Antenna Via
- Except Net for Check: PollEx DFE does not check for vias connected to these net groups.
- Number of Remained Layer: Define via stub layer count to be treated as an antenna.
- Check Dangling VIA: Check that if there exist via that has no net connection.
- Except Via: Select vias to be excluded for this rule checking.
- Padstack Name: Select via using Padstack Name.
- Padstack Size: Select via using Padstack Size.
The report of this rule check includes antenna structure vias and their locations.
For those reported vias, you can view their structures with PollEx Net 2D/3D viewer to investigate more details.
In low frequency, via stubs do not cause many problems. But in high frequency, they can create or receive noise from other routing structures because they act as antenna.
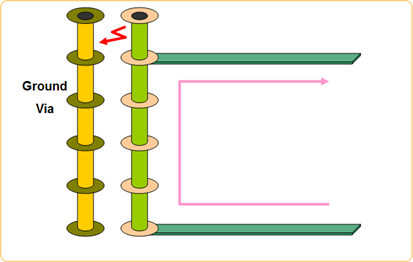
Figure 1.
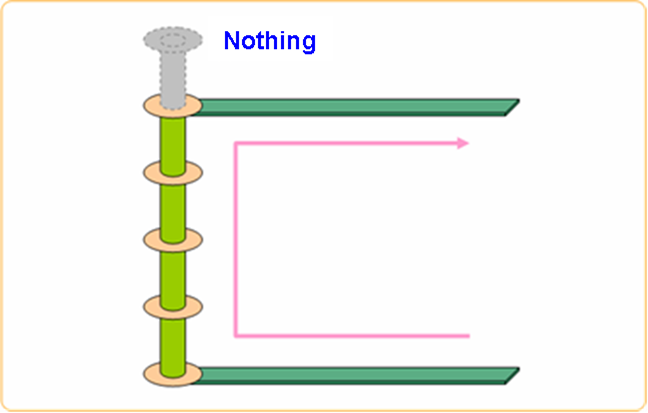
Figure 2.
Via Types
- Micro via
- Hole diameter is usually under 100μm and it is used as a pad for discrete components. It occupies small space on board and reduces power/ground cutting effect which is caused by large via. Instead of using large vias, you can replace them with micro via to reduce inductance at connecting positions.
- Buried via
- This via exists only in inner layers. It cannot be visually observed from top or bottom. It is usually used in high speed signal board to prevent Power/Ground Cutting Effect and also give PCB designer additional spaces for routing.
- Blind via
- This via connect from top or bottom to inner layer only. So, this via could be seen only from top or bottom. When it is used with blind via, it is very effective in cost and routing space control.
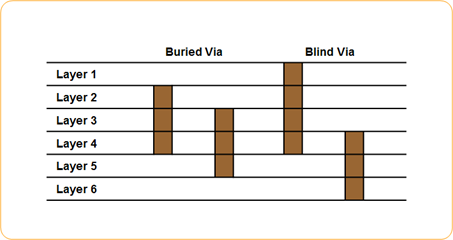
Figure 3.