Feedback PID Steering Controller - Cars & Trucks
A Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) steering controller is a feedback controller that computes a vehicle steering input using the error, the integral of error, and the rate of change of error between the desired vehicle path and the actual vehicle position.
To use a PID control you enter proportional (KP), integral (KI), and derivative (KD) gains, the Demand Path similarly with the Feed-forward steering controller and the type of the controller. The Altair Driver then applies the Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) control law to calculate the steering signal.
Currently, there is only one available PID steer controller type (FOLLOW_PATH). The following section explains the controller’s algorithm.
Algorithm
| Parameters | |
|---|---|
| Path Error | e |
| Proportional gain | Proportional gain |
| Derivative gain | Derivative gain |
| Integral gain | Integral gain |
| Integral control flag | Integral control flag (α) |
| Integral band | Integral band (σ) |
| Driver steering output | O steering |
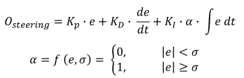
[PID_STEER_CONTROLLER]
TAG = 'PID'
TYPE = 'FOLLOW_PATH'
PATH = 'PREDEFINED'
BLOCK = 'PATH'
KP = 0.2
KD = 1.0
KI = 0.0 | [FEEDFORWARD LONGITUDINAL CONTROLLER] | ||
|---|---|---|
| TAG | Attr - string | REQUIRED <PID> |
| TYPE | Attr - string | REQUIRED <FOLLOW_PATH> |
| I_ACTIVE_BAND | Attr - real | OPTIONAL
If absent:
|
| KP | Attr - Real | OPTIONAL
If absent:
|
| KD | Attr - Real | OPTIONAL
If absent:
|
| KI | Attr - Real | OPTIONAL
If absent:
|
| INITIAL_ERROR | Attr - Real | OPTIONAL
If absent:
|