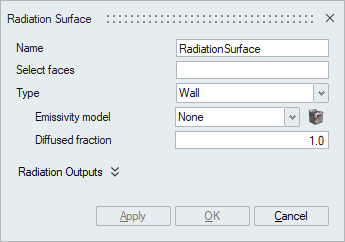
Radiation Surface
![]()
This panel is used to specify the radiative boundary conditions for the Enclosure, P1 and Discrete Ordinates radiation models. Depending on the radiation model selected in the solution, this panel gets updated.
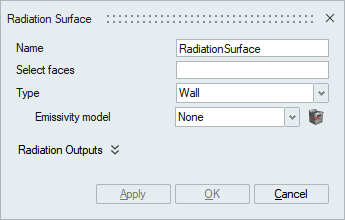
- Emissivity
Emissivity model is required for all the radiation models. This is used to specify an ideal grey-surface emissivity for radiation modeling.
- Select faces
Select the faces on which the radiation boundary condition needs to be specified.
Enclosure Radiation
- Type
Specify the type of boundary surface. Two types are available: Wall and Opening.
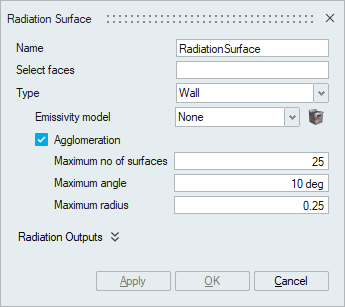
- WallThis is used for Wall boundary surfaces especially where the fluid encounters the solid. It requires an Emissivity model. For Enclosure radiation models, Agglomeration needs to be specified. This flag specifies whether to agglomerate the surface elements that is used with wall type. It requires:
- Maximum number of surfaces – Maximum number of surfaces in one agglomeration.
- Maximum angle – Maximum angle between surfaces allowed in any agglomeration.
- Maximum radius – Maximum radius
of agglomeration.
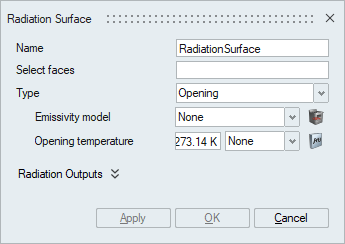
- Opening
The opening type provides a method of fully enclosing a fluid domain that is not completely surrounded by walls. This type is appropriate for inlets, outlets, and surfaces that approximate infinity in external flows. It requires an Emissivity model and an Opening temperature. The Opening Temperature is generally the temperature of the environment from which the fluid is entering, or the fluid is exiting to. An opening is typically modeled as a black body, with an emissivity of one. However, other emissivity models may be used with an opening.
A multiplier may be used with the Opening Temperature to scale the opening temperature.
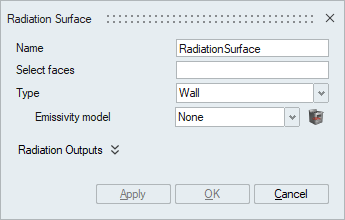
- Wall
P1 Radiation
- TypeSpecify the type of boundary surface. Similar to enclosure, the same two types are available: Wall and Opening.
- Wall
This is used for Wall boundary surfaces especially where the fluid encounters the solid. It requires an Emissivity model.
- Opening
The opening type provides a method of fully enclosing a fluid domain that is not be surrounded by walls. This type is appropriate for inlets, outlets, and surfaces that approximate infinity in external flows. It requires an Emissivity model and an Opening temperature. A multiplier may be used with the Opening Temperature to scale the opening temperature.
- Wall
Discrete Ordinates Radiation
- TypeSpecify the type of boundary surface. Three types are available: Wall, Opening and Radiation Interface.
- WallThis option can be used for the following faces:
- At the interface between participating and non-participating bodies.
- Exterior Wall faces of non-participating
bodies.
- Opening
The opening type provides a method of fully enclosing a fluid domain that is not be surrounded by walls. This type is appropriate for inlets, outlets, and surfaces that approximate infinity in external flows. It requires an Emissivity model and an Opening temperature. A multiplier function can be used with the Opening Temperature to provide inputs that vary with time and uniformly scale the temperature values.
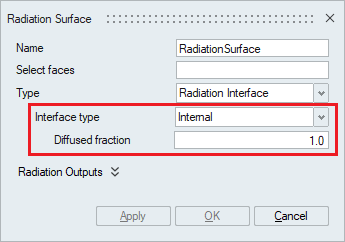
- Radiation InterfaceTRadiation Interface enables the transmission and reflection of radiative intensity at an interface between two participating media. A participating media body is one that have a material assigned which have material radiation enabled. Two different radiation interface types are supported:
- Internal
This option must be used for internal or shared faces between two participating media bodies. You must define the Diffused fraction which defines the proportion of reflected radiation intensity at a surface that is diffused.
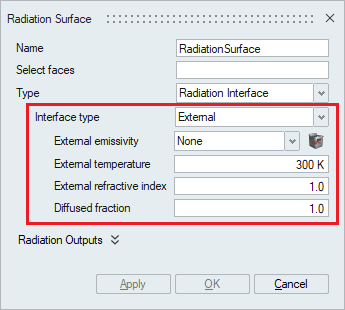
- External
This option must be used for the exterior faces of participating media bodies. The external radiation interface is used with external emissivity model and external temperature.
For this model, the user must specify the following:- External emissivity: Emissivity of the exterior face.
- External Temperature: Temperature of the fluid surrounding the domain.
- External refractive index: Refractive index for the exterior face.
- Diffused fraction: defines the proportion of reflected radiation intensity at a surface that is diffused.
- Internal
- Wall
- Radiation Outputs
The Radiation outputs can be specified. The options available under here are:
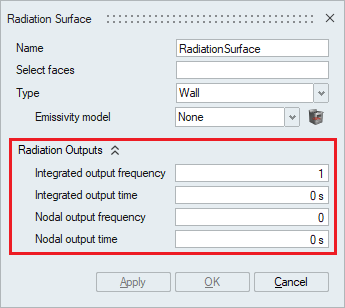
- Integrated output frequency – Time step frequency at which to output the integrated radiation heat flux. If zero, this option is ignored.
- Integrated output time – Time frequency at which to output the integrated radiation heat flux. If zero, this option is ignored.
- Nodal output frequency – Time step frequency at which to output radiation heat flux at the nodes of the surface. If zero, this option is ignored.
- Nodal output time – Time frequency at which to output radiation heat flux at the nodes of the surface. If zero, this option is ignored.