Thin Region - 3D Magnetic Solutions
Introduction
The Thin Region Load and Constraint enables modeling bodies with a small thickness.
It simplifies the model set-up, especially the meshing.
The meshing and solving processes are executed more efficiently and rapidly.
Thin Region types and inputs
Here is an example of Thin Region dialog box of Air gap type:
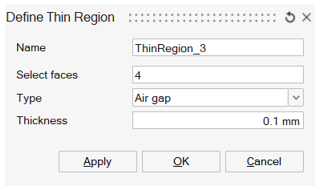
First of all, Thin Region name is entered, and faces defining the Thin Region are selected.
- In 3D AC Magnetic solution, the following 4 Thin
Region types are available:
- Air gap:
- Enter a thickness value
- Magnetic non-conducting:
- Enter a thickness value
- Assign a material with soft magnetic property
- Define the boundary condition with magnetic field direction (tangent / normal / no restriction)
- Perfect insulator in conductor
- Hyperbolic current conductor:
- Enter a thickness value
- Assign a material with electrical properties (Resistivity value) and a soft magnetic property
Note: The Hyperbolic current conductor Thin Region can be circuit connected through a Conductor component or N-pins Conductor component.
- Air gap:
- In 3D Transient Magnetic solution, the following
3 Thin Region types are available:
- Air gap:
- Enter a thickness value
- Magnetic non-conducting:
- Enter a thickness value
- Assign a material with soft magnetic property
- Define the boundary condition with magnetic field direction (tangent / normal / no restriction)
- Perfect insulator in conductor
- Air gap:
- In 3D Magnetostatic solution, the following 2
Thin Region types are available:
- Air gap:
- Enter a thickness value
- Magnetic non-conducting:
- Enter a thickness value
- Assign a material with soft magnetic property
- Define the boundary condition with magnetic field direction (tangent / normal / no restriction)
- Air gap:
Use cases
There are several devices which can use Thin Region.
- Magnetic non-conducting Thin Region with high permeability to build a magnetic shunt around the transformer.
- Surface impedance for the tank usually in steel. Surface impedance is not available in Thin Region Load and Constraint. Please refer to the page Conductor described by Surface Impedance.
Another common use case is motor application with segmented magnets in MT3D solution. In order to reduce the magnets eddy currents generating heat losses which can lead to demagnetization or magnets detachment, the magnets are segmented with thin insulator or air gap layers.
Constraints
Here are some constraints on the Thin Region usage:
-
Thin Region faces of the following types cannot be on the periodicity or symmetry plane:
- Air gap
- Magnetic non-conducting with Boundary condition defined by Almost normal magnetic flux or No restriction in the magnetic flux direction
- Hyperbolic current conductor in MAC3D solution
- If there is a Motion, Thin Region faces and its edges cannot be at the interface of bodies having different Motion information.
- Air gap and Magnetic non-conducting, in MAC3D or MT3D solution, cannot be at the interface between bodies assigned to Passive Solid Conductor LBC or Conductor (or N-Pins Conductor) circuit component. These Thin Regions must be in contact with at least one body defined with a soft magnetic material and not assigned to any Load and Constraint or circuit component.
- Perfect insulator in MAC3D or MT3D solution must be at the interface between bodies assigned to Passive Solid Conductor LBC or Conductor (or N-Pins Conductor) circuit component.
- Hyperbolic current conductor in MAC3D solution can be at the interface of bodies which are either Air or Magnetic non conducting type.
Post processing on the Thin Region
At the end of solving, a shell body associated to each Thin Region is automatically created to allow the post processing on it. The Shell body name corresponds to the Thin Region name.
In order to see Contour/Vectors on the Thin Region shell body:
-
Display the shell body and hide the solid bodies in contact with it
- Select the following option: 2D
Elements
The available quantities are:
- The magnetic flux density B for all Thin Region types.
- The current density J and Joule losses surface density dLossS which are available for Hyperbolic current conductor Thin Region in MAC3D solution.
Concerning the Result Request quantity, total Joule losses value is available for Hyperbolic current conductor in MAC3D solution.
Limitations
Here are some current limitations on the Thin Region:
- If a shell body associated to a Thin Region already
exists in preprocessing, the Infinite box creation does not work.Note: Shell body usually exists in preprocessing when its CAD faces are not belonging to a solid body: faces are immerged inside a solid body.The workaround is to:
- Create a bounding box containing the shell body.
- Tet mesh the bounding box with all the bodies inside. Then, the shell body disappears from the model, but the bounding box solid mesh keeps the shell body surface mesh.
- Hide a face from the bounding box to be able to select the shell body face in the Thin Region Load and Constraint.
-
Concerning the Thin Region of type:
- Air gap
- Magnetic non conducting with Boundary condition defined by Almost normal magnetic flux or No restriction in the magnetic flux direction
- Hyperbolic current conductor in MAC3D solution
there is a potential gap. Therefore the results are different on the considered side. A current limitation is that only one of two sides is displayed.