Solver Settings
![]()
Introduction
This tool is used to define Flux PEEC solver settings. The settings affect the physics and the resolution techniques for Magnetostatic Integral solution.
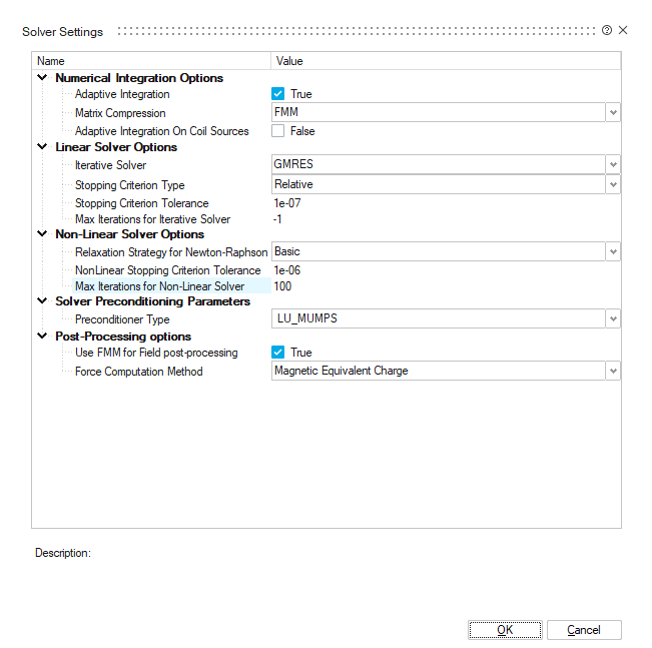
Numerical Integration Options
In this part of the solver settings, three physical options can be defined:
- Adaptive Integration: By default, this option is
checked (True). It improves the calculation of the
integrals. It uses an adaptive Gauss point algorithm to ensure good integral
accuracy on every interaction between two mesh elements. This option can
lead to additional calculation time.Important:
- For Tetrahedral mesh, this option can be unchecked (False) to save lot of calculation time, and the lost precision is negligible.
- For hexahedral mesh, it is recommended to leave this option checked (True) to obtain correct results; unchecking it generally leads to wrong results.
- Matrix Compression: PEEC solver
uses an integral method.
- With the Without option, the method generates full matrices unlike finite element methods which generate sparse matrices.
- With the FMM option, the method uses Fast Multipole matrix compression which drastically reduces the amount of memory to be used.
- Adaptive Integration On Coil Sources: By default, this option is unchecked (False). This option allows when checked to compute with more accuracy the coil - solid interactions. The algorithm behind it is not well optimized and can take a bit more time computation.
Linear Solver Options
In this part of the solver settings, options for the iterative solver used to solve the linear system are set:
- Iterative Solver: Three methods
to solve the system of linear equations
- GMRES: Flexible Generalized Minimal Residual method
- BICGStab: Biconjugate gradient stabilized method
- TFQMR: Transpose Free Quasi-Minimal Residual method
- Stopping Criterion Type: this criterion is applied on the residual norm approximation for each iteration of the iterative solver, it can be Relative or Absolute.
- Stopping Criterion Tolerance: value of the stopping criterion. By default, equals to 1e-6.
- Max Iterations for Iterative
Solver: this option defines the maximum number of iterations
for the iterative solver, it stops even if the tolerance of the stopping
criterion is not reached. The value
-1is used to have no limitation of the number of iterations.Note: For GMRES iterative solver, the solve will not stop at the maximum number of iterations, it will do a restart (orthogonalization) of Krylov sub space instead.
Non-Linear Solver Options
In this part of the solver settings, options for the iterative solver used to solve
the non-linear system are set:
- Relaxation Strategy for Newton-Raphson: this option
allows to choose the relaxation strategy for non-linear solver among 4
methods
- Basic
- Energy Functional Minimization
- Monotonic Decrease
- Residual Minimization
- NonLinear Stopping Criterion Tolerance: this criterion is relative and it is applied on the residual norm approximation for each iteration of the iterative solver. By default, equals to 1e-6.
- Max Iterations for Non-Linear Solver: this option defines the maximum number of iterations for the iterative solver, it stops even if the tolerance of the stopping criterion is not reached. By default, equals to 100.
Solver preconditioning parameters
Preconditioning is a transformation that conditions a given problem in a form more
suited to numerical solving methods. It is usually related to reducing a problem
condition number. After this transformation, the preconditioned problem is then
solved by an iterative method more quickly.
- Preconditioner type: for this option, three variants
are possible
- Without: there is no preconditioner.
- LU_MUMPS: the Mumps solver is used to perform the LU decomposition of a specific preconditioning matrix. Then the decomposed matrix is applied to the iterative solver at each iteration.
- Diagonal: for the linear system A . x = b, the diagonal of the matrix A is used as a preconditioner.
Post-Processing Options
- Use FMM For Field post-processing: This option is used to speed up the computation time in the PEEC solver during post-processing for field computation. For example, this option allows forces to be computed more quickly. The accuracy remains very good, this option is intended for advanced mode.
- Force Computation Method: this option allows to
choose between three methods to compute forces
- Magnetic Equivalent Charge
- Maxwell Tensor
- Virtual Works