/INIMAP1D/FILE
Block Format Keyword Map 1D velocities and thermodynamic values into 2D or 3D space using spherical, cylindrical, or planar mapping methods. The mapped results are used with /ALE/EULER materials.
Format
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | (10) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| /INIMAP1D/FILE/inimap1d_ID | |||||||||
| inimap1d_title | |||||||||
| type | |||||||||
| node_ID1 | node_ID2 | ||||||||
| grbric_ID | grquad_ID | grtria_ID | |||||||
| Filename | |||||||||
Definition
| Field | Contents | SI Unit Example |
|---|---|---|
| inimap1d_ID | Inimap1d block identifier. (Integer, maximum 10 digits) |
|
| inimap1d_title | Inimap1d block title. (Character, maximum 100 characters) |
|
| type | Initial mapping type.
(Integer) |
|
| node_ID1 | Node 1 identifier. (Integer, maximum 10 digits) |
|
| node_ID2 | Node 2 identifier, only if
type=1 or 2. (Integer, maximum 10 digits) |
|
| grbric_ID | Brick group on which initialization is
performed. (Integer) |
|
| grquad_ID | Quad group on which initialization is
performed. (Integer) |
|
| grtria_ID | Tria group on which initialization is performed. (Integer) |
|
| Filename | File generated by previous 1D run with
/STATE/INIMAP1D/FILE. (Character) |
Comments
- The option can be used to initialize a 2D or 3D simulation from the results of a 1D simulation potentially obtained from an external solver.
- Three different initialization types
are available depending on the type parameter:
- type = 1: a planar initialization is performed where the 1D results are mapped onto a plane which is normal to the vector defined from node_ID1 to node_ID2. The abscissa values in an input function are the distance along the plane’s normal vector. The ordinate values from the input function are a constant value for the entire plane at a given distance along the normal. See Figure 1 and Figure 2.
- type = 2: a cylindrical initialization is performed where the local z cylindrical axis is defined from node_ID1 to node_ID2. The abscissa values in an input function are the radial distance from the local z cylindrical axis. The ordinate values from the input function are a constant value for the entire cylindrical surface at given radial distance. See Figure 3 and Figure 4.
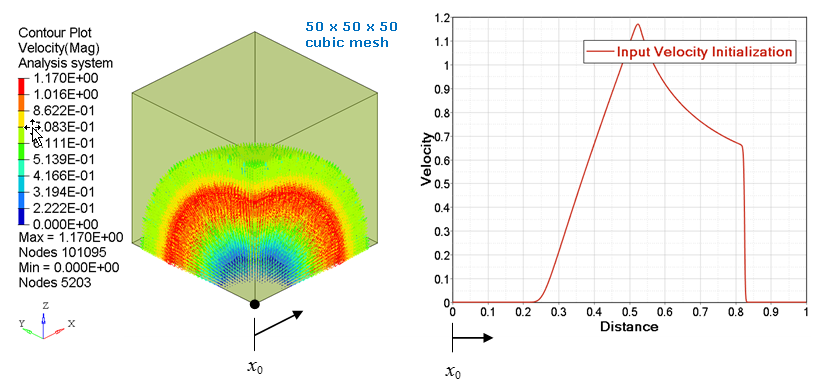
- type = 3: a spherical initialization is performed, using the origin defined by node_ID1. The abscissa values in an input function are the radial distance from origin. The ordinate values from the input function are a constant value for the entire spherical surface at given radial distance. See Figure 5 and Figure 6.
- If explosive material LAW5 (JWL) is
used as submaterial, then mapping will be proceeded considering all explosive was burnt
(burn fraction = 1.0). The mapping will be done with detonation products only with a burn
fraction = 1.0.
Figure 1. Mass density (with input function) planar mapping on a 50 x 50 x 50 cubic mesh 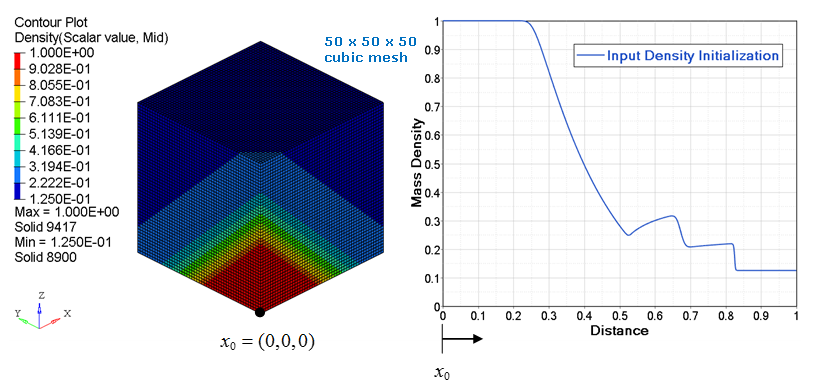
Figure 2. Velocity (with input function) planar mapping on a 50 x 50 x 50 cubic mesh 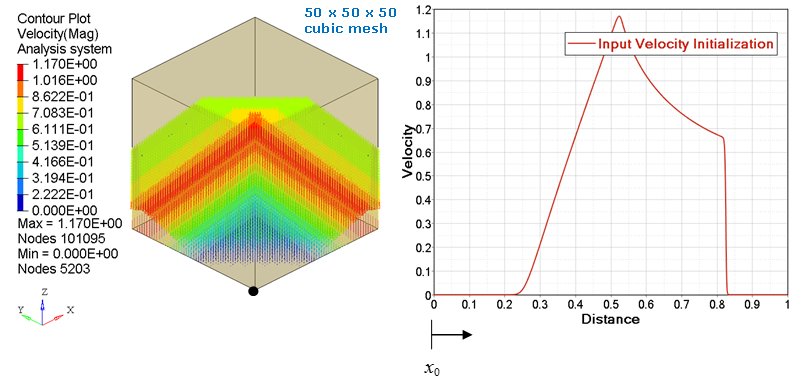
Figure 3. Mass density (with input function) cylindrical mapping on a 50 x 50 x 50 cubic mesh 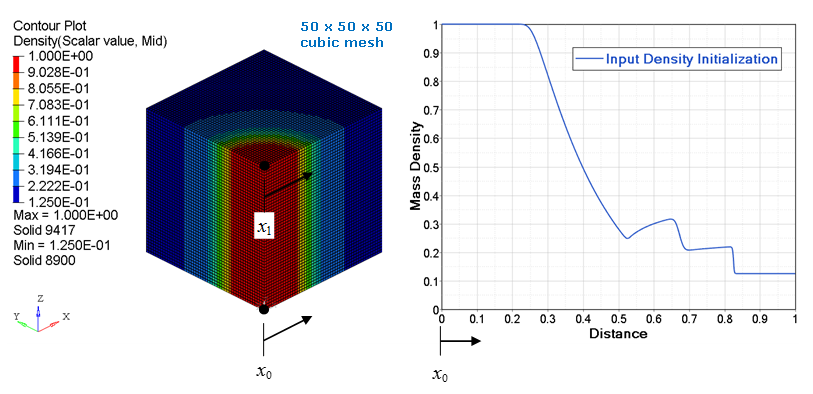
Figure 4. Velocity (with input function) cylindrical mapping on a 50 x 50 x 50 cubic mesh 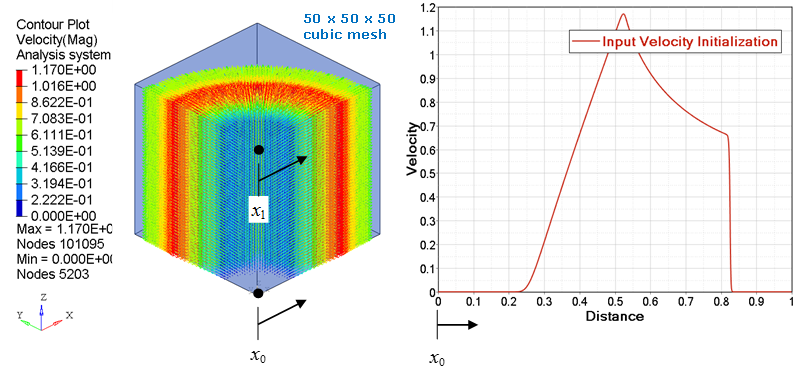
Figure 5. Mass density (with input function) spherical mapping on a 50 x 50 x 50 cubic mesh 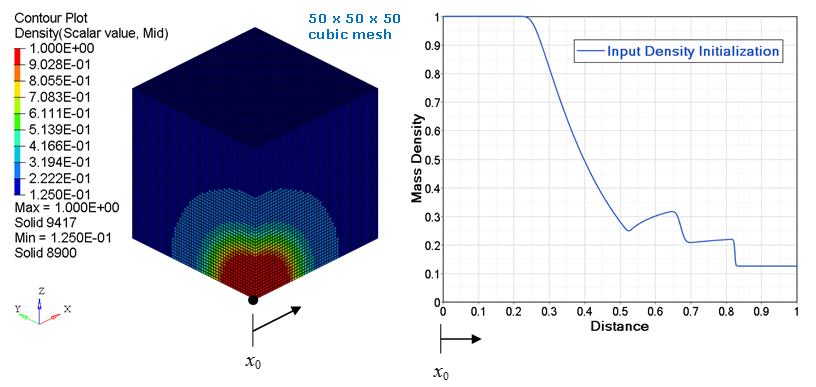
Figure 6. Velocity (with input function) spherical mapping on a 50 x 50 x 50 cubic mesh