Chemical Reaction
![]()
This tool specifies chemical reaction parameters. It is used for AcuSolve-EDEM coupling simulations for blast furnace applications.
Description:
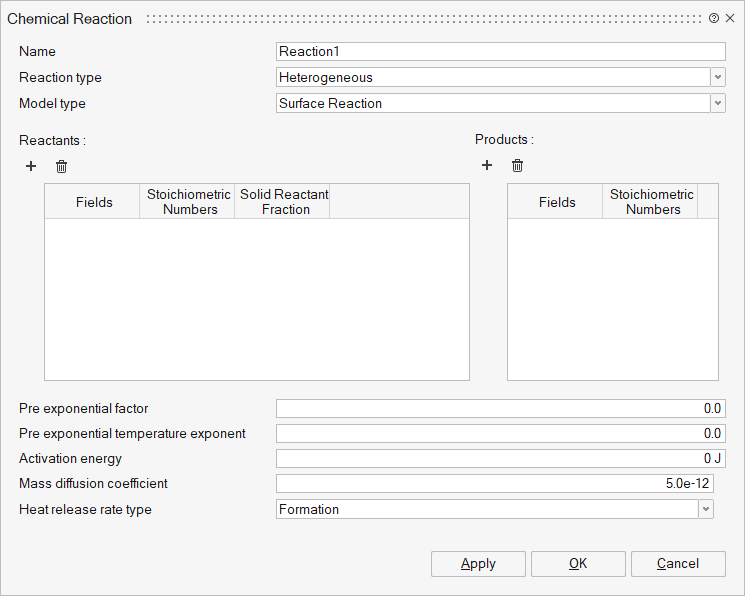
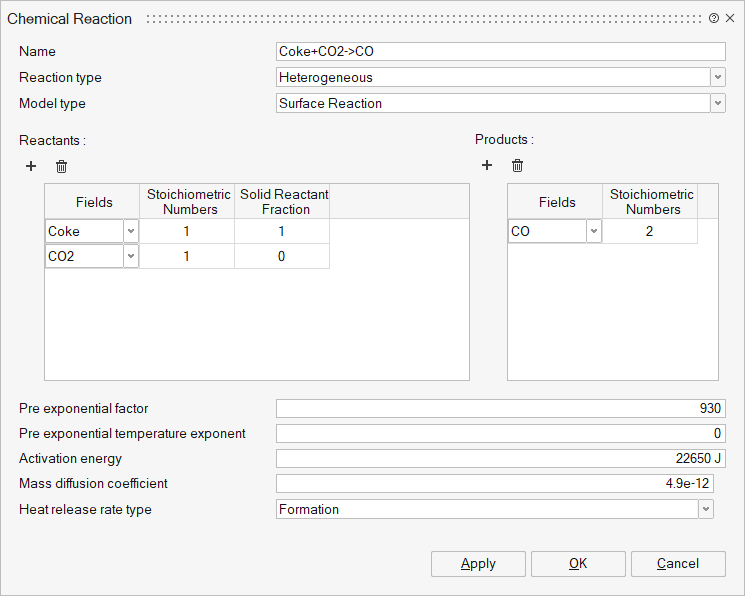
Reaction type: Two types of chemical reactions can be defined,
- Heterogeneous - The reaction involves both solids and gaseous
materials. Model types supported are,'
- Surface Reaction - In this model, the gas surrounding the solid reacts on the solid’s surface. While new gas is produced, the internal composition of the solid remains unchanged.
- Pyrolysis Reaction - In this model, solid particles undergo internal decomposition at high temperatures without the need for surrounding gases. It is assumed that the solid has two initial compositions: one part remains unchanged, while the other part is released as gas during the reaction. For example, in coal particles, volatile matters are released, leaving behind charcoal.
- Shrinking Core - In this model, solid particles undergo both
surface and core reactions. The gas surrounding the particle reacts
with it, changing the internal composition of the solid and
potentially producing new gas. The combined effect of gas diffusion
through the particle’s film layer, gas diffusion through the ash
layer on the particle surface, and chemical kinetics is
modelled.
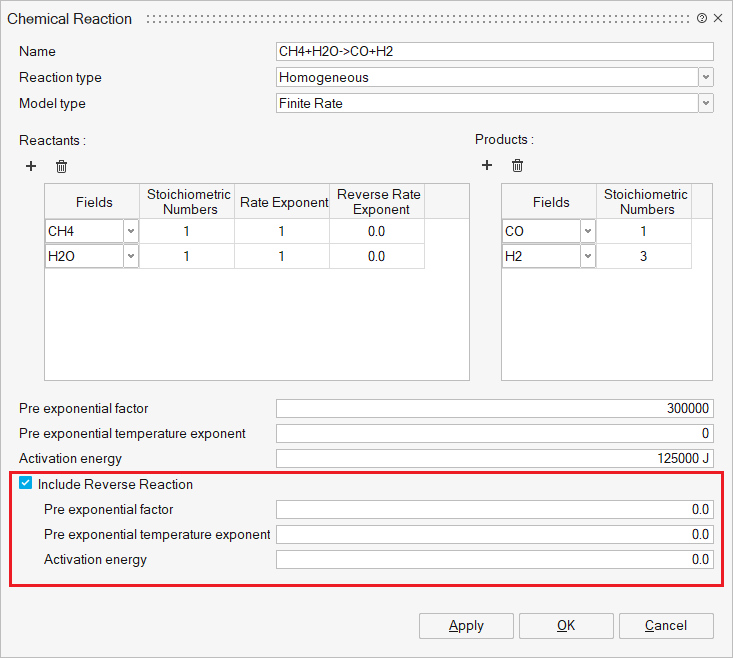
- Homogeneous - The reaction involves both solids and gaseous
materials. Model types supported are,
- Finite Rate – In this model, the exponential temperature-dependent Arrhenius equation is used to determine the rate of reaction.
- Finite Rate Dissipation – The rate of reaction is calculated using the finite rate approach, but the maximum value is constrained by the eddy dissipation model.
- Eddy Dissipation – The Eddy Dissipation model is used to
calculate the rate of reaction. In this model, the rate of reaction
is a function of the turbulent time scale. A two-equation turbulence
model is needed for this approach.
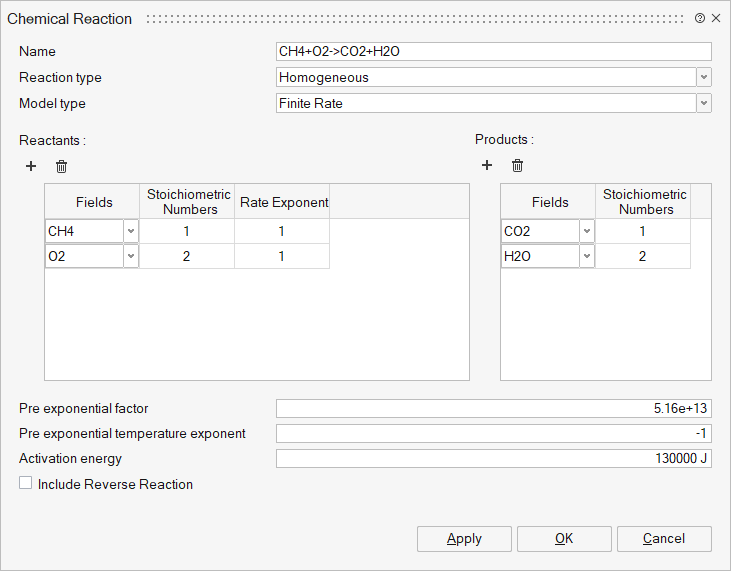
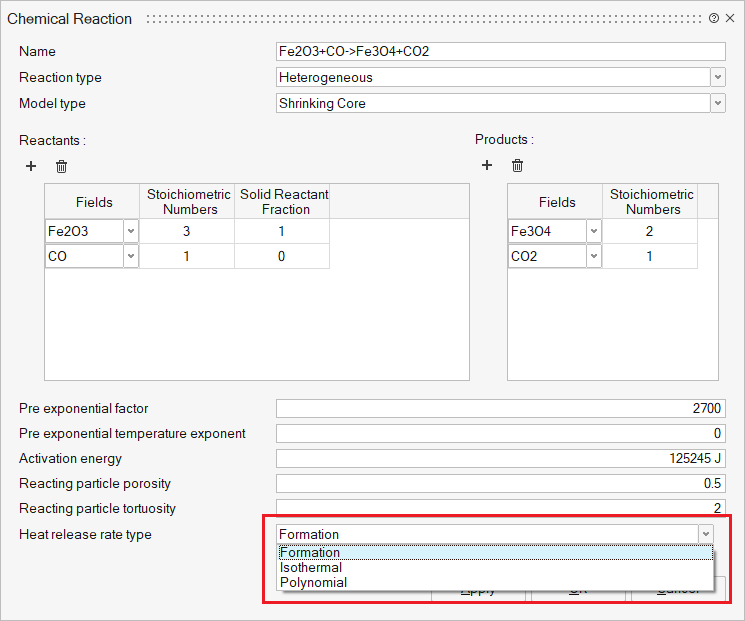
Reactants and Products: The User can define N number of reactants and their
products in respective tables using add and delete buttons.
- Fields – Select the reactant and products. It represents Fluid (Gases) and Solid materials.
- Stoichiometric Numbers - Stoichiometric numbers of the reactants and products.
- Rate Exponents - Exponents of the reactant and product fields.
- Solid Reactant Fraction - Initial mass fraction of the solid field within the reacting particle. If the particle composition is uniform, this value should be set to 1. For coal particles, this can be used to set the initial mass fraction of volatile and solid coal. For coke and ore particles, the values can be set to 1. Gaseous field values should be set to 0. This is used for heterogeneous reactions.
Pre-exponential factor: The pre-exponential factor in the Arrhenius equation.
Pre-exponential temperature exponent: The pre-exponential factor temperature exponent in the Arrhenius equation.
Activation energy: The activation energy in the Arrhenius equation.
Heat release rate type: Type of the heat release rate calculation for solid
particles. Used only for heterogeneous reactions. Three types of heat release
are,
- Formation - If selected, heat rate will be calculated using the enthalpy of formation of the reactant and product fields.
- Isothermal - Reaction heat will be ignored.
- Polynomial - Temperature-dependent polynomial correlation will be used to calculate the heat of reaction. Coefficients of the polynomial should be provided.
Include Reverse Reaction: Flag specifying whether to calculate the reverse reaction for the given forward reaction. Used for homogeneous reaction with the finite rate model.