Element Quality definitions: TRI
TRI element types
The quality measures supported for TRI element types are as follows,
- Aspect Ratio
- Edge Length
- Interior Angle
- Stretch
- Skew
- Element Face Angle
- Area
- Mid-Node Offset : Ratio
- Mid-Node Offset : Distance
- Jacobian Ratio
- Area Skew
- Area Skew : Fluent
- Height
- Surface Grading
- Stable time increment - Radioss
Aspect Ratio
The commonly used quality measure for TRI elements is Aspect Ratio.
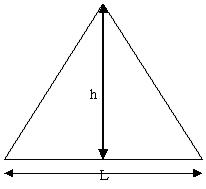
The Aspect Ratio (AR) of a TRI element is defined as the largest of √3 / 2 (L/h), where L is the length of the edge and h is the height of the node opposite to this edge. The scale factor √3 / 2 is to make the AR for an equilateral triangle equal to 1.
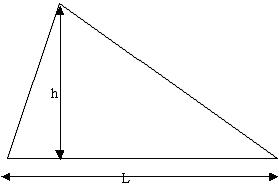
L/h for equilateral triangle is equal to 2 / √3
Click to find the Manual Aspect Ratio Calculation for single TRI3 element.
Edge Length
Minimum and maximum length of the element edge.
Interior Angle
The min and max interior angle is calculated based on angle formed by the edges at each node of the TRI.
Stretch
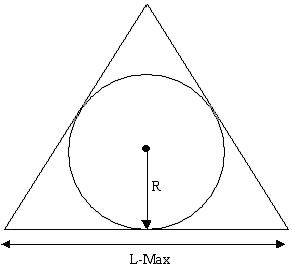
Stretch of a TRI element is √12 (R / L-Max). Where R is the radius of the inscribed circle and L-Max is the longest edge of the TRI element. The scale factor √12 is to make Stretch for an equilateral triangle equal to 1.
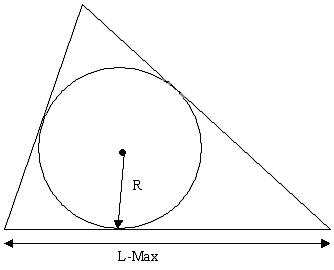
(R / L-Max) for equilateral triangle is equal to 1 / √12
Skew
The skew angle of a TRI3 element is the difference between 90 degrees and the minimum of three angles α1, α2, α3. These angles are defined, for the TRI element, as the smallest of the angles created when a line drawn from a node to the midpoint of the opposing side intersects a line connecting the midpoints of the adjacent two sides. The skew angle has a range from 0 degrees for a perfect triangle to 90 degrees for a collapsed triangle. Skew = 90 - Min (α1, α2, α3).
Element Face Angle
Element Face Angle is the angle between two TRI elements along the common edge.
Area
Area of the TRI element.
Mid-Node Offset: Ratio
It is the ratio between offset distance of mid node from the mid position of the corresponding element edge to element edge length. If EL denote the length of the element edge N1-N2, then d / El represents the Mid-Node Offset ratio.
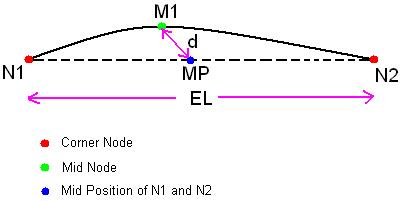
Mid-Node Offset: Distance
It is the offset distance of mid node from the mid position of the corresponding element edge. For example, let N1-N2 be an higher order element edge with mid node M1 and MP be the mid position of the element edge N1-N2. Here, "d" represents the Mid-Node Offset distance.
Jacobian Ratio
Jacobian Ratio is the ratio between the smallest determinant of the Jacobian matrix to largest determinant of the Jacobian matrix at gauss points.
Area Skew
Area Skew is computed as
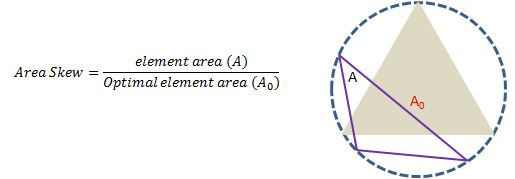
where Optimal element area (A0) is the area of an equilateral triangle with the same circumradius as the element. (The circumradius is the radius of the circle passing through the three vertices of the triangle.)
Area Skew: Fluent
Area Skew : Fluent is computed as

where Optimal element area (A0) is the area of an equilateral triangle with the same circumradius as the element. (The circumradius is the radius of the circle passing through the three vertices of the triangle.)
Height
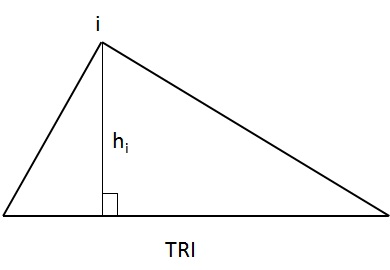
Height is the shortest distance from a corner node to its opposite element edge.
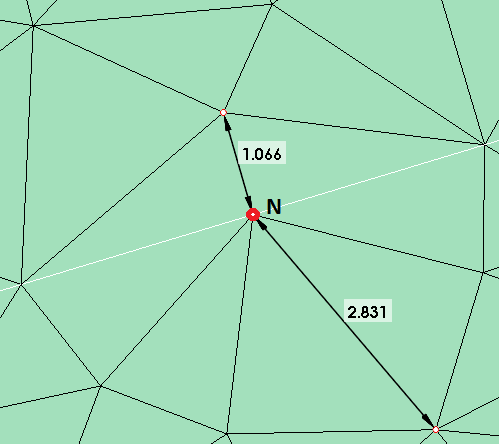
Surface Grading
Surface Grading is computed as the ratio between the maximum and minimum element edge length at each node.
In below image, For Node N, the maximum and minimum element edge lengths are 2.831 and 1.066 respectively. So the Surface Grading will be 2.6557.
Stable time increment - Radioss
The Stable time step is the time needed for a shock wave (stress / pressure wave) to cross the smallest distance in an element. It is used to determine the initial minimum time step required for explicit dynamic analysis. This parameter also depends on the material properties (Young's modulus and Density) assigned to the elements apart from the element dimensions.