WiMAX, Indoor
Perform network analysis for indoor WiMAX coverage.
Model Type
The model consists of a large single-story building. The network planning is based on a description file for the air interface.
Air Interface
Sites and Antennas
Computational Method
The computation method used for this model is the dominant path model (DPM), which focuses on the most relevant path. This method leads to shorter computation times compared to standard ray tracing model (SRT).
Results
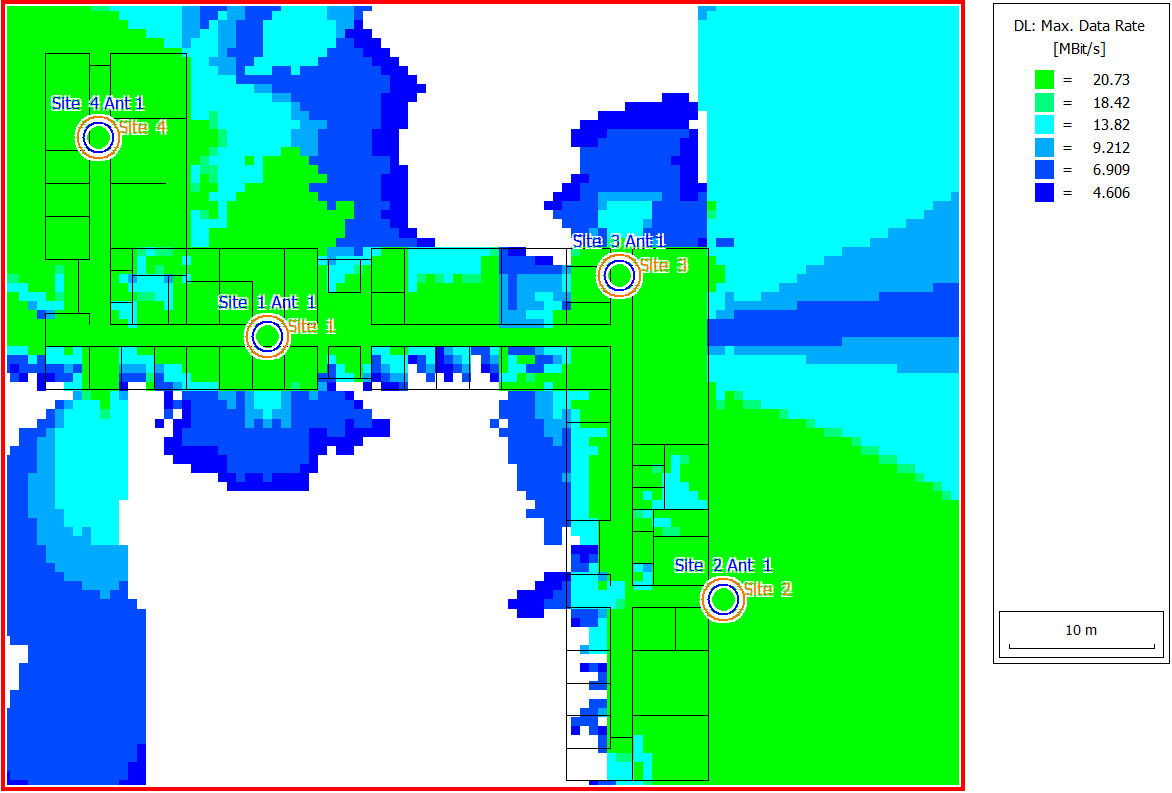
Propagation results show at every location the power received by a hypothetical isotropic receiving antenna from each transmitting antenna. Field strength and path loss are also available.
The network result show results such as cell area, signal-to-noise-and-interference ratio, and maximum achievable data rate, as well as quantities for specific modulation schemes. Because pairs of antennas interfere in this example, the SNIR is sometimes too low for successful communication. In this example, however, communication is still possible almost everywhere inside the building. Figure 1 shows the maximum achievable data rates.