/MAT/LAW48 (ZHAO)
Block Format Keyword This law describes the Zhao material law used to model an elasto-plastic strain rate dependent materials. The law is applicable only for solids and shells.
The global plasticity option for shells (N=0 in shell property keyword) is not available in the actual version.
Format
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | (10) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| /MAT/LAW48/mat_ID/unit_ID or /MAT/ZHAO/mat_ID/unit_ID | |||||||||
| mat_title | |||||||||
| E | |||||||||
| A | B | n | Chard | ||||||
| C | D | m | EI | k | |||||
| Fcut | |||||||||
Definition
| Field | Contents | SI Unit Example |
|---|---|---|
| mat_ID | Material identifier. (Integer, maximum 10 digits) |
|
| unit_ID | Unit identifier. (Integer, maximum 10 digits) |
|
| mat_title | Material title. (Character, maximum 100 characters) |
|
| Initial density. (Real) |
||
| E | Young's modulus. (Real) |
|
| Poisson's ratio. (Real) |
||
| A | Plasticity yield
stress. (Real) |
|
| B | Plasticity hardening
parameter. (Real) |
|
| n | Plasticity hardening exponent. Default = 1.0 (Real) |
|
| Chard | Plasticity Iso-kinematic hardening factor.
Default = 0.0 (Real) |
|
| Plasticity maximum stress. Default = 1030 (Real) |
||
| C | Relative strain rate
coefficient. Default = 1.0 (Real) |
|
| D | Strain rate plasticity factor. Default = 0.0 (Real) |
|
| m | Relative strain rate exponent. Default = 1.0 (Real) |
|
| EI | Strain rate coefficient. Default = 0.0 (Real) |
|
| k | Strain rate exponent. Default = 1.0 (Real) |
|
| Reference strain
rate. (Real) |
||
| Fcut | Cutoff frequency for strain rate
filtering. Default = 0.0 (Real) |
|
| Failure plastic strain. Default = 1030 (Real) |
||
| Tensile failure strain 1. Default = 1030 (Real) |
||
| Tensile failure strain 2. Default = 1030 (Real) |
Example (Metal)
#RADIOSS STARTER
#---1----|----2----|----3----|----4----|----5----|----6----|----7----|----8----|----9----|---10----|
/UNIT/1
unit for mat
g mm ms
#---1----|----2----|----3----|----4----|----5----|----6----|----7----|----8----|----9----|---10----|
#- 2. MATERIALS:
#---1----|----2----|----3----|----4----|----5----|----6----|----7----|----8----|----9----|---10----|
/MAT/LAW48/1/1
metal
# RHO_I
.008
# E nu
200000 .3
# A B n Chard sig_max
145 550 .42 1 0
# C D m E1 k
35 47 .3 185 .3
# eps_rate_0 Fcut
.05 0
# eps_max eps_t1 eps_t2
0 0 0
#---1----|----2----|----3----|----4----|----5----|----6----|----7----|----8----|----9----|---10----|
#ENDDATA
/END
#---1----|----2----|----3----|----4----|----5----|----6----|----7----|----8----|----9----|---10----|Comments
- The stress-strain function is based
on the formula published by Zhao:Where,
- Plastic strain
- Strain rate
- Except for the strain rate
formulation, the plasticity curve is strictly identical to a Johnson-Cook model:
Figure 1. 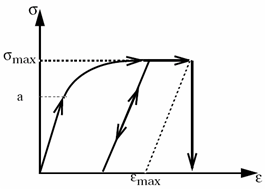
However, compared to Johnson-Cook, the Zhao law allows a better approximation of a nonlinear strain rate dependent behavior.
- Yield stress should be strictly positive.
- The hardening exponent
n must be less than 1.
Figure 2. 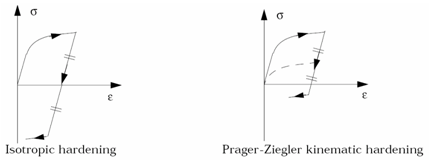
- The iso-kinematic hardening
parameter is defined as:
- If Chard = 0, hardening is a full isotropic model
- If Chard = 1, hardening uses the kinematic Prager-Ziegler model
- If 0 < Chard < 1, hardening is interpolated between the two models
- If
, the term
, and Equation 1 becomes:
- The strain rate filtering is used to smooth strain rate. It is only available for shell and solid elements.
- When
reaches
in one integration point, then based on the element type:
- Shell elements: The corresponding shell element is deleted.
- Solid elements: The deviatoric stress of the corresponding integral point is permanently set to 0, however, the solid element is not deleted.
- If
(
is the largest principal strain), the stress is reduced
as:
- If , the stress is reduced to 0 (but the element is not deleted).