Specify Heat Exchangers
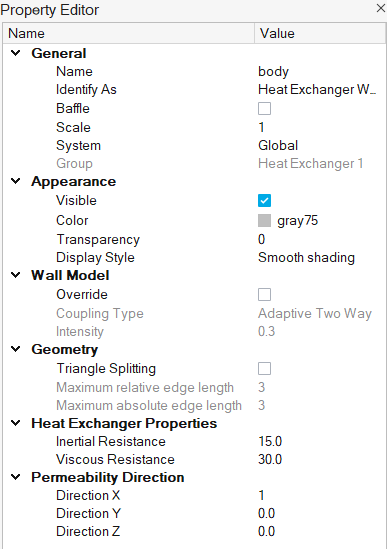
Identify the inflow, outflow, inertial resistance, and viscous resistance of heat exchangers, which are modeled as a porous medium.
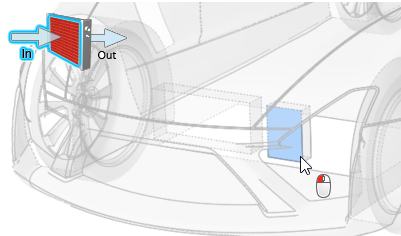
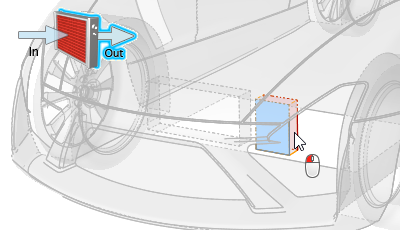
Identify the heat exchangers in one of the following ways: as a series of
in/out surfaces or as a single solid. Setting up a single solid heat exchanger is
more straightforward but requires you to define the permeability
direction.
-
Use the Identify Heat Exchanger tool. You can
choose to define each part of the heat exchanger solid, or define the solid as a
whole. To define the heat exchanger using in/out surfaces:
-
- Constant heat
- Applies a constant heat through the heat exchanger, defined in W.
-
- Fluid temperature
- Simulates a fluid moving through the heat exchanger, defined in K.
-
- Coolant temperature
- Simulates a coolant moving through the heat exchanger. This
thermal mode requires more properties to be defined, as well as
selecting a reference surface.
Figure 6. 
Figure 7. 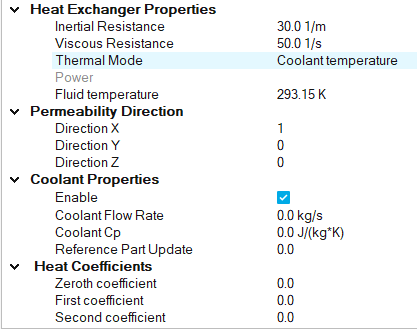
-
- Right-click on a part in the modeling window or the Model Browser and select from the context menu.
- Select a part in the modeling window or the Model Browser then change the Identify As field to Heat Exchanger Inlet/Outlet/Wall in the Property Editor.
-
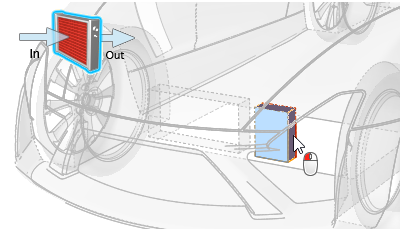
To define the heat exchanger as a whole solid:
Tip:
- Open the Property Editor and review the parameters associated with a particular heat exchanger by left-clicking on parts identified as a heat exchanger in the Model Browser. Heat exchanger properties that can be set include: inertial and viscous resistance, permeability direction, and thermal properties.
- Define additional heat exchangers by clicking
 in
the Heat Exchangers dialog. This will increase an
internal index to number all heat exchangers.
in
the Heat Exchangers dialog. This will increase an
internal index to number all heat exchangers. - Use the right-click context menu in the Heat Exchangers dialog to delete and rename heat exchangers.