Electrostatic solution
![]()
Introduction
The electrostatic physics allows the study of electric charges that are in equilibrium. This solution can be used to study high voltage devices, spark gaps, insulators, capacitors etc.
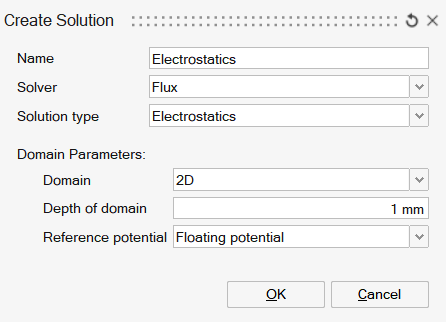
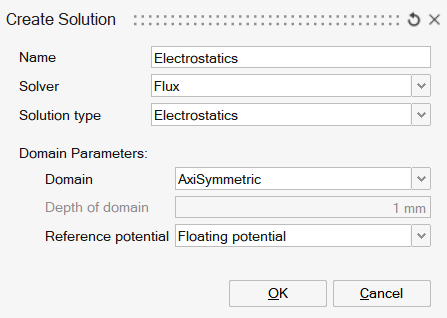
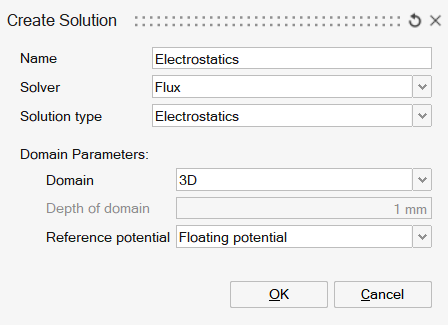
| 2D | Axisymmetric | 3D |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
Note: For more information about the
Electrostatic workflow, please consult:
- 2D Electrostatic (same workflow for Axisymmetric)
- 3D Electrostatic
Solution dialog box
- The Electrostatic solution is available for 2D, AxiSymmetric and 3D cases.
- For 2D cases, the domain depth must be defined to include electromagnetic effects in the third dimension.
- For 3D cases, the user can select the floating potential formulation. Imposed potential will be supported once we add infinite region support for the solution.
Typical example
A typical example of problem treated as an Electrostatic application is presented in the figure below.
 : Regions representing the
main parts of the studied device (volume regions in 3D and face regions in 2D)
: Regions representing the
main parts of the studied device (volume regions in 3D and face regions in 2D)
 : Regions representing the
sources (face regions in 3D and line regions in 2D)
: Regions representing the
sources (face regions in 3D and line regions in 2D)