Element Quality definitions: HEX
HEX element types
The quality measures supported for HEX element types are as follows,
- Aspect Ratio
- Warpage
- Skew
- Interior Angle
- Volume
- Edge Length
- Stable time increment
- Stable time increment - Radioss
- Mid node alignment ratio
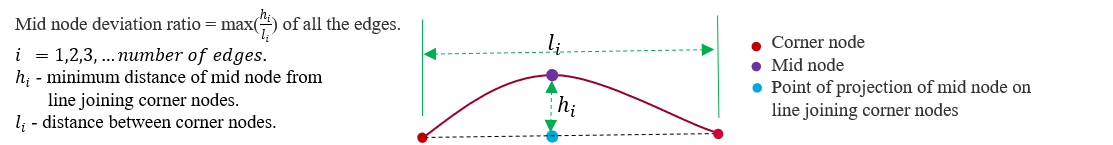
- Mid node deviation ratio
- Jacobian-Ratio
Aspect Ratio
Aspect ratio of a HEX element is defined as the ratio of its longest edge to its shortest edge.
Warpage
The face warpage of a HEX element is defined as the maximum warpage among its six faces. Each face is treated as a QUAD element.
Skew
The face skew angle of a HEX element is defined as the maximum skew angle among its six faces. Each face is treated as a QUAD element.
Interior Angle
Interior Angle is the angle between the edges of a rectangular face of HEX. Minimum and maximum value of the interior angle of each HEX element is calculated by considering all the six faces of the HEX element.
Volume
Volume of the HEX element.
Edge Length
Length of Hex Edges.
Stable time increment
The Stable time step is the time needed for a shock wave (stress / pressure wave) to cross the smallest distance in an element. It is used to determine the initial minimum time step required for explicit dynamic analysis. This parameter also depends on the material properties assigned to the elements apart from the element dimensions.
Stable time increment - Radioss
The Stable time step is the time needed for a shock wave (stress / pressure wave) to cross the smallest distance in an element. It is used to determine the initial minimum time step required for explicit dynamic analysis. This parameter also depends on the material properties (Young's modulus and Density) assigned to the elements apart from the element dimensions.
Jacobian-Ratio
It is ratio between the smallest determinant of the Jacobian matrix to largest determinant of the Jacobian matrix at gauss points. Jacobian of hex8 and hex20 are calculated based on 8 point Integration Rule and 27 point Integration Rule respectively.
Mid node alignment ratio
It describes how close a mid node can be displaced towards corner node along element edge.

Mid node deviation ratio
It describes how far a mid node is displaced from the line joining corner nodes.