Create a Thing Schema for Input/Output
You need to define the Thing that is going to represent and store the data from the FMU simulation.
The following schema has the minimum required properties for use in this tutorial:
{
"description": "",
"properties": {
"inputs": {
"properties": {
"inputHeatFlow": {
"type": "number"
}
},
"type": "object"
},
"outputs": {
"properties": {
"outputTemperature": {
"readOnly": true,
"type": "number"
}
},
"type": "object"
},
"state": {
"properties": {
"lastRun": {
"readOnly": true,
"type": "string"
},
"stopTime": {
"readOnly": true,
"type": "number"
}
},
"type": "object"
}
},
"title": "Simple Thermal"
} This schema has three properties of type object:
- inputs: where all input variables needed to run the FMU are defined
- outputs: where all the (selected) output from the FMU is stored
- state: where runtime state is stored
For this tutorial you only have a single input (inputHeatFlow) and a
single output (outputTemperature). Both are defined with type
number because they are defined as Real in the
FMU (inspect the /inputs and /outputs API
responses as described in an earlier section).
-
Go to and click New Thing.
Figure 1. 
-
Click on Skip to Schema in the modal:
Figure 2. 
-
Copy the example schema from the earlier section and paste it into the Schema
Editor. Click on Save.
Figure 3. 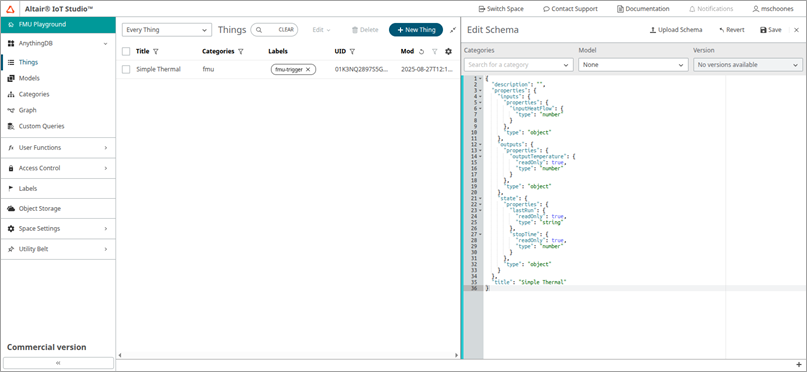
- On the Thing’s Details pane, click Add label + to add the MQTT label created in a previous step.
-
Copy the Thing’s UID and keep locally for later use.
Note: The Free trial of IoT Studio allows a maximum of 1000 messages per day. Upgrade to the Commercial version to increase the limits.