Results
Introduction
The following possibilities exist for postprocessing of results:
- inside SimLab
- Contour / Arrows / Isoline
- XY Plot
- Iso Surface
- Plot
- Node Path
Contour / Arrows / Isoline
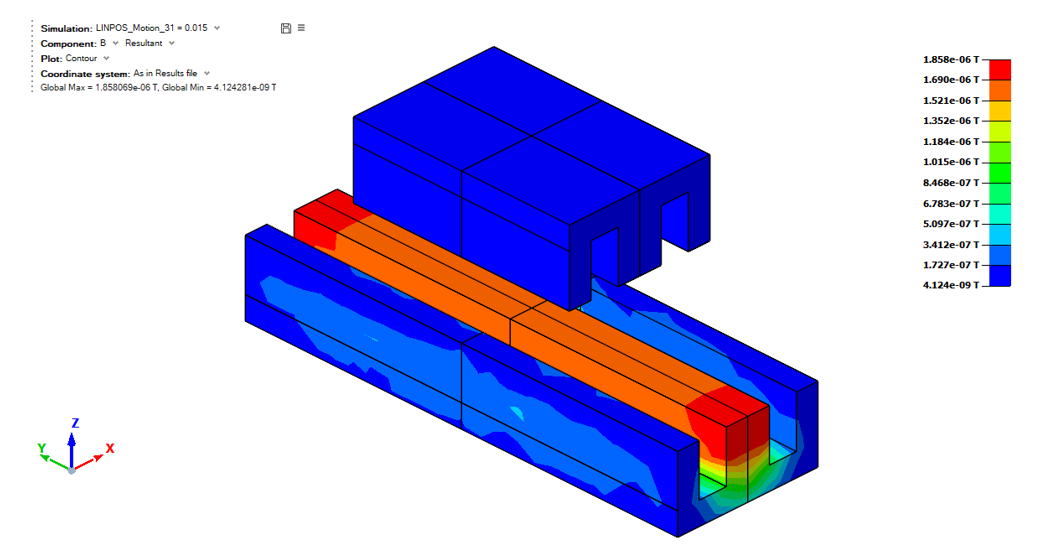
At the end of the solving, the contour results are displayed automatically. The contour or arrows and isoline options are visible on the graphical window top-left part.
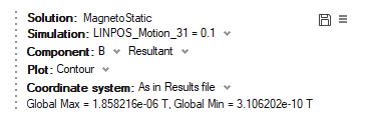
- The Simulation allows selecting the current step
(angular position or linear position)
To see the bodies animation, please use the animation tool bar:
 Note:
Note:The tool bar can be used in Transient Animation Mode, Modal Animation Mode and Linear Animation Mode:
- For Magnetostatic Integral solution, please choose Transient Animation Mode
- The possible Component for a Magnetostatic Integral solution is magnetic flux density B.
- The Plot allows to choose between
contour or arrows:
- to display the color shade, choose Contour
- to display the arrows, choose Vector
- to display the isolines, choose Iso Line
For more details about the result panel, consult Result Panel.
For more details about the options of the scale, consult Result title and Legend bar.
For more details about the animation of the motion, consult Animate.
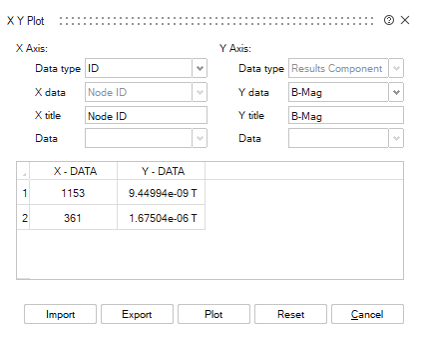
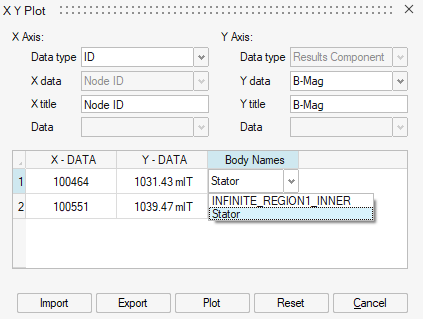
XY Plot
![]()
The XY Plot allows the user to do point computations.
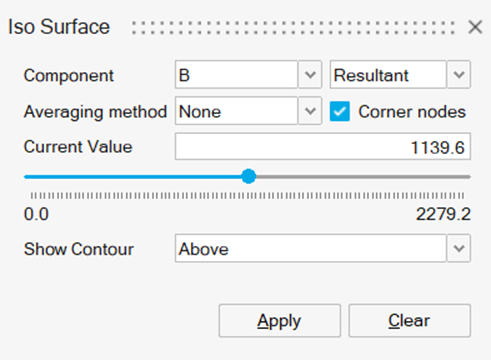
Iso Surface

The Iso Surface menu allows you to display for example the locations where B is greater or lower than a certain value, it allows to display the hot or cold spots.
Plot
![]()
The Plot allows to post process global quantities chosen in the Result Request dialog box by the user.
- Circuit (Self Inductance, Mutual Inductance, Flux and Energy of Coils)
- Global (energy and flux over the entire domain)
- Motion (torque, force)
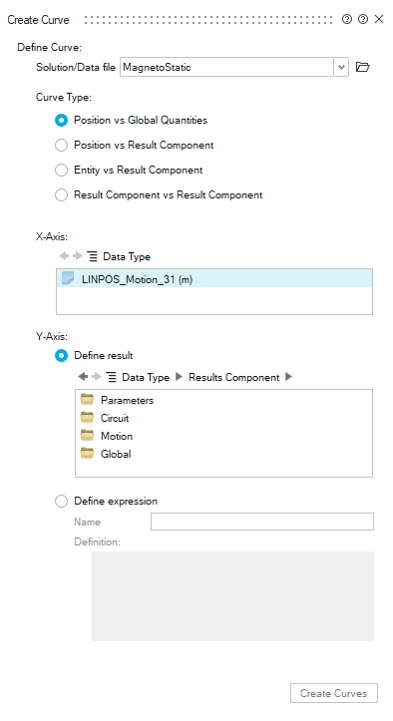
Examples of Plots:
-
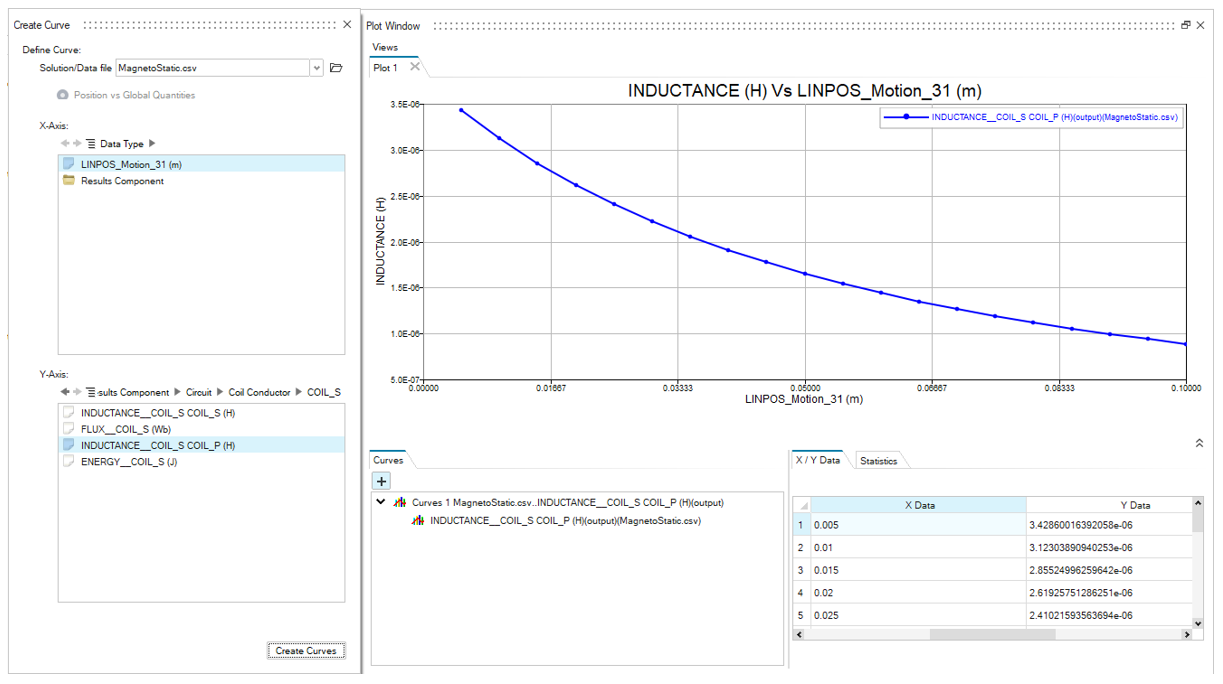
In the Circuit category:
The mutual inductance of a non-meshed coil vs the linear position:
-
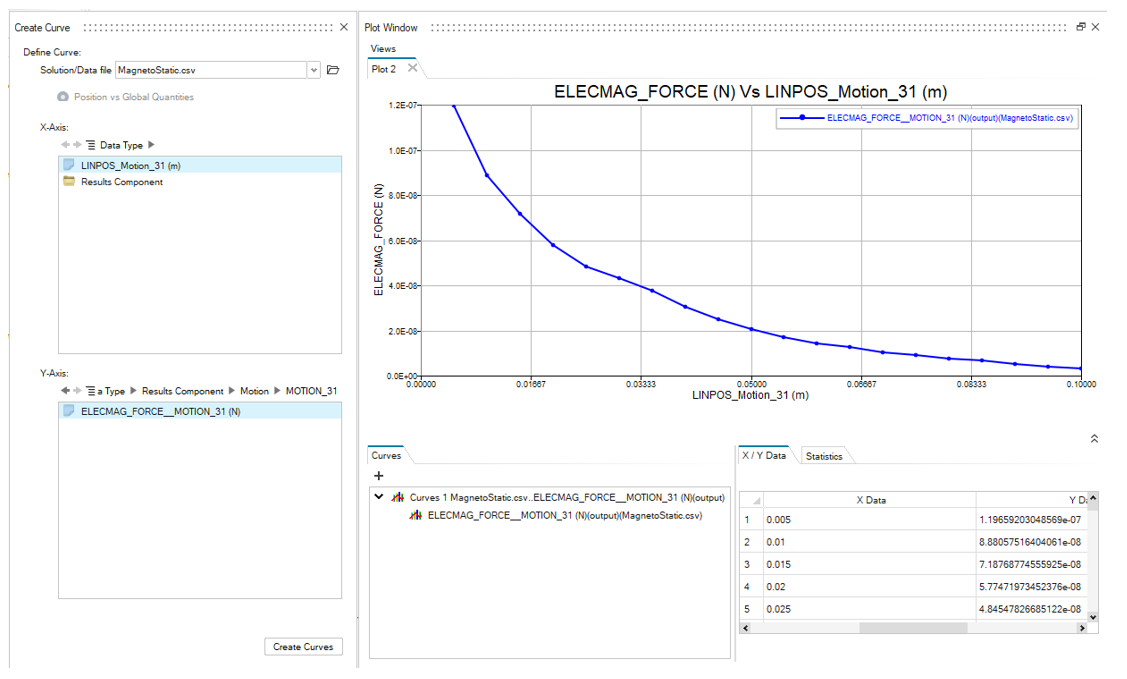
In the Motion category:
The electromagnetic force vs the linear position:
The created Plots are saved in the Solution Browser in Plots.
Node Path
Node Path allows to create the user defined paths and visualize the contour and vectors on the defined paths.
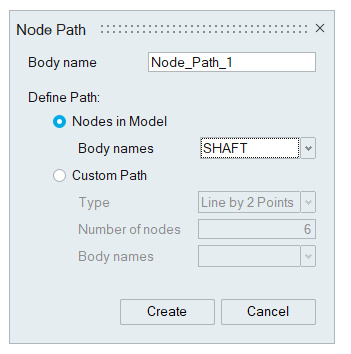
For more details about the node path, refer Node Path.