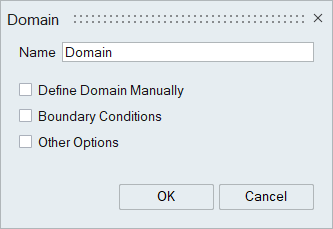
Domain
![]()
Introduction
This tool is used to define the domain and global parameters of the nanoFluidX case.
For a typical drivetrain simulation, the user only needs to define the Body Force for the simulation. For other cases, especially those with open boundaries the domain size and/or reference values should be specified.
Define Domain
Define Domain is used to set ultimate extent of the simulation, defining a bounding box from which the minimum and maximum dimensions (corner points) will be calculated.
If the simulation is of a closed geometry, e.g. a gearbox, the solver will automatically calculate the domain dimensions, so they do not need to be specified.
If the simulation has an open boundary, or if there are periodic boundary conditions associated with the domain, it is necessary to manually prescribe the size of the domain (bounding box).
Use Define Box | Bodies and select all of the particle bodies – the padding around the particles should be set to 3*dx.
Boundary Conditions
These domain parameters are used to define the boundary conditions at minimum and maximum boundary. Boundary options supported are PERIODIC, OUTLET and SIMPLEOUTLET.
The SIMPLEOUTLET boundary simply deletes all the particles that cross it.
OUTLET boundary is different from a SIMPLEOUTLET in that, by default, it has an associated zero-gradient velocity condition. Alternatively, with OUTLET user can specify the outlet velocity and add the influence of the gravitational force on the outgoing fluid. There can be multiple OUTLET boundaries specified in the domain.
Other Options
A free text box where additional parameters can be specified.