Defining a Unit Cell
Define a layered unit cell using layers of substrate, free space and metal.
-
On the Periodic Structures tab, in the
Structure group, select
 Unit Cell.
Unit Cell.
Figure 1. The Create Unit Cell dialog. 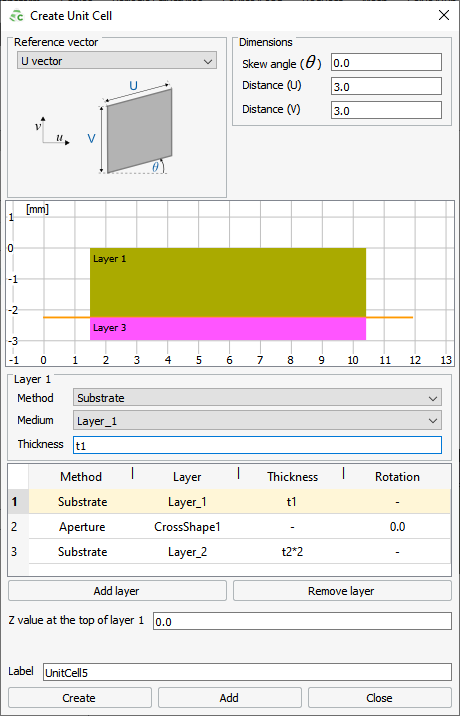
-
From the Reference Vector
drop-down list, select one of the following:
- To specify the skew angle relative to the U axis, select U vector.
- To specify the skew angle relative to the V axis, select V vector.
-
Under Dimensions, specify dimensions and orientation of
the unit cell:
-
For each layer:
- In the Z-value at the top of layer 1 field, specify the Z axis position of the top of layer 1.
- Click OK to define the unit cell and to close the dialog.