TCP Align Hole
Check the rule of align hole usage.
TCP component is a tape carrier package. TCP align hole is used to fix the TCP components.
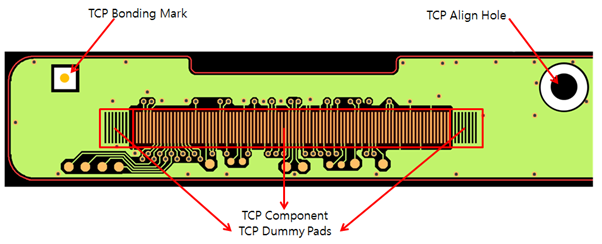
Figure 1.
- TCP Align Hole Definition: TCP align hole can be defined with the hole size
and distance from the TCP component.
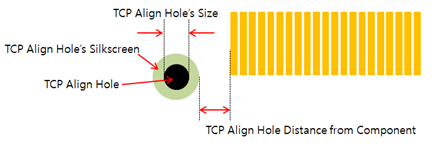
Figure 2.- Definition with Hole Size: Define the align hole with its size. Using the floating value input tool, set the size or range of hole size.
- Define with Distance from TCP Component Group: TCP align hole should
not be apart from the TCP component. They should be placed close
together.

Figure 3.- Component Group: Select the TCP component group from the component group list.
- Maximum Distance: Set the maximum distance between the TCP component and the TCP align hole.
- Silk Hole Mark Definition: TCP align hole can have two types of shapes for
silkscreens: circle and line types. Define the diameter and width/height
value for the circle and line types.
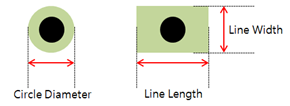
Figure 4.- Circle Diameter: Set the circle diameter for the circle type silkscreen.
- Line: Set the line type silkscreen with its width and length.
- Width: Set the width of line for line type silkscreen.
- Length: Set the length of line for line type silkscreen.
- TP(Test Point) Definition: To check the clearance between a TCP align hole
and a test point, set the test point components.
- TP Component Group Selection: If test points are registered with footprint, select the test point component group from the component group list.
- Pads’ Diameter in Routing: If test points are used with pads, set the size of the pad diameter.
- Via’s Diameter: If test points are used with vias, set the size of the via diameter.
- TCP Align Hole Clearance Checking: Check clearances between the TCP align
hole and the TCP component pad/test points in the design.
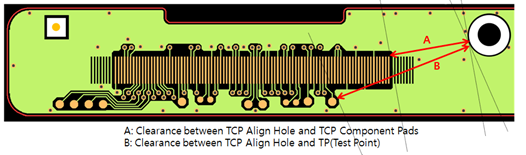
Figure 5.- Clearance between TCP Align Hole and TCP Pads: Set the clearance value between the TCP align hole and the TCP component pads.
- Clearance between TCP Align Hole and TP (Test Point): Set the clearance value between the TCP align hole and the test points.
- TCP Align Hole Checking: Check TCP align hole location and placement.
- Existence Check for both Edge Components: Check if all edge TCP
components have a TCP align hole within the given area. Hole
searching area is defined in the TCP Align Hole Definition. If one
of them doesn’t have a TCP align hole, it is a fail.
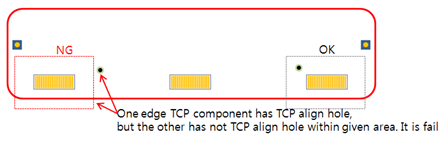
Figure 6. - Silk Hole Mark Alignment with TCP Align Hole: Check if the TCP align
hole and silkscreen are aligned along the given axis.
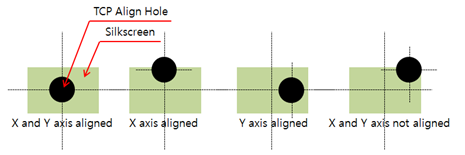
Figure 7.- X: Check if the TCP align hole is aligned with silkscreen along the X-axis. If they are not aligned along the X-axis, it is a fail.
- Y: Check if the TCP align hole is aligned with silkscreen along the Y-axis. If they are not aligned along the Y-axis, it is a fail.
- Clearance between PCB Outline to TCP Align Hole Center: Set the
clearance value between the TCP align hole and the PCB outline.
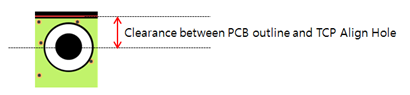
Figure 8. - Alignment between Side Edge TCP Align Holes: Check if the side
edge’s TCP align holes are aligned with each other along the
Y-xis.
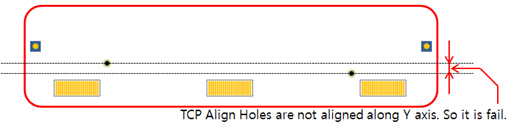
Figure 9.- Tolerance: For the two location values, if they are less than the tolerance, PollEx DFM recognizes them as the same value.
- X/Y: Select alignment axis.
- Number of TCP Align Holes’ Counting: Check the number of TCP align holes in the design. Choose the maximum/minimum/same value counting condition.
- Existence Check for both Edge Components: Check if all edge TCP
components have a TCP align hole within the given area. Hole
searching area is defined in the TCP Align Hole Definition. If one
of them doesn’t have a TCP align hole, it is a fail.