Use Turbo VNC and Tight VNC
Virtual Network Computing(VNC) is an alternative to Remote Desktop. This comes with a client to be installed on your machine and a server to be installed on the processing machine, which can be a Windows or Linux processing machine. Generally, Administrator privileges are required for setup.
-
Use Tight VNC for the server on the processing machine and Turbo VNC for the
user machine.
The advantage of using Turbo VNC is that you can use the advanced graphics card options (do not select Legacy Particle Display).
-
For more information about installing and using Turbo VNC and Tight VNC, see
the following links:
- Turbo VNC website: http://www.turbovnc.org/.
- Turbo VNC download page: https://sourceforge.net/projects/turbovnc/files/.
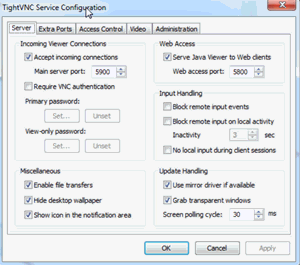
- Tight VNC website and download link: http://www.tightvnc.com/download.php.Note: It is recommended to reduce the Screen polling cycle for the Server to 30 ms (allows EDEM to display at 30 frames per second) for improved visualization speed, the default 1000 ms polling cycle resulted in slow EDEM display speeds.
Use Turbo VNC on Linux
On Linux systems, VirtualGL, and TurboVNC support remote rendering of OpenGL which is required by EDEM.
- Ensure that Virtual GL is installed using the following link: https://linuxcluster.wordpress.com/2010/07/25/using-turbovnc-0-6-and-virtualgl-2-1-4-to-run-opengl-application-remotely-on-centos/
-
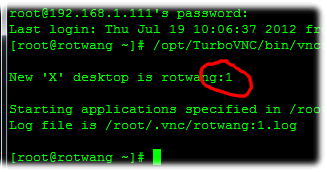
SSH to the machine first (using putty for example) and start the VNC server
(under your user account) using the following command:
/opt/TurboVNC/bin/vncserver -
After the server starts, note the number at the end of the line starting
with "New ‘X’ desktop", and then exit Putty.
-
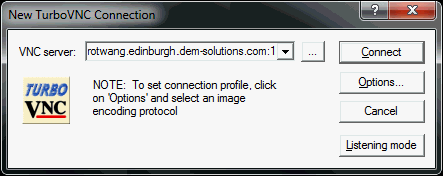
From your machine, start the VNC client and enter the
FQDN of the machine followed by a colon and the
number that you have previously noted.
-
Click Connect.
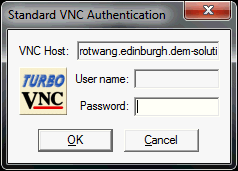
The VNC Authentication dialog box is displayed. -
Specify your password.
Your desktop now works as a console.
-
To use EDEM, enter the following command:
/opt/VirtualGL/bin/vglrun edem -
After you are finished, SSH back into the machine and stop the VNC Server
using the following command:
/opt/TurboVNC/bin/vncserver -kill :1 <replace 1 with the number from step 2>