Motion
![]()
This option is used to specify translational or rotational mesh motion.
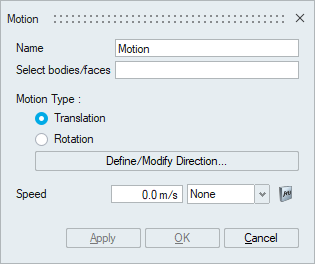
- Select bodies/facesSelect the bodies or faces on which the mesh motion needs to be specified.
- Mesh Motion to Bodies
When mesh motion is applied to a body, the complete body moves along with all the surfaces in the body. This feature can be used for rotating machinery applications such as pumps, fans, blowers, where the entire body is moving (rotating) and the exterior body is fixed with mesh sliding at the interface of both bodies.
- Mesh Motion to Surfaces
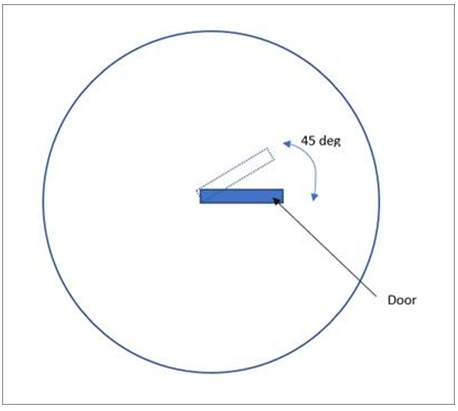
Mesh motion is applied to surfaces only when those surfaces are required to move keeping the rest of the body fixed. For example, this feature can be used while modeling the motion of a door which opens and closes at 45 degrees back and forth and there is only one body for Air with door surfaces inside it as shown in below schematic. Mesh motion is applied to the door surface and the mesh around it will be deformed to accommodate the motion of the door.
- Mesh Motion to Bodies
- Motion TypeThe different kinds of mesh motion that can be specified are:
- Translation - Used to specify linear
translation motion.
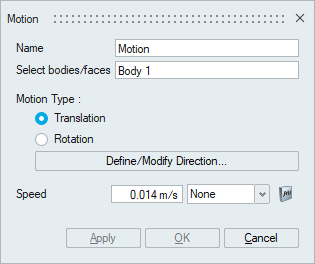
For example, in the below image a translation motion of the valve is defined.
 To apply linear mesh motion, the user must specify:
To apply linear mesh motion, the user must specify:- Direction - Specify the
direction in which the linear motion is occurring.
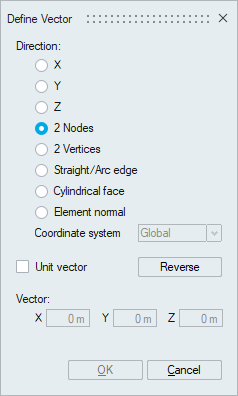
This can be defined using the
Define/Modify Direction
panel shown below:
- Speed - The speed at which
the selected bodies/faces are translating.
- A multiplier function may be used to provide inputs that vary with time and uniformly scale the values.
- Direction - Specify the
direction in which the linear motion is occurring.
This can be defined using the
Define/Modify Direction
panel shown below:
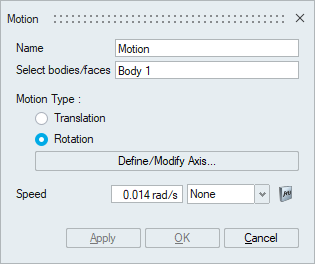
- Rotation - Used to specify rotational
mesh motion.
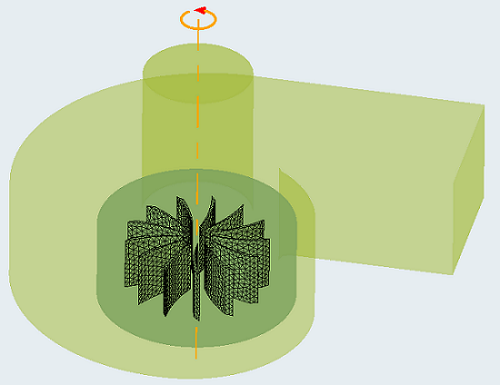
For example, rotational mesh motion can be applied on the impeller of a centrifugal blower as shown below:
 To apply rotational mesh motion, the following information is required.
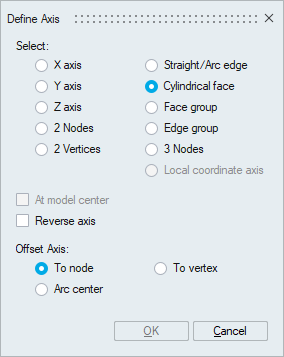
To apply rotational mesh motion, the following information is required.- Axis: Specify the axis of
rotation. This can be defined using the
Define/Modify Axis panel
shown below.
- Speed: The speed at which the
bodies/faces are rotating.
- A multiplier function can be used to provide inputs that vary with time and uniformly scale the values.
- Axis: Specify the axis of
rotation. This can be defined using the
Define/Modify Axis panel
shown below.
- Translation - Used to specify linear
translation motion.