Element Quality definitions: QUAD
QUAD element types
The quality measures supported for QUAD element types are as follows,
- Aspect Ratio
- Edge Length
- Interior Angle
- Warpage
- Skew
- Area
- Mid-Node Offset : Ratio
- Mid-Node Offset : Distance
- Height
- Stable time increment - Radioss
- Fux: Ratio of area to the square of perimeter
Aspect Ratio
The aspect ratio of a QUAD element is the ratio of longest edge to shortest edge.
Edge Length
Minimum and maximum length of the element edge.
Interior Angle
The min and max interior angle is calculated based on angle formed by the edges at each node of the QUAD element.
Warpage
The warpage of a QUAD element is calculated by splitting the QUAD into two TRIs and finding the angle between the two planes formed by the TRIs. The QUAD is then split again, using the opposite corners, forming the second set of TRIs. The angle between the two planes formed by the second set of TRIs is found. The maximum angle found between the planes is the warp angle of the element.
| Angle 1 | Angle 2 |
|---|---|
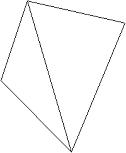 |
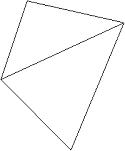 |
Skew
The skew angle of a QUAD element is calculated by finding the minimum angle between two lines joining opposite mid-sides of the element. 90 degrees minus the minimum angle is skew.
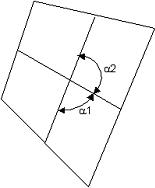
Skew = 90 - Min(α1, α2).
Area
Area of the QUAD element.
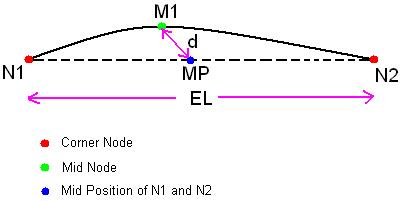
Mid-Node Offset: Ratio
It is the ratio between offset distance of mid node from the mid position of the corresponding element edge to element edge length. If EL denote the length of the element edge N1-N2, then d / El represents the Mid-Node Offset ratio.
Mid-Node Offset: Distance
It is the offset distance of mid node from the mid position of the corresponding element edge. For example, let N1-N2 be an higher order element edge with mid node M1 and MP be the mid position of the element edge N1-N2. Here, "d" represents the Mid-Node Offset distance.
Height
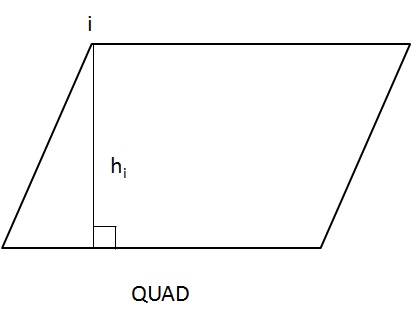
Height is the shortest distance from a corner node to its opposite element edge (or) shortest element edge length.
Stable time increment - Radioss
The Stable time step is the time needed for a shock wave (stress / pressure wave) to cross the smallest distance in an element. It is used to determine the initial minimum time step required for explicit dynamic analysis. This parameter also depends on the material properties (Young's modulus and Density) assigned to the elements apart from the element dimensions.
Flux: Ratio of area to the square of perimeter
It is the ratio between the area and the square of QUAD perimeter.
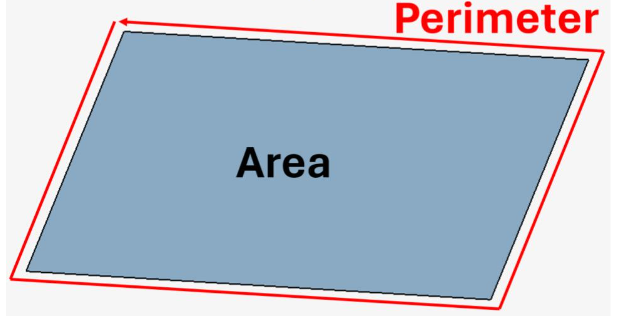
By default, for Flux solver, we consider a QUAD to be of satisfactory quality if the ratio is greater than or equal to 1/30.