Perform Additional Operations on Data
The MinMax/Ranking/Envelope tool is an extension of the Results Query tool, and can be used to perform additional operations on data and get dedicated reporting.
-
From the Post ribbon, click Tools.
Figure 1. 
- Select MinMax/Ranking/Envelope
-
Click Start.
A new dialog opens.
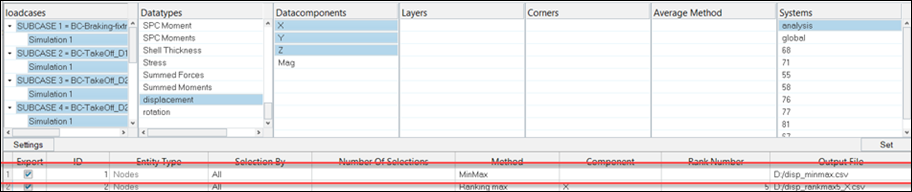
- Select the loadcases.
-
Select the data type.
Once the data type is selected, related data components, layers, corners, average method and systems are populated. You can select multiple data components, multiple layers, single corner option, single average method, and single system.
- Click Set to create a new query entry.
-
Select or deselect the Export option.
You can have multiple query items and decide what to finally export among those available.Note: The ID is automatically generated, and cannot be modified. The entity type is automatically populated based on the binding among query setting and available entities. The number of selections is generated based on what you selected for Selection By. If you selected All, the widget is not active. For all of the other options, by clicking in the blank entry cell, the panel selection relative to either entity, component or set selection opens.
- Make your selections in the Method column.
-
Select the components.
This defines the sorting of Ranking and Envelope tools, as they will operate using that component, and will output other ones for the found entities.
- Make your selections in the Rank Number column.
-
Select the file where the data will be stored (.csv
format).
The same file entry can be used for different queries. In this case, result blocks will be appended.
- Click Settings to set up the result precision and the separator for the CSV.
Min Max Example
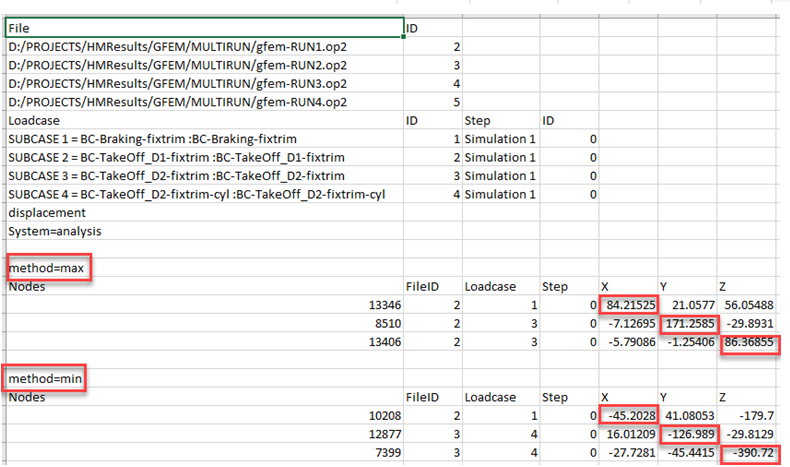
The first column shows the source files, selected load cases, the data type, and all other relevant information, if any.
The column corresponding to the method=max shows what the entity expects for the maximum X, Y and Z components, for displacement in this example, as well as for the same entity the relevant values for the other components. The same is true for method=min.
Ranking Method Example
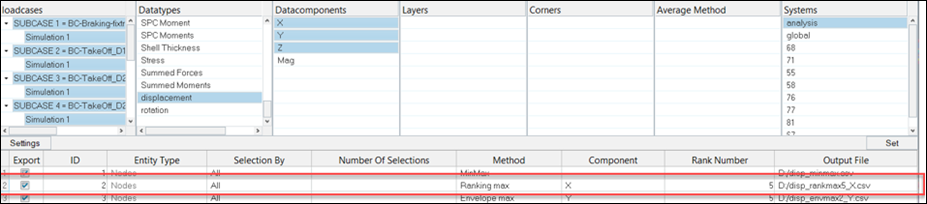
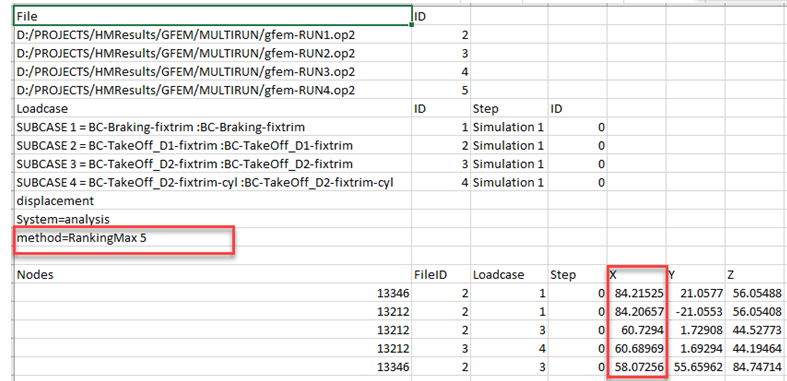
In this case, the top five combinations among nodes and loadcases are shown based on the sorting on maximum displacement X.
- Node | Loadcase
- Element | Loadcase
- Element | Loadcase | Layer
- Element | Loadcase | Corner (no average)
- Element | Loadcase | Layer | Corner (no average)
- Node | Loadcase | Layer (when average is applied to change binding from element to node)
Ranking entities can be repeated several times, as shown in the example above, where node 13212 is found at rank two, three and four from loadcase one, three and four, respectively.
Envelope Example
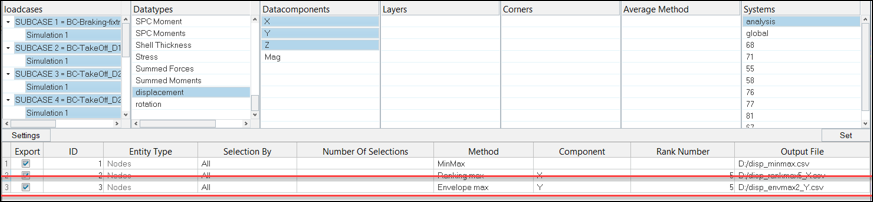
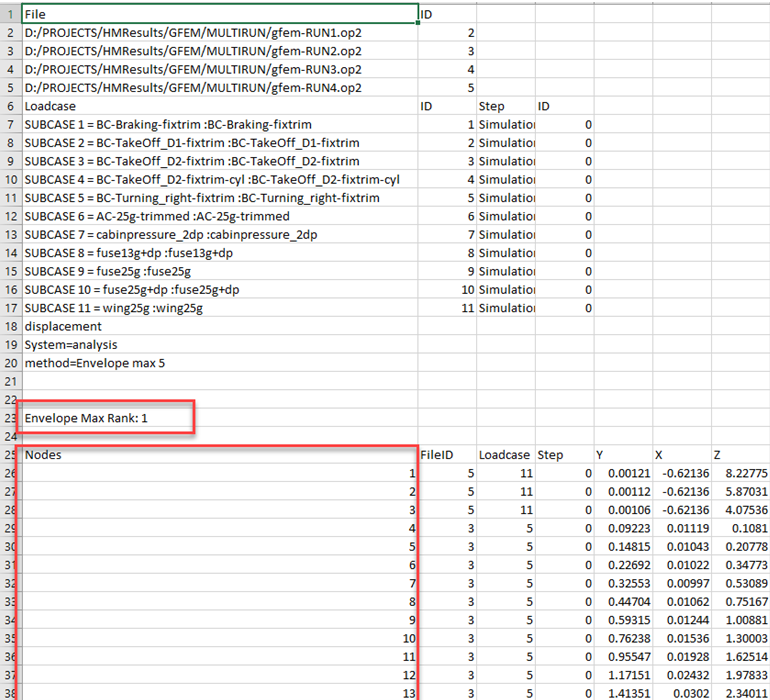
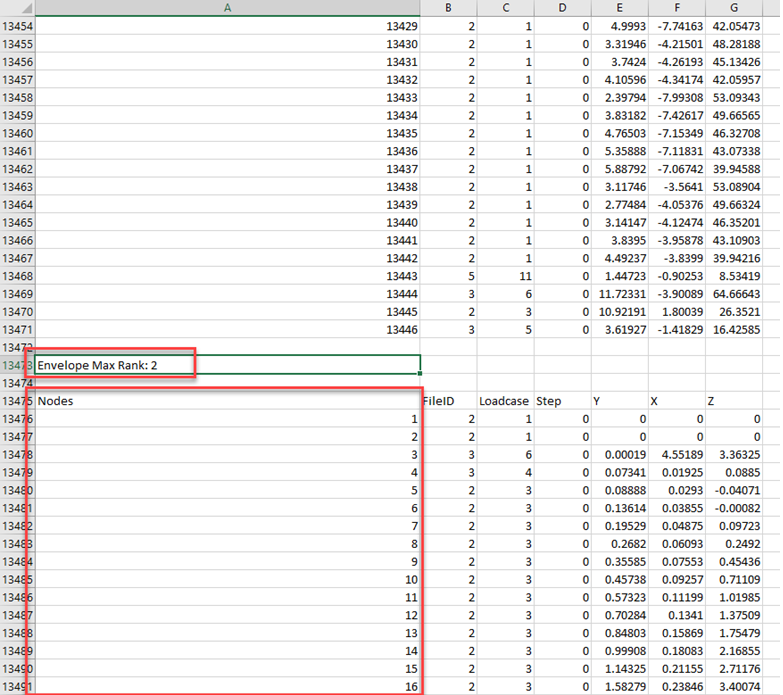
The Envelope tool shows a block of information for each selected entity, which is the top combination ranked based on the selected component.
Using the Ranking and Envelope method, you can input a dedicated ranked number. If the number of combinations allowed is below this value, the utility uses the number of allowed combinations that are possible.
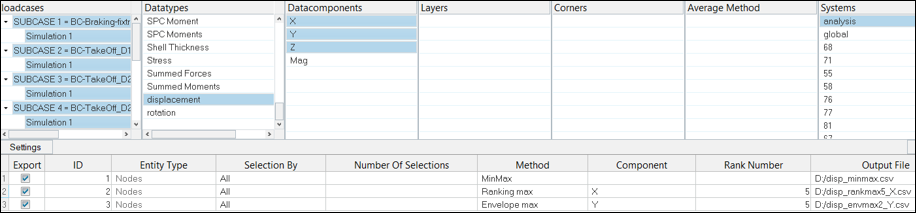

Perform Additional Operations on Data - Batch Mode
-
From the Post ribbon, click Tools.
Figure 11. 
-
Select Batch.
Figure 12. 
-
Click Start.
The utility creates a new instance, loads model and results, creates the result entity and uses the settings defined in the .xml file.