Since version 2026, Flux 3D and Flux PEEC are no longer available.
Please use SimLab to create a new 3D project or to import an existing Flux 3D project.
Please use SimLab to create a new PEEC project (not possible to import an existing Flux PEEC project).
/!\ Documentation updates are in progress – some mentions of 3D may still appear.
Magnet (vector): linear approximation
Presentation
These models ( Linear magnet described by the Cartesian / cylindrical / spherical vector Br ) define a B(H) dependence of linear demagnetization in Flux (not available in material manager).
Main characteristics:
- the mathematical model and the direction of magnetization are associated
- same number of materials and/or coordinate systems than regions
Mathematical model
In the direction of magnetization the model is a straight line.
The corresponding mathematical formula is written as follows:
Β(Η)=μ0μrΗ+ Br
where:
- μ0 is the permeability of vacuum, μ0 = 4 π 10-7 H/m
- μr is the relative permeability (recoil line slope)
- Br is the remanent flux density (T)
The shape of the B(H) dependence is given in the opposite figure:
Direction of magnetization
The direction of magnetization is “associated” with the model. Three models are provided: Cartesian, cylindrical or spherical vector.
Cartesian magnetization
The mathematical model is the linear model previously described.
The B(H) dependence is defined by the following relationship
in a Cartesian coordinate system: ![]()
where:
-
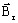 is the remanent flux density defined by three components following the three axes
of the Cartesian coordinate system: ( Brx, Bry,
Brz)
is the remanent flux density defined by three components following the three axes
of the Cartesian coordinate system: ( Brx, Bry,
Brz) - μr is the tensor of relative permeability; the three numerical values ( μrx, μry, μrz) correspond to the three axes of the Cartesian coordinate system
Cylindrical magnetization
The mathematical model is the linear model previously described.
The B(H) dependence is defined by the following relationship in a cylindrical coordinate
system: ![]()
where:
-
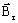 is the remanent
flux density defined by three components following the three axes of the cylindrical
coordinate system: ( Brr, Brθ and Brz)
is the remanent
flux density defined by three components following the three axes of the cylindrical
coordinate system: ( Brr, Brθ and Brz) - μ r is the relative permeability
|
|
|
|
| radial (Brr ) | orthoradial (Brθ) | axial (Brz) |
Spherical magnetization
The mathematical model is the linear model previously described.
The B(H) dependence is defined by the following relationship in a spherical coordinate
system: ![]()
where:
-
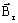 is the remanent flux
density defined by three components following the three axes of the spherical
coordinate system: ( Brr, Brθ et Brφ)
is the remanent flux
density defined by three components following the three axes of the spherical
coordinate system: ( Brr, Brθ et Brφ) - μ r is the relative permeability
radial (Brr ):