Modifying the Auto-Generated Mesh
When the frequency is set or local mesh settings are applied to the geometry, the automatic mesh algorithm calculates and creates the mesh automatically while the GUI is active using default mesh settings. When required, these mesh settings may be modified.
-
Open the Modify Mesh Settings dialog using one of the
following workflows:
- On the Mesh tab, in the
Meshing group, click the
 Modify Mesh icon.
Modify Mesh icon. - Press Ctrl+M to use the keyboard shortcut.
- On the Mesh tab, in the
Meshing group, click the
- On the Modify Mesh Settings, set the Mesh size to Coarse.
-
Set the Wire segment radius to
0.001.
Figure 1. The Modify Mesh Settings dialog. 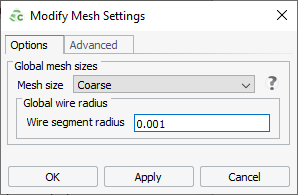
- Click OK to create the mesh and to close the dialog.