WiMAX, Urban, Fixed
Perform network planning for fixed WiMAX coverage in an urban scenario.
Model Type
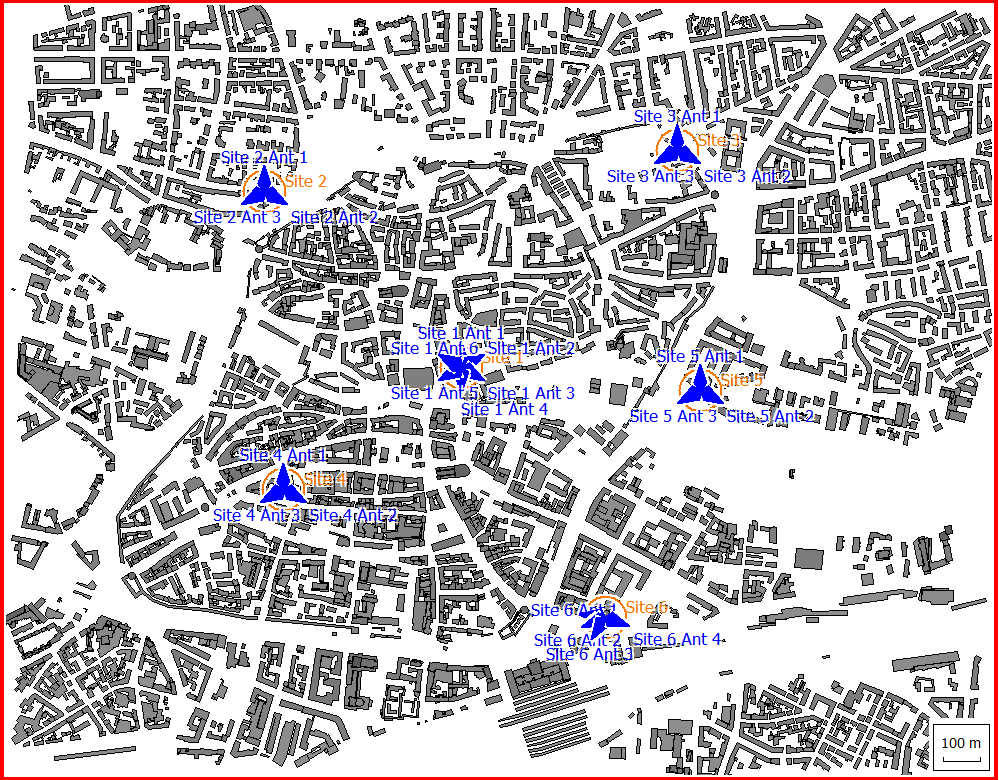
The geometry is described by urban buildings, see Figure 1. There is no additional topography meaning the terrain is flat.
Sites and Antennas
There are six sites in this scenario at different locations. Site 1 has six directional antennas at a height of 40 m. Sites 2 to 5 have three directional antennas, each at a height of 32 m. Site 6 has four directional radiators at a height of 32 m. The antennas use twelve different carrier frequencies between 3.5 and 3.6 GHz. Since the number of carriers is smaller than the number of antennas, there will be some interference.
Air Interface
A list of different modulation and coding schemes are added to this interface on the Air Interface tab, under Transmission Modes.
Computational Method
The dominant path model (DPM) is selected as this method focuses on the most relevant path, which leads to shorter computation times compared to ray tracing.
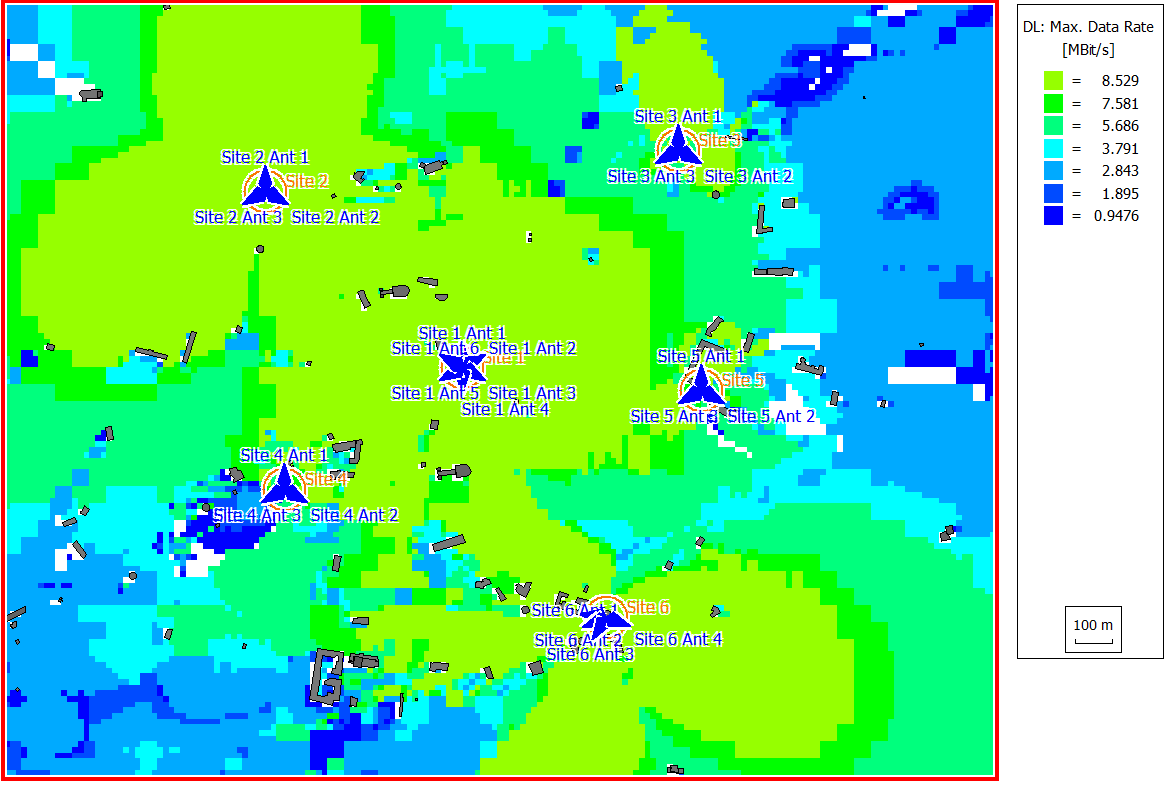
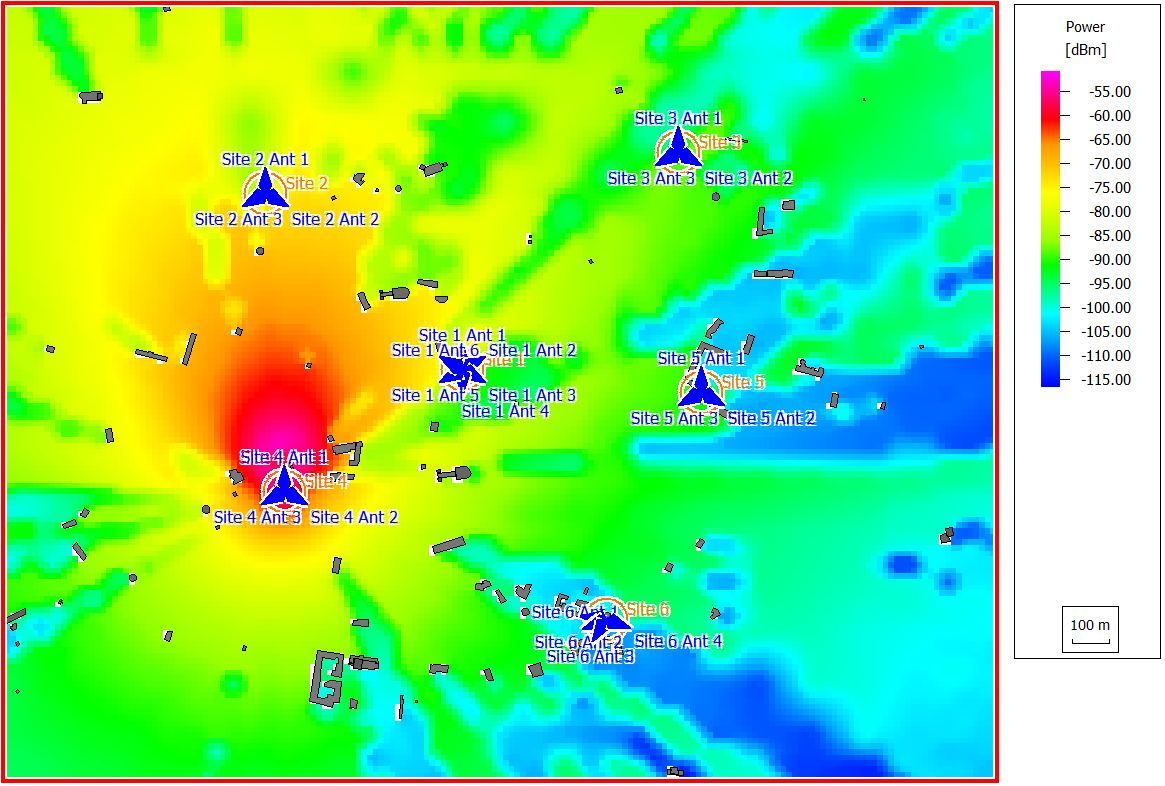
Results
- cell area
- site area
- best server
- maximum data rate for both uplink and downlink
- minimum required transmitter power
- reception probability
- SNIR (max) for all modulation and coding schemes for uplink and downlink