Material

Introduction
The Material has secondary ribbon, which consists of the following tools:

The Create
Create Materials allows you to
allows you toThe Built-in DB
Open the Material Database manager allows you to
allows you toThe AMDC
Open the AMDC Material Database manager allows you to
allows you to-
The Material Calibration
 tool allows you to run the Material Calibration
tool.
tool allows you to run the Material Calibration
tool.
Materials already created by default
There are already some materials created by default in a new SimLab project (.slb project).
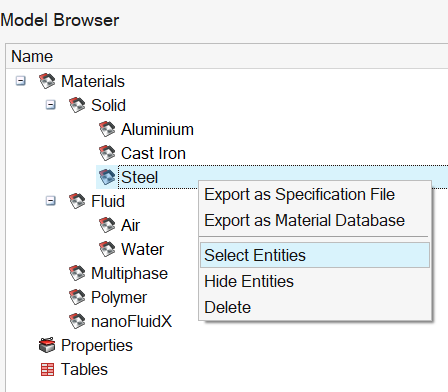
We can see the materials, in the Property Browser (5th tab):
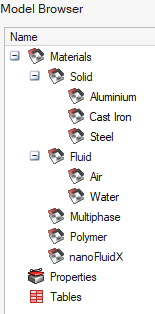
- 3 Solid Materials: Aluminium,
Cast Iron and Steel
Aluminium Cast Iron Steel Magnetic Properties Type: Soft Magnetic Type: Soft Magnetic Type: Soft Magnetic BH model: Analytical (Linear) BH model: Analytical (Nonlinear) BH model: Analytical (Nonlinear) Saturation set False Saturation set True Saturation set True - Knee adjustment set True Knee adjustment set True Relative permeability: 1 Initial relative permeability: 16108.8 Initial relative permeability: 2022.68 Saturation magnetization: 1.98809 T Saturation magnetization: 1.9 T Knee adjustment coefficient: 4.84016 Knee adjustment coefficient: 0.933609 - 1 Fluid Material: Air
Air Magnetic Properties Type: Soft Magnetic BH model: Analytical (Linear) Saturation set False Relative permeability: 1
Create Materials
In order to create materials, In the Analysis ribbon click on
click on Material and click on Create
 .
.
It opens the Create Material dialog box:
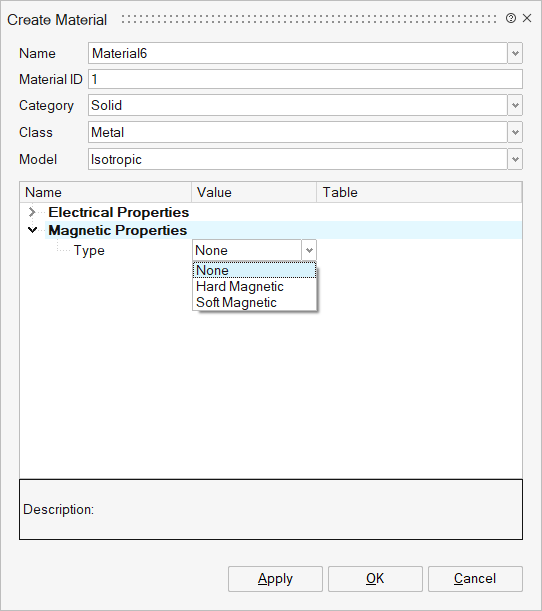
In MAC 2D and 3D solutions, you can create 1 type of magnetic materials:
a Soft Magnetic material
For the BH model, there are 3 models available:
- if you choose a
Analytical BH model, then you will
have to define:
- Relative permeability µr
- Saturation set False for a linear model
- Iron losses computation : none or Bertotti model
- Thermal dependence (optional)
- Temperature exponential constant C
- Curie temperature Tc
- if you choose a
Analytical BH model, then you will
have to define:
- Relative permeability µr
- Saturation set True for a nonlinear
model
- Saturation magnetic polarization Js
- Knee adjustment
- false: (without knee adjustment)
- true: set a value
- Iron losses computation : none or Bertotti model
- Thermal dependence (optional)
- Temperature exponential constant C
- Curie temperature Tc
- if you choose a Raw
data BH model, then you will have to:
- define the points of the BH data or import a .csv file or a .txt file or a .dat file
- Iron losses computation : none or Bertotti model
About Iron loss
- is the hysteresis losses coefficient;
- is the classical losses coefficient;
- is the excess losses coefficient;
- is the hysteresis losses exponent;
- is the classical losses exponent;
- is the excess losses exponent.
A material with modified Bertotti model is needed to compute iron losses in a Sheet Lamination part.
About Thermal properties
For electromagnetic analysis thermal properties can be defined for:
- Electrical properties:
In case of electrical properties, temperature dependence can be defined for the electrical resistivity. Here the electrical resistivity is defined as a linear function of the temperature.
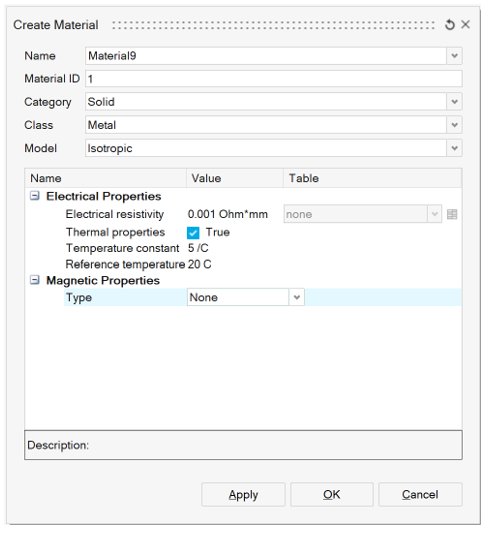
- Magnetic properties:
- Soft Magnetic material: In the case of
soft magnetic materials, thermal properties can be defined for
non-linear BH curve type. In this case the B(H) behaviour law is
defined as an exponential function of the temperature.
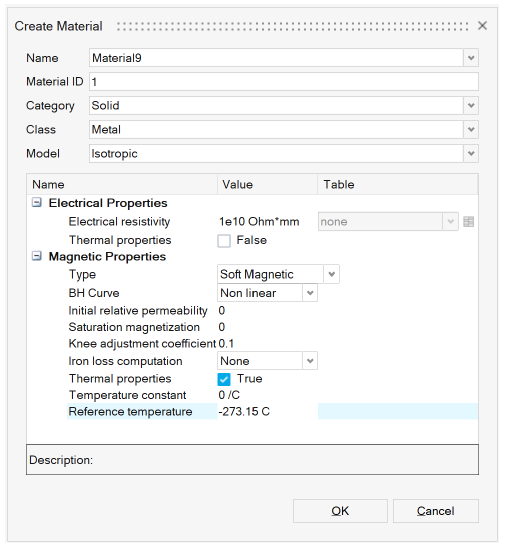
- Soft Magnetic material: In the case of
soft magnetic materials, thermal properties can be defined for
non-linear BH curve type. In this case the B(H) behaviour law is
defined as an exponential function of the temperature.
Steps for creating materials
- Click on the Create

- Enter a name for the material.
- You can keep the default values in the 4 following
fields:
- Material ID
- Category: Solid
- Class: Metal
- Model: Isotropic
Note: This information has no impact on the electromagnetic simulation. -
Define magnetic properties: Magnetic Properties.
Warning: In MAC 2D and 3D, Hard Magnetic material cannot be used. - Enter the characteristics of the material.
-
Click on the OK button.
The material is created.
You can see it in the Property Browser (5th tab).
Note: The following step is: Assign materials to bodies
Open the Material Database manager
In order to open the material database manager, click on the
Built-in DB

It allows to open:
-
the SimLab Material Database
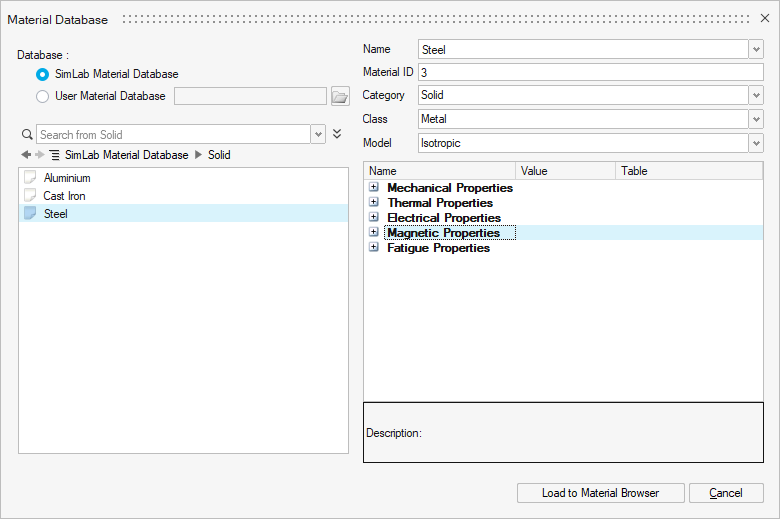
You can import materials from the predefined SimLab Material Database into the SimLab project using the Load to Material Browser button.
This database contains many materials of electric, hard magnetic and soft magnetic types.
-
a User Material Database if you have already created one
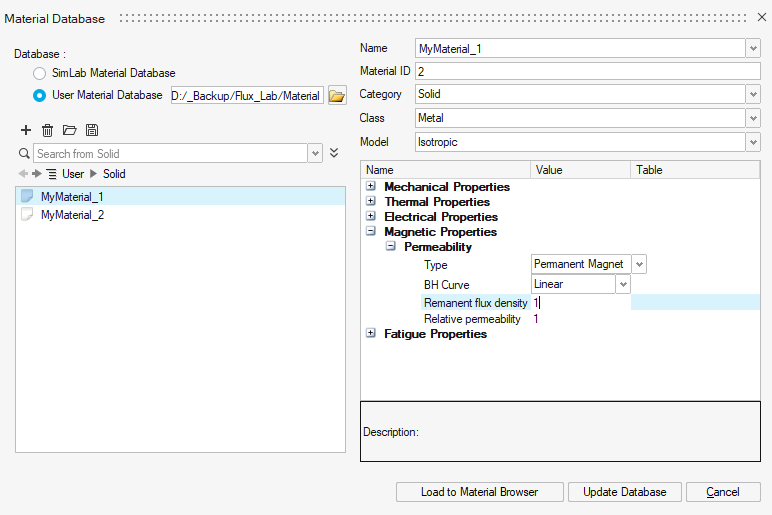
You can import materials from a User Material Database into the SimLab project using the Load to Material Browser button.
You can modify the material properties using the Update Database button.
Open the AMDC Material Database manager
In order to open the Altair Material Data Center (AMDC), click on
the AMDC

- the Altair Material Data Center (AMDC)
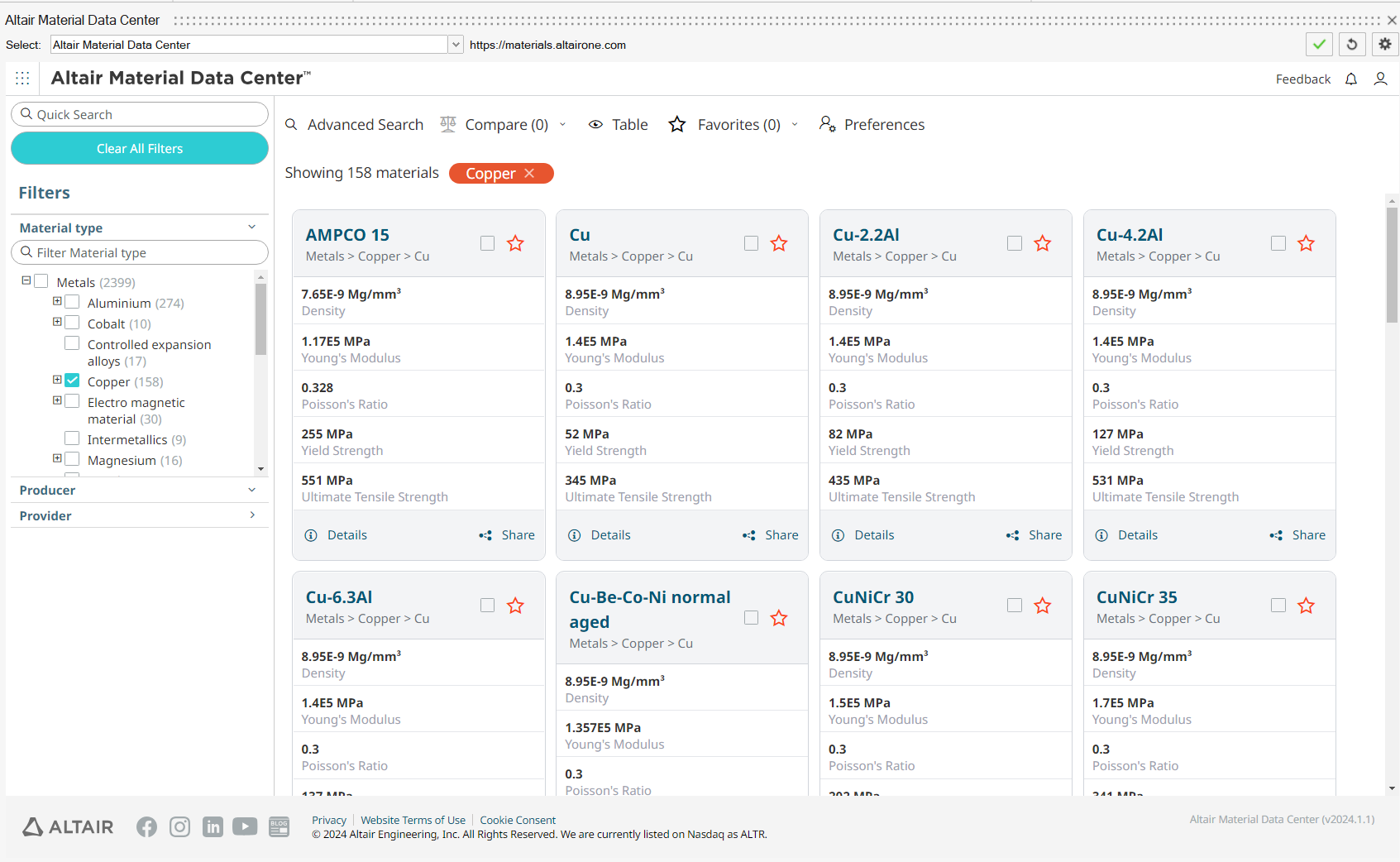
Altair Material Data Center (AMDC) is allowing you to choose best suited material from the huge collection of material from trusted suppliers. It permits search, compare data, and plots the material parameters using different filters like material type, provider, physics type.
SimLab provide the direct access to the AMDC, to download the appropriate material for multi physics solutions.
You can download materials from AMDC by following the steps below:- Select the required material.
- Go to CAE Model tab, then click on "Save to My material" option.
- Now the material added to the SimLab material browser.
- The downloaded material will be retained in the subsequent databases.
- Use "Reset Remembered Materials" in Material right click menu to delete the downloaded materials.
Assign materials to bodies
For example, in our contactor project, here is the material assignment to the bodies:
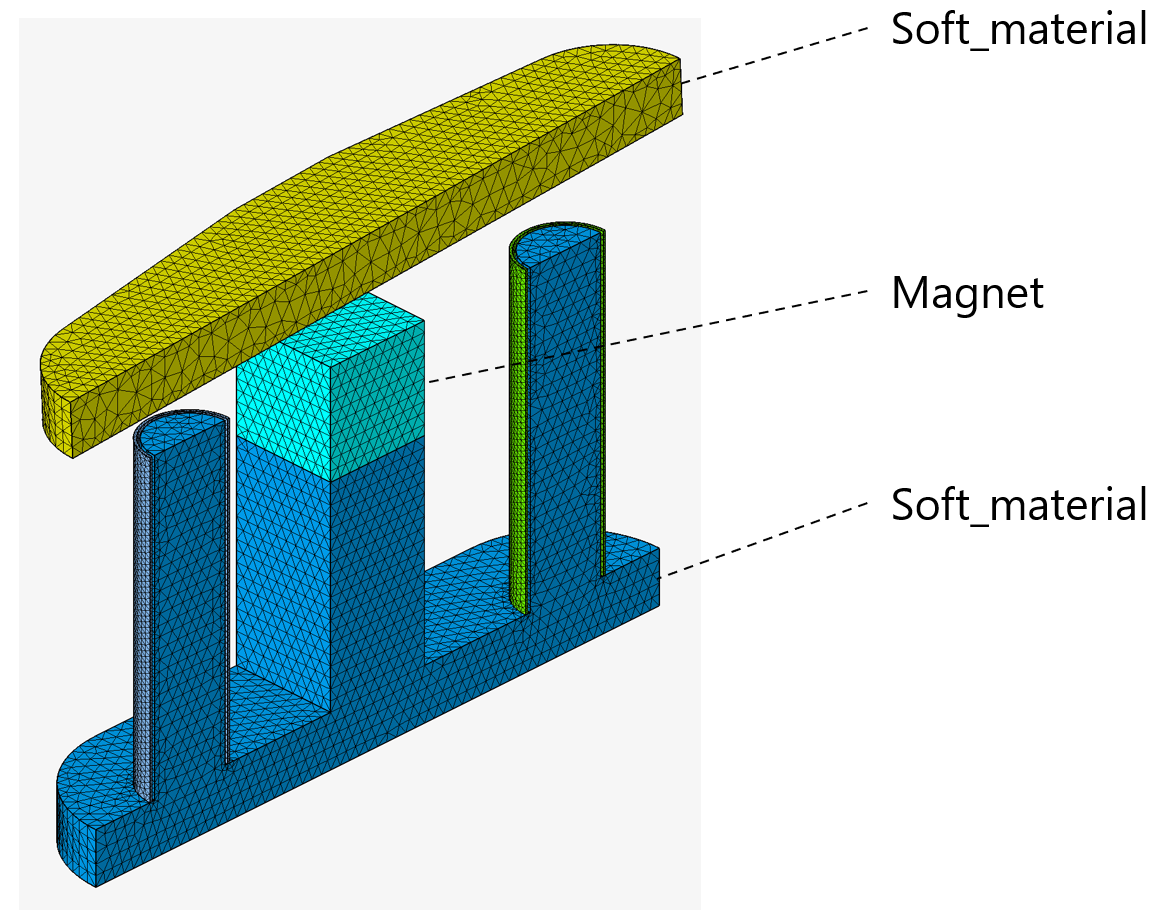
There are 3 possibilities to assign materials to bodies:
-
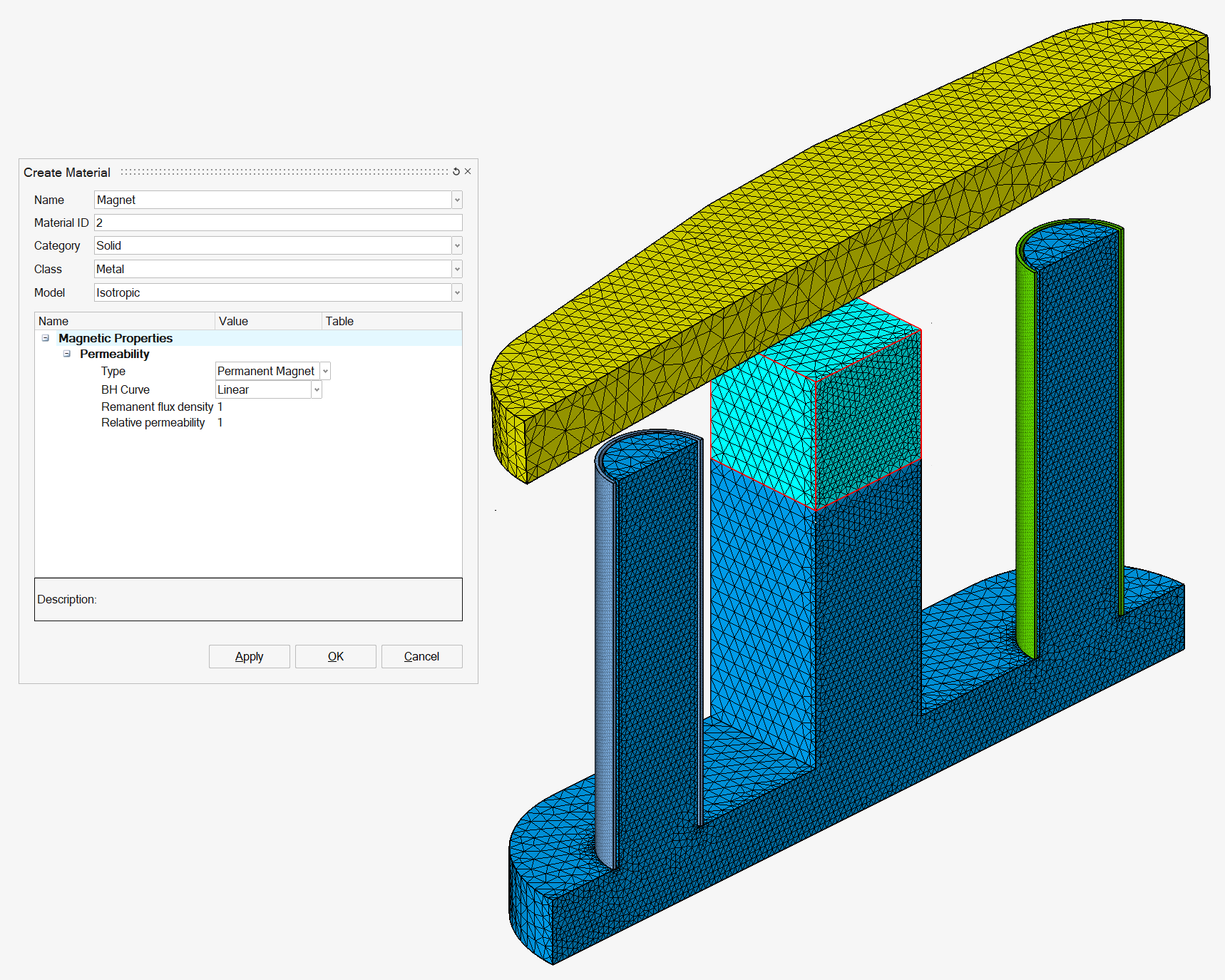
In the Create Material window:
After having entered the material properties, you can select the body which is composed of this material (the outline of this body is displayed in red), and then click on the OK button.
-
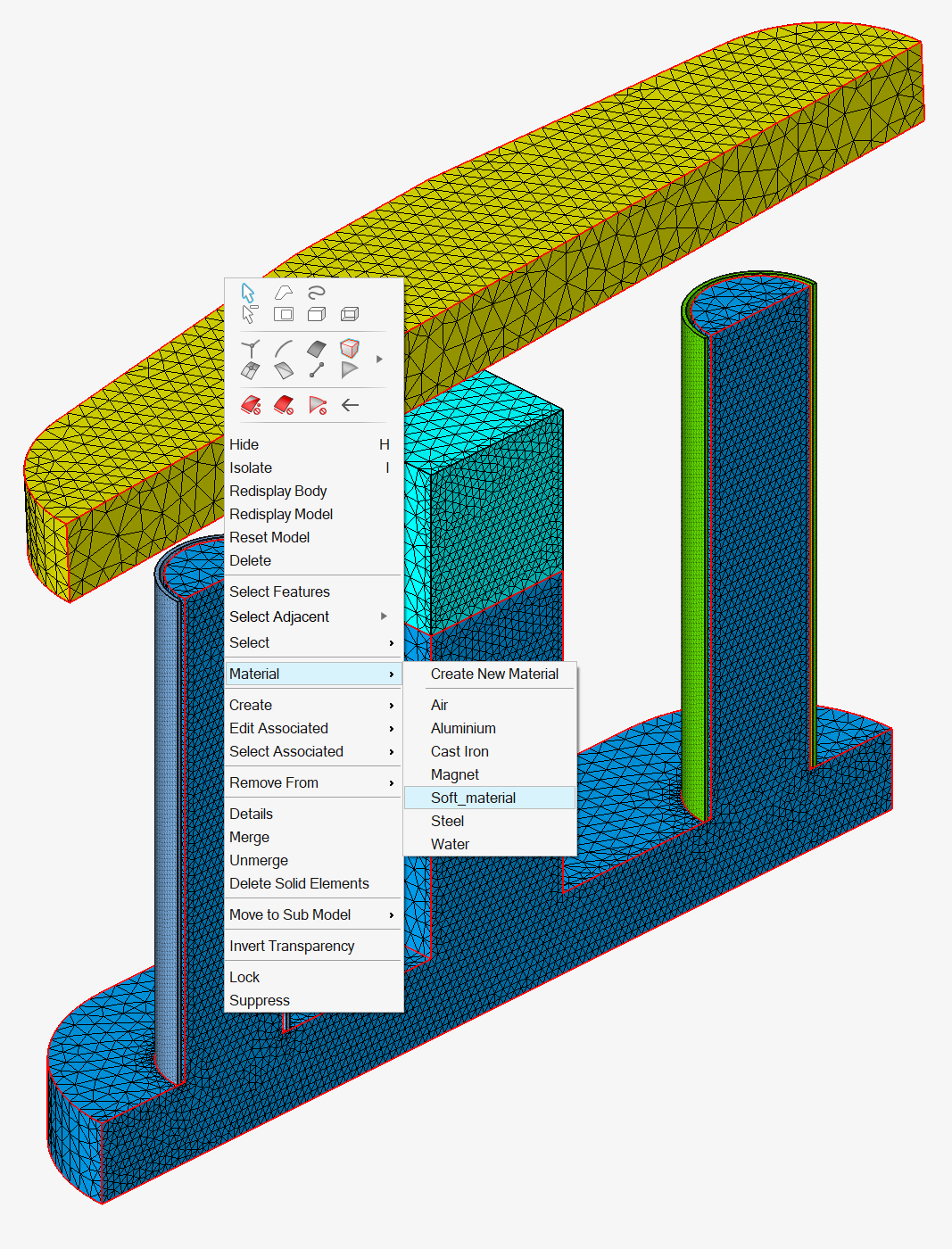
In the graphic window:
After having created the materials, select the body you want to assign a material to (the outline of this body is displayed in red), then right-click and select the contextual menu Material and then select the wanted material.
-
In the Assembly Browser (1st tab):
-
Display the Material column:
Right-click on the Name column title bar then check Material and then click on the OK button.
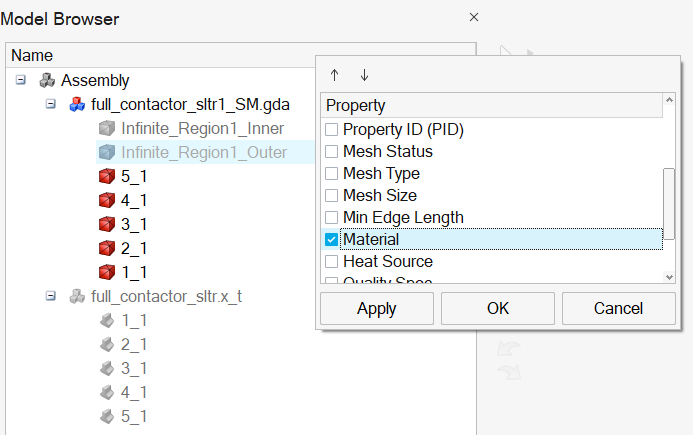
-
Assign the material to the body:
After having created the materials, in the column Material and in front of the body (of the .gda model), left-click and then select the material you want to assign to this body.
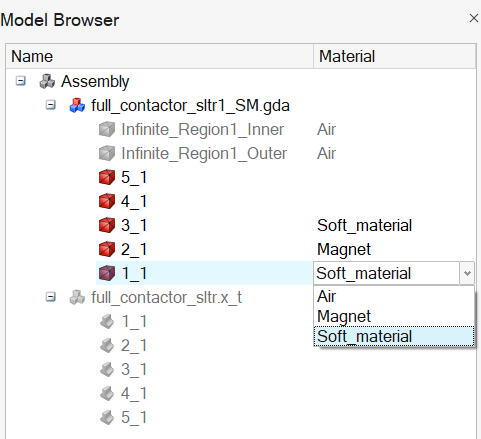
-
In the Property Browser (5th tab), right-click on a material and the 2 contextual menus Select Entities and Hide Entities allow you to select and hide the bodies assigned to a material.