Suspension Model
![]()
Introduction
This feature helps to model a simplified vehicle suspension model. With 3-degrees-of-freedom double roller motion, it enhances the fidelity of the water-wading simulations without the need for complex multi-body-dynamics coupling simulation.
Description
Suspension Type
- Rigid (Double Roller 1DOF Motion)
- Linear Spring/Damper (Double Roller 3 DOF Motion)
Rigid
Rigid suspension model or 1DOF is used where fluid forces on the body are negligible, such as shallow cases. In cases where small changes in the road path slope between different segments is small, using the 1DoF variant is sufficient.
Linear Spring / Damper
Linear suspension model or 3DOF is recommended only when the modeled linear spring/damper response results in non-negligible differences in body position and angle when passing between different road segments. n double roller 3DoF, the wheels remain rigid and follow the road in the same way as a rigid body motion model while the car body is free to move in the Z direction and rotate about the Y axis. This provides two more degrees of freedom for a total of three, hence double roller 3DoF. Double roller 3DoF is like a half-car model where tire deformation is ignored.
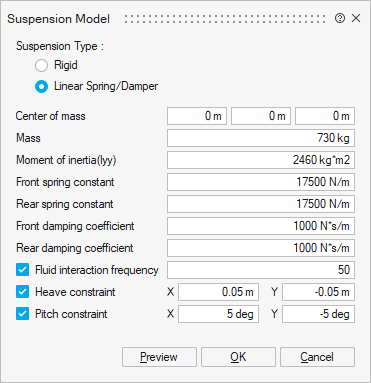
- Center of mass
Center of mass of the body phases and reference point used for calculating moments on the body phases. This is the internal center of rotation though apparent center of rotation may be different.
- Mass
Total mass of the body phases.
- Moment of inertia (Iyy)
Mass moment of inertial of combined body phases about Y.
- Front spring constant
Effective front wheel spring constant.
- Rear spring constant
Effective rear wheel spring constant.
- Front damping coefficient
Effective front wheel damping coefficient.
- Rear damping coefficient
Effective rear wheel damping coefficient.
- Fluid interaction frequency
Frequency of sampling fluid force and torque on the body phases. The force and torque will remain constant in between sampling points.
- Heave constraint
Constrain body Z-position by equivalent 1DoF motion. In combination with pitch constraint, it has a similar effect to limiting the stretch/compression of the suspension.
- Pitch constraint
Constrain body the Y-angle by equivalent 1DoF motion. In combination with heave constraint, it has a similar effect to limiting the stretch/compression of the suspension.
Preview
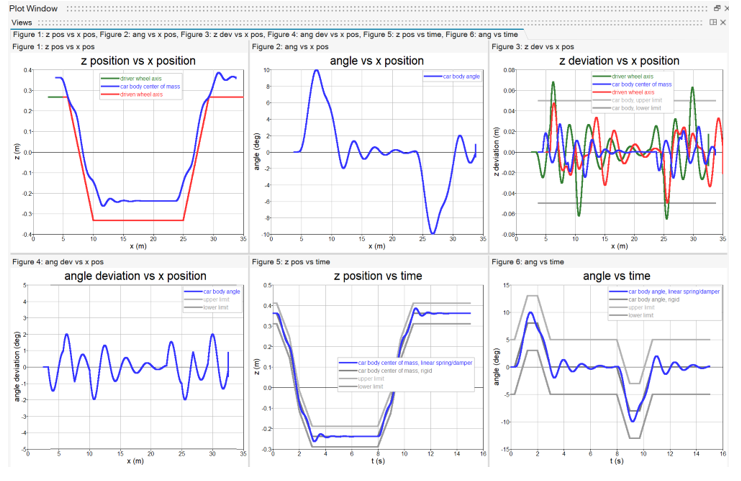
- Rigid
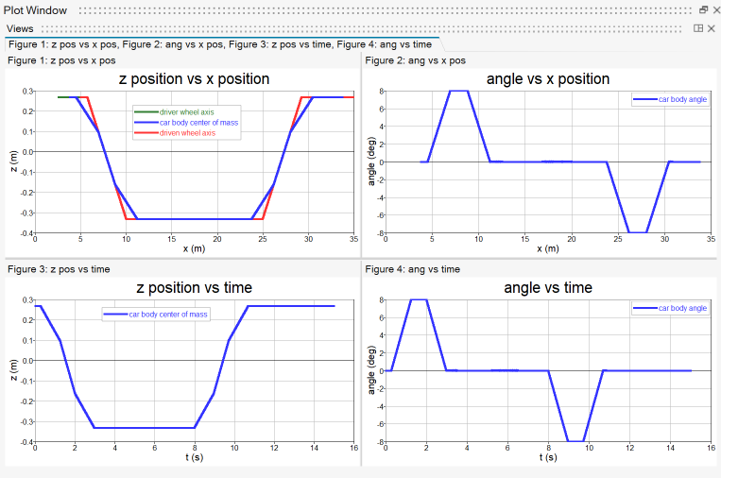
- Linear Spring/Damper