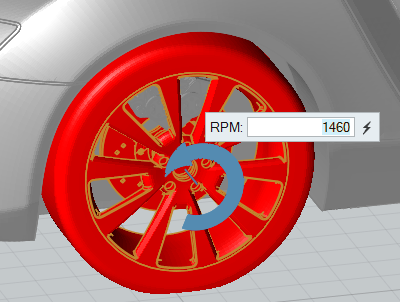
Specify Wheels
Identify the components that represent the model's wheels.
You need to select the parts forming the wheel, for example tire and rim. All other parameters like center of rotation, axis of rotation, and the angular velocity (in RPM) are computed automatically. If multiple parts are selected, VWT will group the parts into one or more wheels. For example, if you select the brake disc, the rim and the tire of the left front wheel, all three parts will be identified as wheel_1. If you also select the rim and the tire of the left rear wheel, those parts will be grouped into wheel_2.
-
Use the Identify Wheels tool.
- Right-click on a part in the modeling window or the Model Browser and select from the context menu.
- Select a part in the modeling window or the Model Browser then change the Identify As field to Wheel in the Property Editor.
Define MRF Regions
MRF regions define a volume in which the governing equations are solved in a rotating reference frame. This transformation of the equations can lead to higher accuracy for rotating bodies due the addition of centrifugal and Coriolis forces.
-
From the Setup ribbon, click the
Identify Parts tool.
Figure 5. 
-
From the secondary tool set, click MRF tool.
Figure 6. 
A guide bar appears below the tool. -
Make sure Wheel is active on the guide bar then select a wheel in the modeling window.
Parts previously identified as wheels are automatically grouped together.
The angular velocity and center of rotation of the rotating frame are extracted from the wheel definition.
- On the guide bar, click MRF.
-
In the modeling window, select regions to solve in the
rotating frame.
Regions solved in the rotating reference frame need to form closed volumes.
Figure 7. 
-
On the guide bar, click
 .
.
Figure 8. 
The MRF region is marked in the Model Browser.