OLC
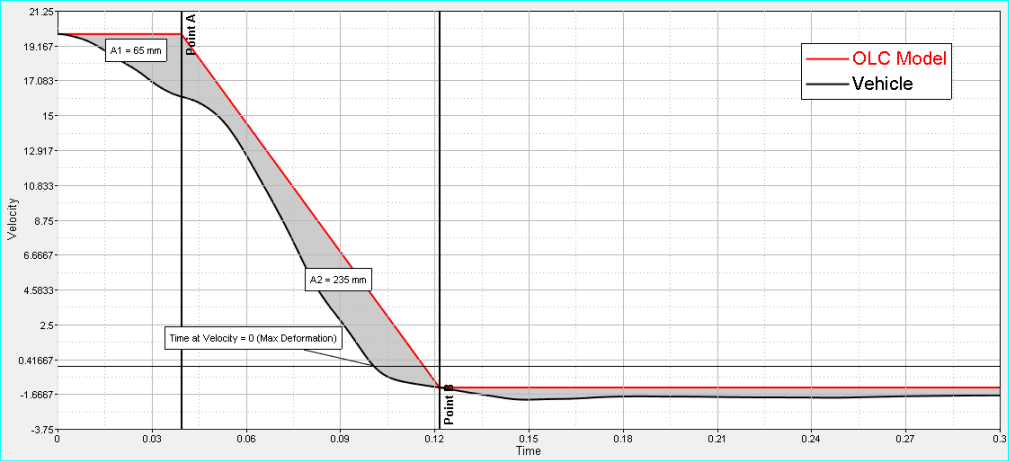
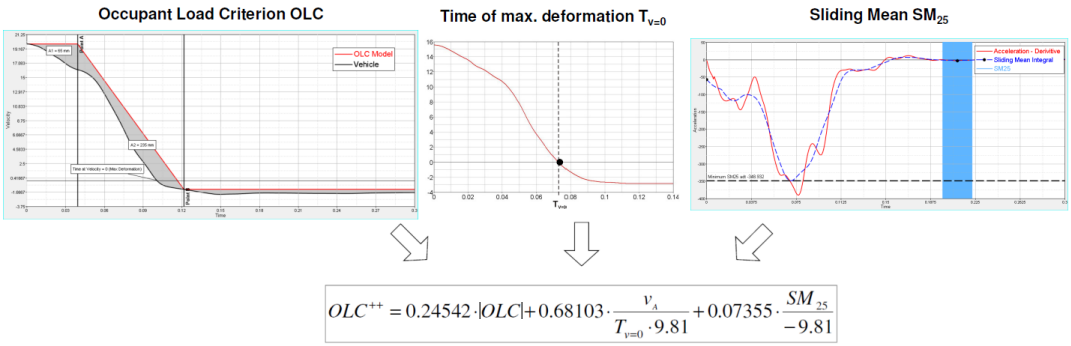
The OLC function is able to calculate both the Occupant Load Criteria (OLC) and OLC++. OLC++ combines OLC with the time of maximum deformation (Tv=0) and the sliding mean integral over a window of 25 ms (SM25), as shown in the formulas below.
Syntax
OLC(time_vec, velocity_vec, flag, precision)
Argument
- time_vec
- Time vector of the maximum deformation.
- velocity_vec
- Velocity vector.
- flag
- The return argument specifies which value(s) should
be returned by the function, and has the following options:
- 0
- OLC (the absolute value of the slope).
- 1
- OLC++ (returns one scalar value only).
- 2
- Returns OLC curve X (time) vector.
- 3
- Returns OLC curve Y (velocity) vector.
- 4
- Returns Tv0 value.
- 5
- Returns SM25 value.
- 6
- Returns V0 value.
- 7
- Returns OLC, TV0, SM25, and V0 values.
- precision
- Define precision for the algorithm. (default = 0)
Algorithm for OLC
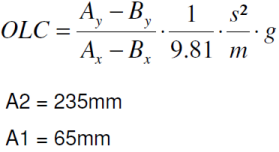
Example

Note Text
High Precision
-------------
OLC = {olc(c1.x,c1.y,0,1)}
Low Precision without optional four arguments
--------------------------------------------
OLC = {olc(c1.x,c1.y,0)}
OLC++ = {olc(c1.x,c1.y,1)}
OLC curve X (time) vector = {olc(c1.x,c1.y,2)}
OLC curve Y (velocity) vector = {olc(c1.x,c1.y,3)}
Time at V=0 value = {olc(c1.x,c1.y,4)}
SM25 OLC function= {olc(c1.x,c1.y,5)}
V0 value = {olc(c1.x,c1.y,6)}
OLC, OLC++, TV0, SM25, and V0 values = {olc(c1.x,c1.y,7)}Comments
Units are supported:
- If available, units will be detected.
- An error is raised for the wrong unit type (acceleration, displacement, and so on).
- If a curve has no units, the expected units are s for the X vector and m/s for the Y vector.
- To calculate OLC++, the starting velocity needs to be > 0.