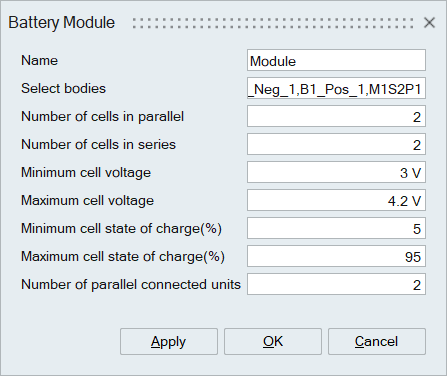
Battery Module
![]()
Introduction
The Battery module is a hierarchical unit in the battery pack that is made up of cells arranged in serial and parallel. The command provides an avenue to identify electrical bodies that belong to the module as well as the datasheet operating limits of the cell. The operating limits supported in the battery solutions are the maximum and minimum individual cell voltage as well as the SOC range (i.e. maximum and minimum SOC).
Description
- Select bodies
The identification of the electrical bodies (e.g. cells) allows for the identification of a cell in a pack based on the module number and cell numbering. For example, if the label is M2S1P4, this means the cell in the pack belongs to module 2 and is the 4th cell in the first parallel bank connected in series. These bodies are added under a separate subassembly with user-given name.
- Number of cells in parallel
Number of cells connected in parallel in a battery module for each series unit.
- Number of cells in series
Number of parallel units connected in series.
- Minimum cell voltage
Minimum allowed voltage of an individual battery cell
- Maximum cell voltage
Maximum allowed voltage of an individual battery cell. This avoids overcharging.
- Minimum cell state of charge
State of charge at which a battery cell is considered fully discharged.
- Maximum cell state of charge
State of charge at which a battery cell is considered fully charged.
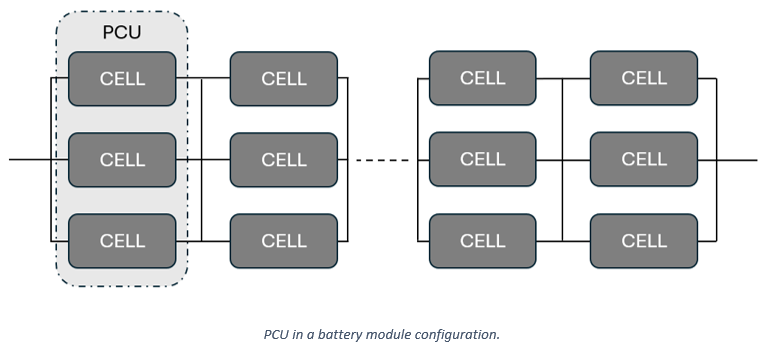
- Number of parallel connected units
The number of parallel connected units (PCU) represents how cells are wired or connected in the module. This parameter only needs to be set when the state of charge differs between cells. Conceptually, a PCU in a module is given below.
For example, in a 4s2p case, where the number PCUs = 1, 2, or 4. The corresponding electrical connection of the battery cells would be represented by the circuits shown below.
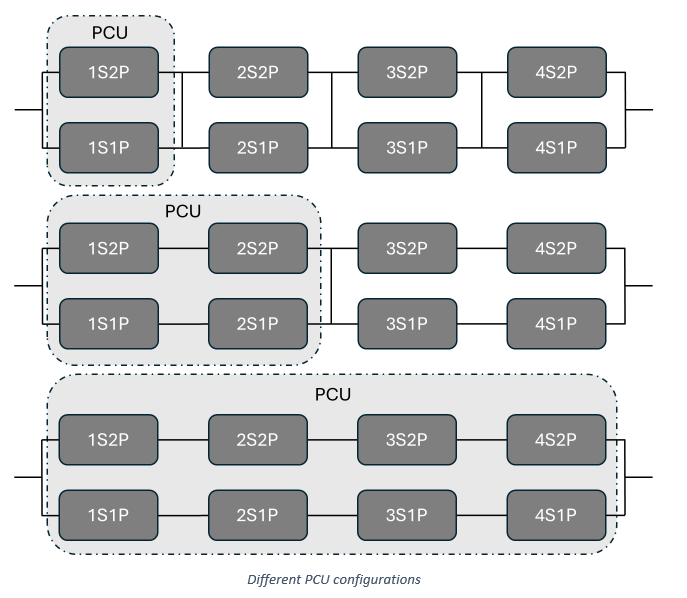
The importance of understanding this connectivity is related to how current is distributed through the battery pack when cells (and therefore modules) connected in parallel have cells of differing states. For instance, with a single PCU, it is essential for voltage to be uniform across each cell in the circuit to ensure conservation.