Two Way Coupling
![]()
- AcuSolve - OptiStruct Two Way Coupled Simulation
- AcuSolve - MotionSolve Two Way Coupled Simulation
Description
- AcuSolve-OptiStruct two-way coupling can be used where there is large
structural deformation and the material has non-linear material properties.
This type of simulation is expensive and more accurate when compared with
the P-FSI technology that is also available in SimLab. P-FSI is recommended
for small structural deformations and linear material properties.
- AcuSolve-MotionSolve two-way coupling can be used where there are multiple
rigid bodies in a flow solution and the objective is to compute the motion
of the rigid body due to the effect of fluid flow. AcuSolve solution will be
setup in SimLab and MotionSolve model must be set up in MotionView.
- The first section named Coupling Parameters specifies communication parameters for coupling the Flow solution with an external solid/structural solution.
- The second section named Fluid-Solid Interaction specifies the fluid surface that interacts with the solid/structural surface from external code.
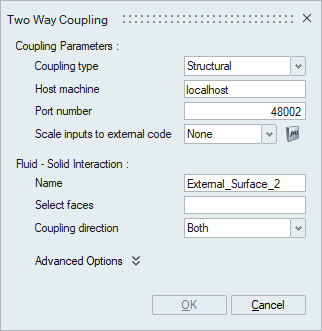
Coupling Parameters
- Coupling type
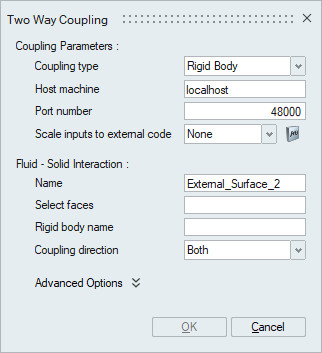
The type of coupling needs to be selected. For AcuSolve-OptiStruct simulation, type of Structural must be selected. For AcuSolve-MotionSolve simulation, type of Rigid Body must be selected.
- Host machine
The name of the machine on which OptiStruct/MotionSolve will be running. If both AcuSolve and OptiStruct/MotionSolve are running on the same machine, then localhost can be used.
- Port number
This is the socket port for communication with OptiStruct/MotionSolve.
- Scale inputs to external code
A multiplier function can be created and used for scaling the computed forces, moments, and heat fluxes from AcuSolve before sending them to OptiStruct/MotionSolve. If none, no scaling is performed.
Fluid-Solid Interaction
- Select faces
Specifies the fluid faces that interacts with a solid/structural surface from OptiStruct/MotionSolve.
- Coupling directionThis option defines the coupling direction for the selected faces.
- Both - Exchanges information with the external code object in both directions. AcuSolve sends loading to the external code and the external code sends displacements back to AcuSolve.
- To External Code - AcuSolve sends loading information to the external code, but no displacement information is returned.
- From External Code - AcuSolve does not send loading information to the external code, but displacement information is provided to AcuSolve at each step.
- Advanced Options
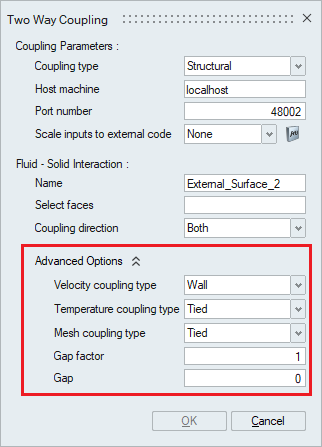
- Velocity coupling typeSpecifies the type of velocity boundary condition.
- Wall - Fluid follows the solid (no-slip wall).
- Slip - Fluid slips on the solid.
- Temperature coupling typeSpecifies the type of temperature boundary condition.
- None - No fluid temperature boundary condition (adiabatic).
- Tied - Fluid temperature same as solid wall.
- Mesh coupling typeSpecifies the type of mesh displacement boundary condition.
- Tied - Fluid mesh is fixed to surface.
- Slip - Fluid mesh slides on the solid.
- Gap factor
Specifies the Nondimensional (with respect to the length of an element face) maximum gap allowed for two element faces to be in contact. No maximum if zero.
- Gap
Specifies the dimensional maximum gap allowed for two element faces to be in contact. No maximum if zero.
- Velocity coupling type