Since version 2026, Flux 3D and Flux PEEC are no longer available.
Please use SimLab to create a new 3D project or to import an existing Flux 3D project.
Please use SimLab to create a new PEEC project (not possible to import an existing Flux PEEC project).
/!\ Documentation updates are in progress – some mentions of 3D may still appear.
Linear approximation * exponential function of T
Presentation
This model defines a B(H) behavior law:
- linear (without taking the saturation into consideration)
- for an isotropic material
- through a magnetic susceptibility χ (where χ = μr - 1) which decreases in an exponential way when the temperature increases
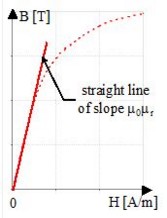
It can be used for low magnetic fields as long as saturation is not reached.
Mathematical model
This model is based on a straight line equation whose μr slope varies with the temperature.
The corresponding mathematical formula is written:
where:
- μ0 is the permeability of vacuum; μ0 = 4 π 10-7 H/m
- μr0 is the relative permeability of the material for T = 0 °C
- coeff(T) is the temperature coefficient function which describes how the magnetic susceptibility χ decreases when the temperature increases
The shape of the B(H) curve for several temperature values is presented in the figure below.