Defining a Workplane
Define a workplane to create an oblique plane. Workplanes simplify the process of creating geometry on oblique planes in comparison to using transforms.
Note: A workplane can be defined
relative to another workplane.
-
Open the Create Workplane dialog using one of the
following workflows:
- On the Construct tab, in the Define group, click the
 Add Workplane icon.
Add Workplane icon. - On the model tree, a right-click context menu is available on the Workplanes group.
Select Add Workplane from the drop-down list.
Figure 1. The Add Workplane group is available on both the Construct and Configuration tabs in the model tree. 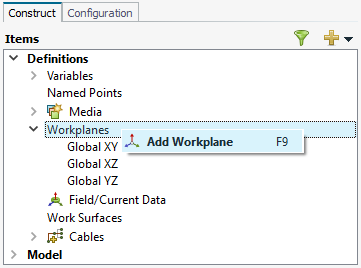
- On the model tree, click the
 icon. From the drop-down list, select Add
Workplane.
icon. From the drop-down list, select Add
Workplane. - Press F9 to use the keyboard shortcut.
- On the Construct tab, in the Define group, click the
- On the Create Workplane dialog, from the drop-down list, select Global YZ.
-
Use the default workplane label, Workplane1.
Figure 2. The Create Workplane dialog. 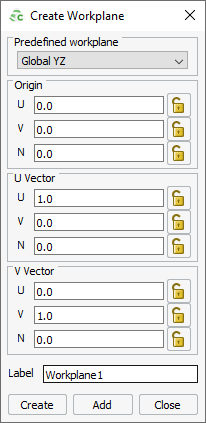
- Click Create to create the workplane and to close the dialog.
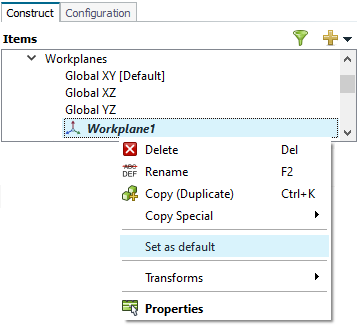
The default workplane is used when creating new geometry primitives. For
this example, set the new workplane as the default workplane.
-
In the model tree, select
Workplane1.
Note: The current default workplane is indicated by the text,
[Default].