B(H) law: Nonlinear analytical hard magnetic material with knee adjustment
Presentation
This model (Nonlinear magnet described by HcB and Br, plus knee adjustment) defines a nonlinear B(H) dependence. Non-linearity is considered in the direction of magnetization whereas the model's behavior is linear in the transversal directions.
This magnet model is noted as unidirectional because the mathematical model and the direction of magnetization are dissociated. The mathematical model defines the demagnetization curve, while the direction of magnetization is defined by the orientation in the region.
Mathematical model
The mathematical formula used in Flux for the demagnetization curve is:
For H ≥ -HcB
with
where:
- μ0 is the permeability of vacuum, μ0 = 4 π 10-7 H/m
- μr is the relative permeability of the material (for H = -HcB)
- HcB is the normal coercivity (A/m)
- a is the knee adjustment coefficient (a > 0 and a ≠ 1), enabling to adjust the shape of the curve "knee" for a better approximation of the experimental curve. The smaller the coefficient, the sharper the knee is.
- J's is computed by bisection method from Br, HcB
and μr, knowing that
The shape of the B(H) dependence in the direction of magnetization is given in the figure below:
In transversal directions one can write:
where μr ┴ is the transversal relative permeability.
Direction of magnetization
The direction of permanent magnet magnetization is “dissociated” from the model. In the software, it is defined separately.
The various possibilities available to the user are shown in the table below. (The basic plane is a plane XOY.)
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Unidirectional |
Radial positive |
Radial negative |
Orthoradial positive | Orthoradial negative |
Dialog Box
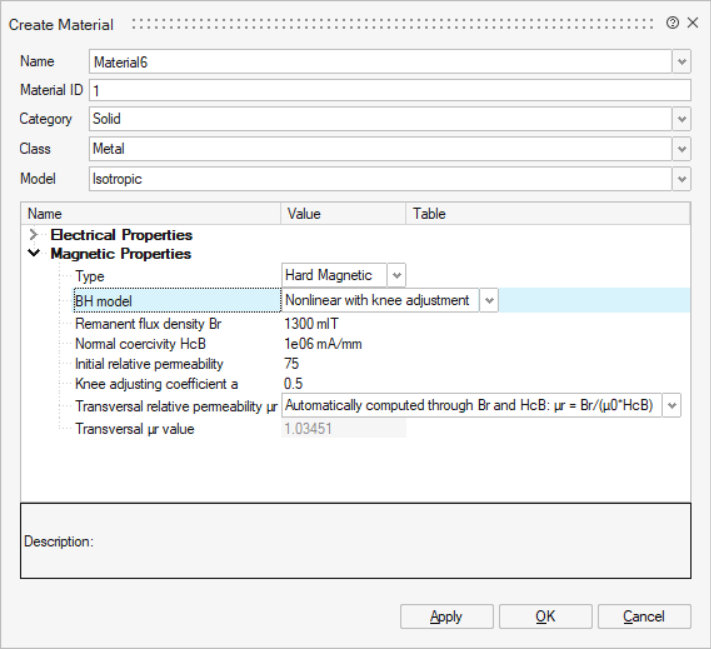
- Open a Create Material dialog box in menu
- Choose Solid as Category field
- Choose Metal as Class field
- In Magnetic Properties:
- Choose Hard Magnetic type
- Choose Nonlinear with knee adjustment BH model
- Define Remanent flux density Br
- Define Normal coercivity HcB
- Define Initial relative permeability
- Define Knee adjusting coefficient a
- Define Transversal relative permeability
μr
2 possibilities:
- Automatically computed through Br and HcB: μr =
Br/(μ0*HcB)
→ Transversal μr value is automatically computed an display in the Transversal μr value field below

-
User-defined

→ the user must enter a value in the Transversal μr value field
- Automatically computed through Br and HcB: μr =
Br/(μ0*HcB)