initial part of the event, before steering input is applied.
- MANEUVER_2 corresponds to the part of the event after the swept sine input is applied to the steering wheel.
The total simulation time for each maneuver is calculated using the following equations:Maneuver Simulation Time Equation Maneuver 1 Start timeManeuver 2 (Maximun Frequency-Minimun Frequency)/ Frequency Change RateThe total simulation time corresponds to the sum of the total simulation times for Maneuver 1 and Maneuver 2.
Controller Settings
- LONGITUDINAL – TRACTION CONTROLLER SETTINGS
- Use additional control: Enables the additional feedback control for the traction
control. The gains for the controller can be edited by toggling this check
box.
Kp Proportional gain for the feedback PID controller Ki Integral gain for the feedback PID controller Kd Derivative gain for the feedback PID controller
- Use additional control: Enables the additional feedback control for the traction
control. The gains for the controller can be edited by toggling this check
box.
Signal Settings
Use the signal settings to set minimum, maximum, smooth frequency and initial values for Steering, Throttle, Brake, Gear, and Clutch signals output by the driver.
The smoothing frequency is used to control how fast the Driver changes signals. Only closed loop control signals from the Driver are smoothed. Open loop signals are not smoothed.
Road Settings
- Flat Event
- Uses a flat smooth road for the event with no required road file.When the Flat Event is selected, the Graphics Setting option is available with the following parameters:
- View path centerline: Enables the visualization of the event path.
- This check box is disabled for open loop events without a path.
- View grid graphics: Enables the visualization of the road grid graphics.
- When view grid graphics check box is toggled, road grid parameters can be edited in the Grid Settings tab.
Grid length Defines the length of the road. Enter a positive value in the model units. Grid Width Defines the width of the road. Enter a positive value in the model units. Grid X offset Gives a distance offset to the road graphics in the longitudinal direction. Enter a positive value in the model units. Grid Y offset Gives a distance offset to the road graphics in the lateral direction. Enter a positive value in the model units.
- View path centerline: Enables the visualization of the event path.
- Road File
- The road file option enables the selection of a road file to be used in the event. The road property file used in this option overrides the road property files used in the Tire entities within the model. The road property file should be compatible with the tire property file that is used in the vehicle.
- Tires
- Using Tire as road selection option, the road file specified in the tire entity is used in the events simulation.
Simulation Settings
- Analysis Parameters
- Define the numerical and output settings for the simulation:
Parameter Name Description Print interval The time step between successive outputs of simulation results. Real-Time Empowered When enabled, MotionSolve builds the FMU of the vehicle and solves it in real-time. Code generation When enabled, the C code for the MotionSolve Vehicle model excluding the driver and tire will be generated. This code can be used to compile and build an FMU, which can be used with any FMU compatible software. For more information see the Parameters: Simulation - Attributes topic.
- Dynamic Settings
- Defines the simulation control parameters for a time-domain-based nonlinear dynamic analysis. For more information see the Parameters: Transient Solver - Attributes topic.
- Static Settings
- Defines the solution control parameters for static and quasi-static analysis. For more information see the Parameters: Static Solver - Attributes topic.
Automated Output Report
| Report Name | Report Signals |
|---|---|
| SWA, Torque, Vehicle Velocity, Lateral Acceleration, Yaw Rate, Roll |
|
| Frequency Plots, Magnitude and Phase |
|
| Frequency Plots, Magnitude and Phase |
|
| Frequency Plots, Magnitude and Phase |
|
| Vertical Tire Forces |
|
| Lateral Tire Forces |
|
| Tire Lateral Slip |
|
| Wheel Aligning Torques |
|