Magnet
Magnet physical properties
- Example for an inner magnet
Here is an example of regions in an inner magnet. Note that the same principles apply to the outer magnet.
Table 1. Regions for inner magnet 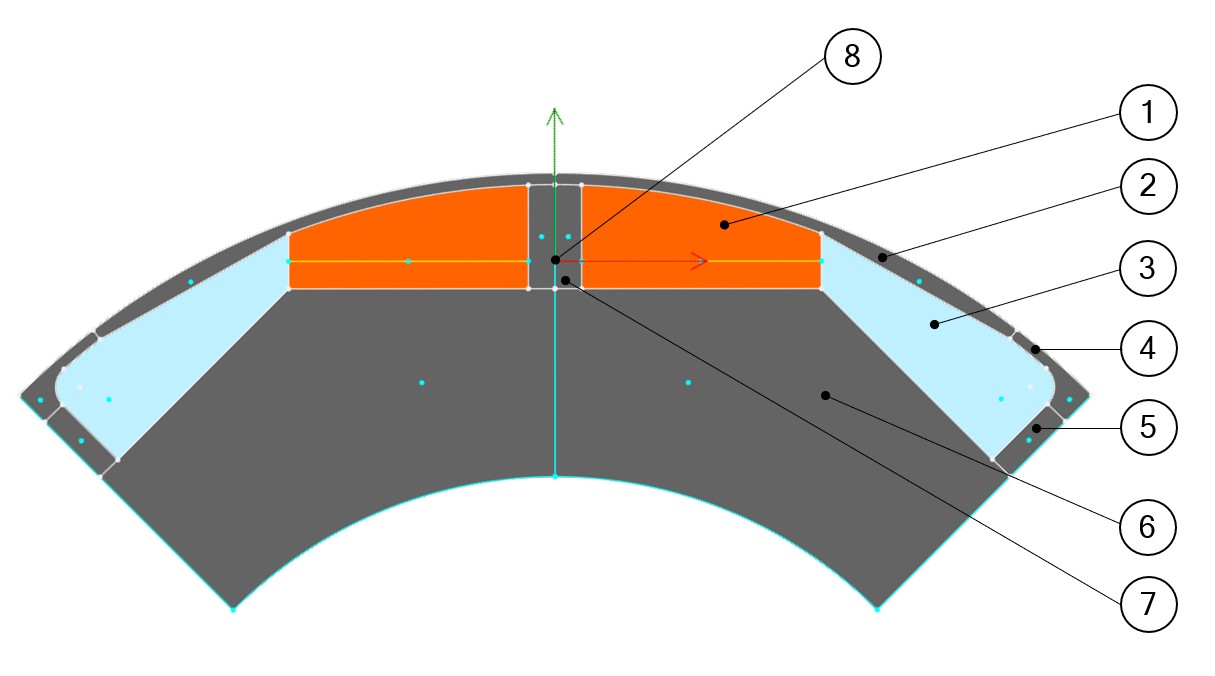
1 Magnet 2 Pole shoe 3 Edge 4 Bridge 5 Web 6 Yoke 7 Web 8 LOCAL coordinate system for defining the polarization of the magnet A coordinate system is dedicated to the magnet. This is what we call the LOCAL coordinate system.
It is used to define the magnet’s polarization.Note:- By default, a GLOBAL coordinate system is defined. Its reference point is located at the center of the rotor.
- For spoke magnets, the coordinate system defining polarization must be along the symmetry axis. Otherwise the polarization will not be consistent.
Figure 1. Definition of the local coordinate system for spoke magnets 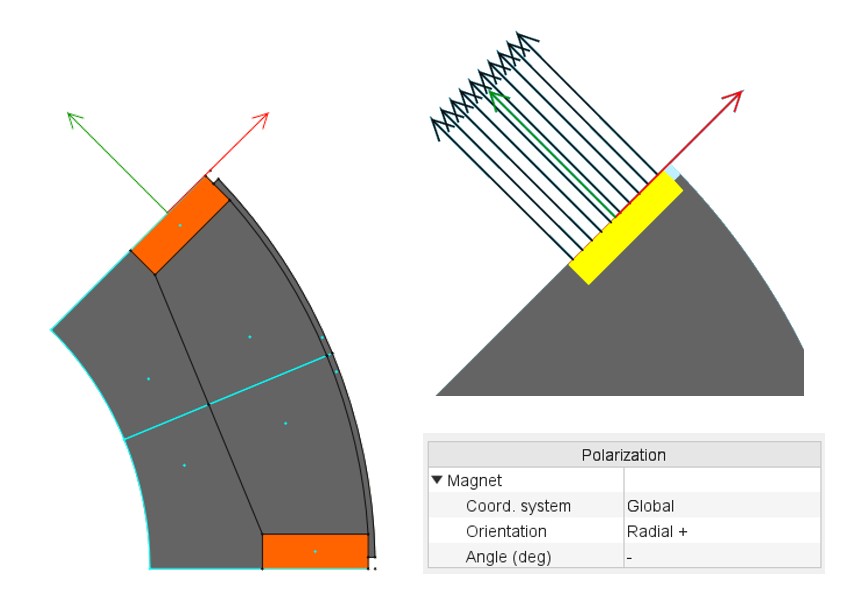
- List of possible elementary regions for an inner magnet.
- Magnet, Pole shoe, Edge, Bridge, Web, Yoke is illustrated above.
- Pole core, Interpole or Hub
Description of different ferromagnetic zones in the magnetic circuit associated with the magnet.- Hole or Slit
Figure 2. Example of slit 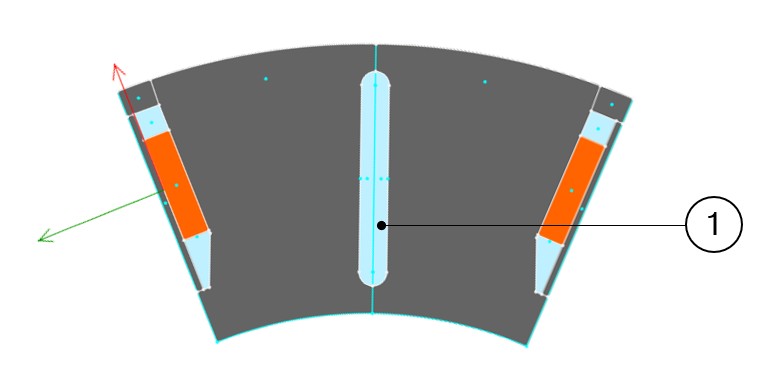
- Cooling hole
- Mechanical device to represent rivet for example
- Ferromagnetic wedge