Define Linear Periodic Boundaries
You can define Linear Periodic Boundaries to control what happens to a particle once it leaves the domain.
-
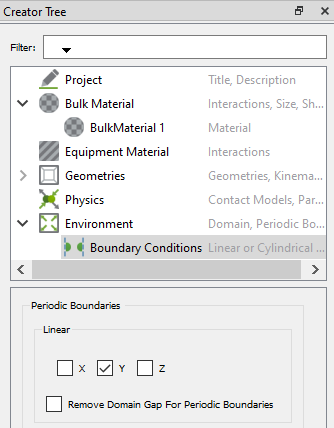
In the Creator Tree, expand the Environment menu and then select
Boundary Conditions.
Any particles exiting the boundary along the Y axis will enter the simulation on the opposite boundary. Linear Periodic Boundaries also allow particles to interact with material on the opposite side of the boundary. In the following example, the particle on the left will be visualized as a whole on the left side of the screen until its center point passes the boundary. However, the particle will still contact material on the other side of the boundary as follows: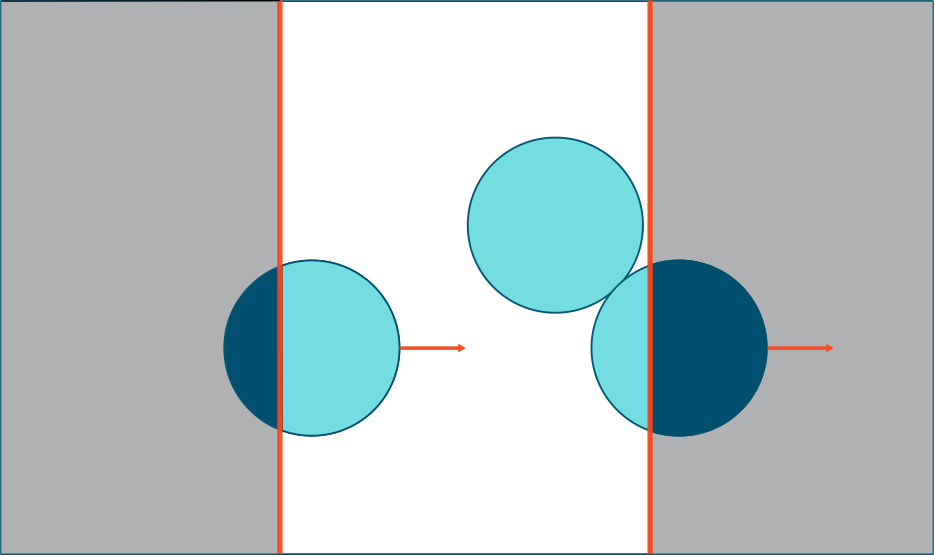
-
Select any of the X, Y, or
Z checkboxes to enable the periodic boundaries in
that direction. You can select more than one direction.
If the option is selected for a particular direction, any particle leaving the domain in that direction will instantly re-enter it on the opposite side.
-
Select the Remove Domain Gap For Periodic Boundaries
checkbox to resize the domain to the exact extent of the Geometry.
By default, to prevent particles from being deleted from the simulation when there is a significant overlap with geometries at the boundary of the domain, EDEM provides a little space around Geometries. In order to have linear periodic boundaries, this gap must be filled. When applying this condition, this should be done in the linear boundary direction.