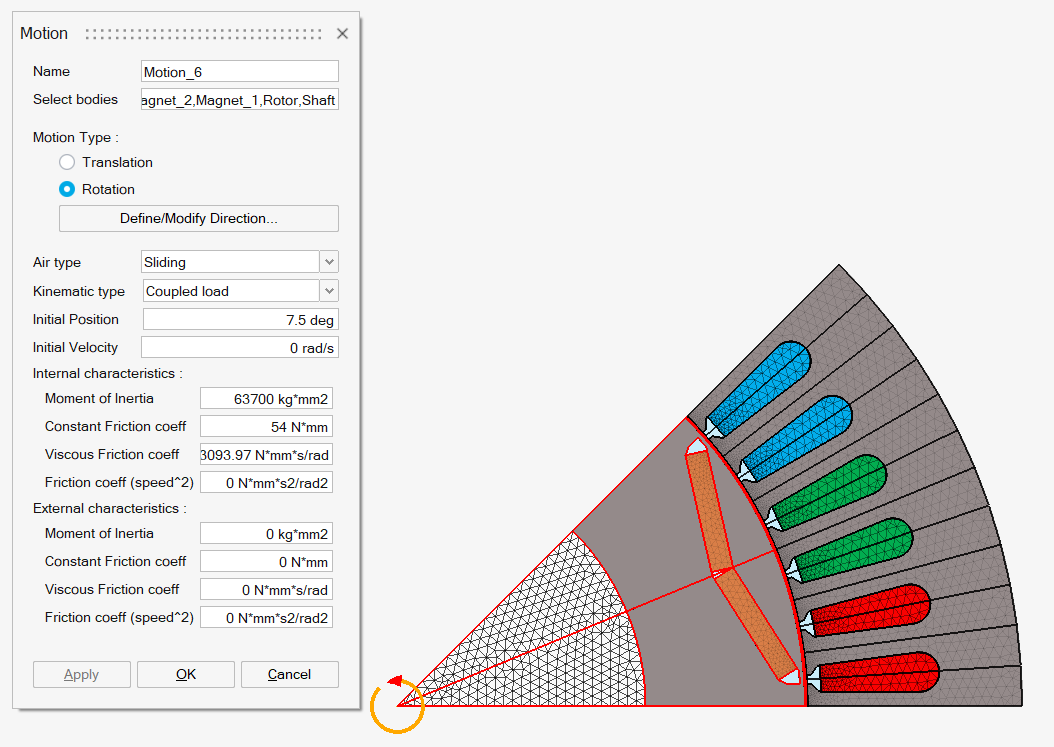
Motion

Introduction
The Motion allows you to define the motion of some bodies of the solution.
Dialog Box
| Imposed position | Imposed speed | Coupled load | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Translation |
 |
 |
 |
| Rotation |
 |
 |
 |
- Select bodies which are moving. At least, one body must be selected.
-
Motion Type: Two choices are proposed:
- Translation
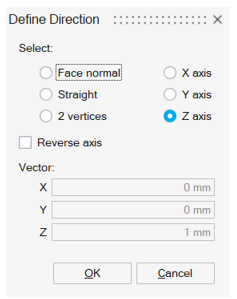
Translation direction has to be chosen through Define/Modify Direction button:
- Rotation
Rotation axis has to be chosen through Define/Modify Axis button:
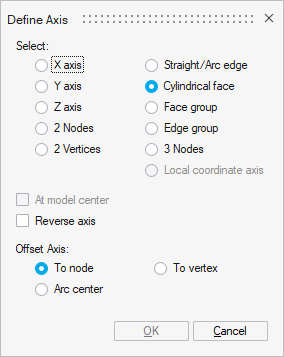
- Translation
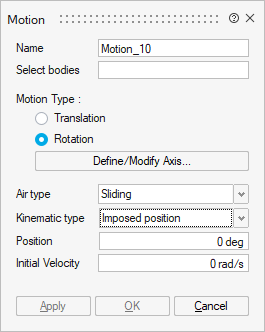
- Kinematic type: three choices possible
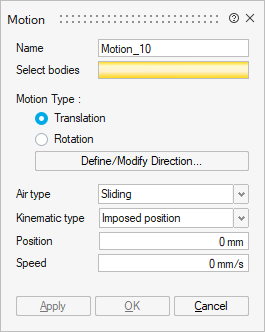
- Imposed position
The selected bodies are considered as fixed at the imposed position and have an initial speed at t = 0s.
The solving must be controlled by the time.
The mechanical equations are not considered.
It is necessary to define:Attention: If you use an imposed position, check that the solution is controlled by time and not by angle, it is mandatory to be able to solve.- Initial speed at t = 0s
- Imposed position
- Mechanical characteristics: Optionally, it is possible to define the mechanical stops (min and max)
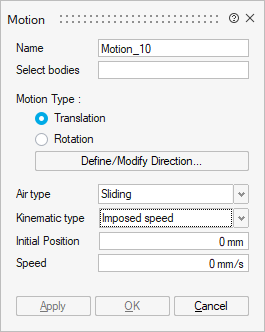
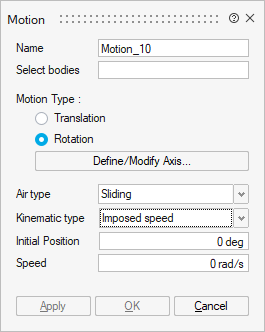
- Imposed speed
The moving part is considered as moving at a constant speed with respect to the fixed part. The computation of the electromagnetic field is carried out for the different positions defined by the imposed speed of the moving part. The mechanical equations are not considered.
The solving could be controlled by time or by angle.
It is necessary to define:
-
Initial position at t = 0s
-
Imposed speed
-
Mechanical characteristics: Optionally, it is possible to define the mechanical stops (min and max)
-
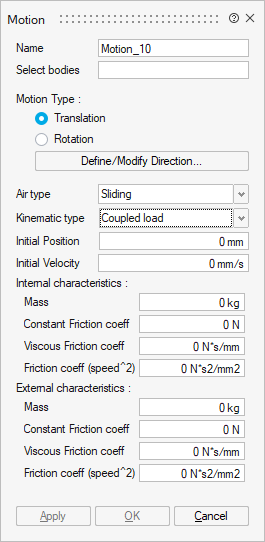
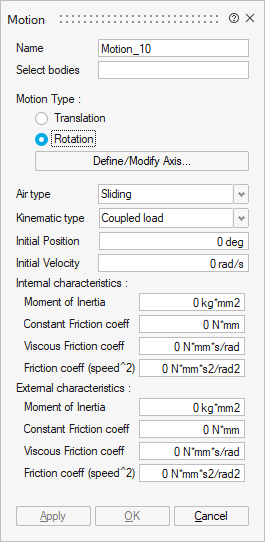
- Coupled load
The moving part drives an external device that represents the mechanical load of the studied device.
This is the model in which the magneto-mechanical coupling is considered, that is to say, both the magnetic aspects and the kinematic aspects of a problem
-
Initial speed at t = 0s
-
Initial position at t = 0s
-
Mechanical characteristics:
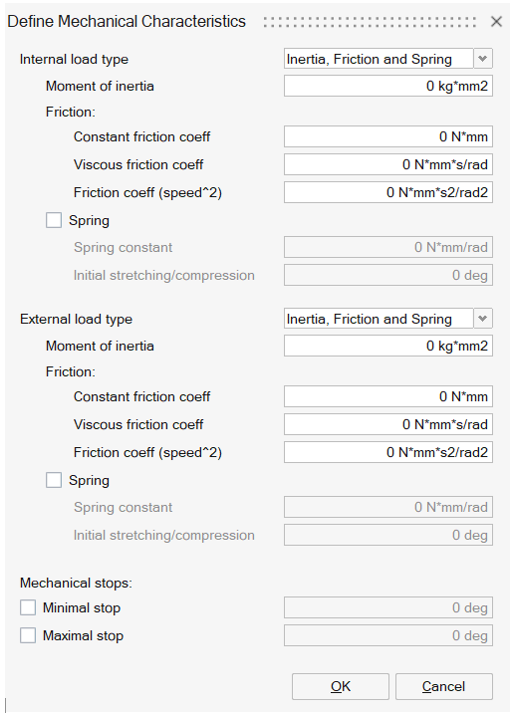
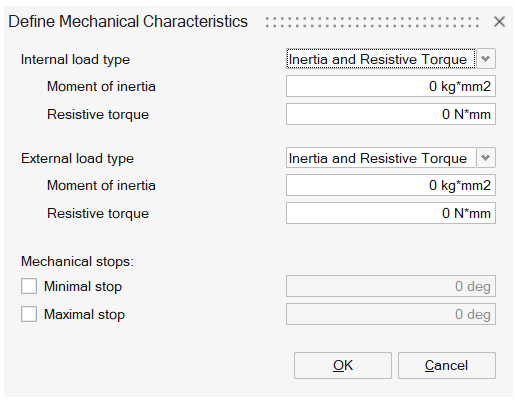
- Internal load for the moving part. It can be defined by Inertia, Friction and Spring or Inertia and Resistive Torque.
- External load for the coupled load. It can be defined by Inertia, Friction and Spring or Inertia and Resistive Torque.
- Mechanical stops. Minimal and Maximal stops can be entered.
-
- Imposed position
- Air type: Two choices are proposed, available for both
Translation and Rotation:
- Immersion
This air type is chosen when the moving bodies are immersed into a large air volume.
Mostly used for sensors and actuator applications.
- Sliding
This air type is chosen when the moving bodies are sliding with respect to the fixed part. The sliding surface is located inside the airgap and separates the airgap into two bodies: moving airgap and fixed airgap.
Mostly used for eMotor cases.
- Immersion
- SimLab parameters:
- Position
- Speed
- Acceleration (coupled load)
- Electromagnetic force (Linear motion)
- Electromagnetic torque (Angular motion)
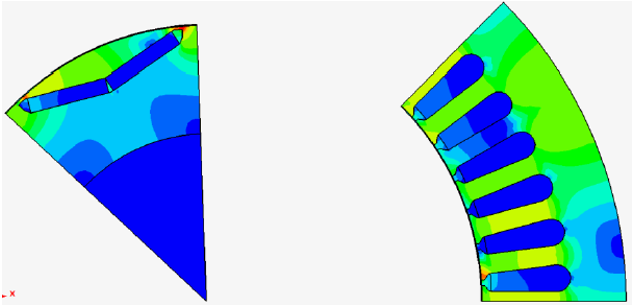
Examples
- Motion with Imposed speed
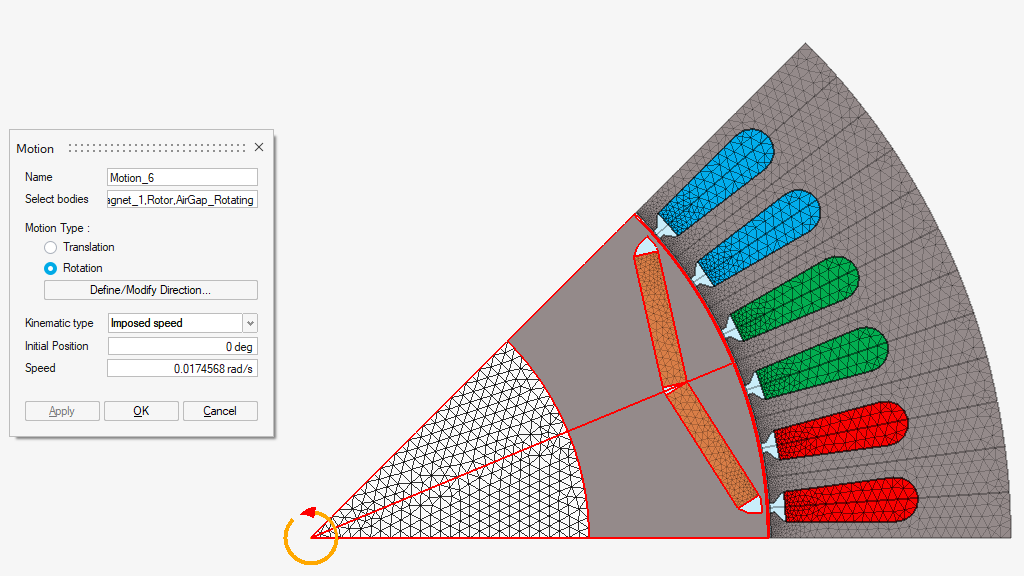
- Motion with Coupled load (without friction)
- An example to see the motion of the bodies after a solving.