Stability Copper
This DFE rule searches isolated copper patterns.
- Item: Enter item name.
- PWR/GND: Select Power/Ground net group
- Via Qty: Assign number of vias needed in plane to get stable power plane. The minimum value is 2.
- Area Size: Skip to test if area size is smaller than this area.
- Connection: The tool considers one net connection as a one via.
- Include Pin Count: The tool considers one pin as a one via.
- Pin on Copper: If pin count on copper is greater than pin count, the tool considers it as passed. (Even though the number of via are less than the required number.)
- Pin Count: Required pin count for ⑦.
- PTH Via Pass: Upon selecting this option, if at least one through-hole via exists, the test will pass.
Ground surface has influence on the ground signal’s stability. Improper ground structure causes ground fluctuation, signal distortion and EMI problems. If ground planes are located at all layers, they should be connected with vias, and it gets a good current path with proper distance among vias.
In many high-speed design practices, all signal nets are routed first and then the ground structure is constructed by automatically filling copper in empty areas.
Sometimes this automatic feature leaves isolated coppers (islands) without via connecting to ground. The isolated coppers cause a voltage floating status. If they are triggered by other signal traces, they will act as an antenna. Because of lack of electronic paths, they also make fluctuation of power and ground signal.
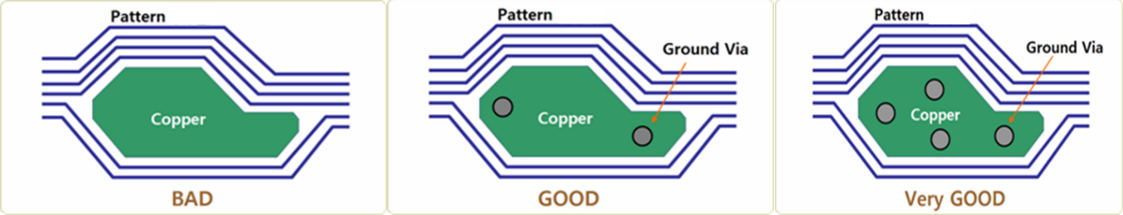
Figure 1.