Since version 2026, Flux 3D and Flux PEEC are no longer available.
Please use SimLab to create a new 3D project or to import an existing Flux 3D project.
Please use SimLab to create a new PEEC project (not possible to import an existing Flux PEEC project).
/!\ Documentation updates are in progress – some mentions of 3D may still appear.
Cut plane: about
Definition
A cut plane is a face support, on which the user can evaluate a spatial quantity.
Use
A cut plane is used for:
- plotting of scalar spatial quantities as color-shading isovalues
- plotting of scalar spatial quantities as arrows
Types of cut planes
A cut plane can be:
- a plane parallel to one of the planes XY, YZ or XZ
- a tilted plane passing through one of the axes X, Y or Z
- a plane defined by the equation Ax+By+Cz=D
Cut plane and infinite box
The spatial support of the cut plane type cannot be extended beyond the bounded study domain. (A cutting plane stops at the border of the infinite box. It does not exceed the infinite box.)
Mesh
The mesh of a cut plane is a surface mesh, which corresponds to the intersection of the cut plane with the volume elements that it cuts out.
XY, XZ, YZ planes
A plane parallel to one of the planes XY, YZ or XZ is characterized by:
- a coordinate system
- an offset position with respect to a plane
An example of the XY plane is presented below.
Tilted planes
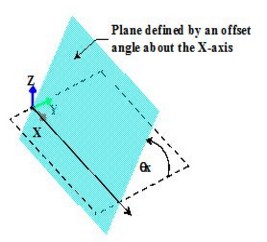
A tilted plane passing through one of the axes X, Y or Z is characterized by:
- a coordinate system
- a rotation angle around an axis
An example of the plane defined by an offset angle about the X-axis is presented below.
Plane defined by the equation Ax+By+Cz=D
A plane defined by the equation of the form Ax+By+Cz=D is characterized by:
- a coordinate system
- 4 coefficients of the equation
An example of the plane defined by the equation Ax+By+Cz=D with the coefficients of the equation different from 0 is presented below (the plane is rotated around two principal axes).