Timing Margin
This item analyzes and checks setup/hold time margin of SDR/DDR memory system.
The SDR means that the operating frequency of signal is half of the operating frequency of strobe signal.
The DDR means that the operating frequency of signal is the same as the operating frequency of strobe signal.
- The setup time margin of SDR/DDR memory system.
- The hold time margin of SDR/DDR memory system.
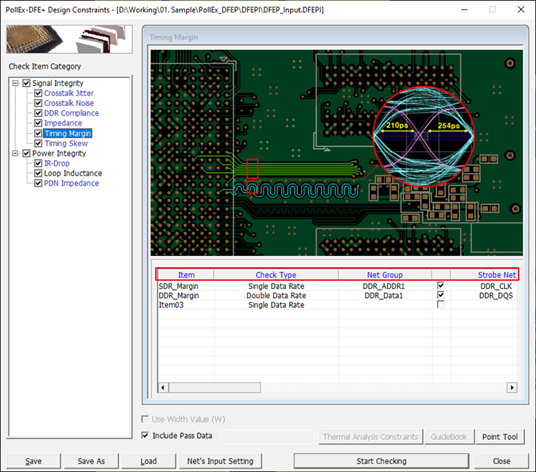
Figure 1. - Item: Sub item name. You can enter arbitrary name.
- Check Type: Select the clock operation structure of the memory system.
- Single Data Rate: Select if the operating frequency of signal is half of the operating frequency of strobe signal.
- Double Data Rate: Select if the operating frequency of signal is the same as the operating frequency of strobe signal.
- Net Group: Select target net groups to be tested. Allow multiple net groups.
- Strobe Net: Option to select target strobe net groups to be tested.(Clock, DQS, and so on)
- Start Component: Select component group to be used as signal driver.
- Except Component: Select component group to be excluded. Allow multiple component groups.
- Period(nS): Enter operating period in nS unit.
- The pulse period of input signal is automatically filled if user use Import DDR Spec option.
- Setup Time: Enter required setup time in nS unit.
- The setup time of input signal is automatically filled if you use Import DDR Spec option.
- Hold Time: Enter required setup time in nS unit.
- The hold time of input signal is automatically filled if user use Import DDR Spec option.
- Setup Margin: Enter minimum required setup time margin in nS unit.
- Hold Margin: Enter minimum required hold time margin in nS unit.
- Tolerance(%) option: Enter allowable tolerance of setup/hold time margin.
- Use Default Vth(Option): This option specifies the reference voltage for
timing checks.
- Uncheck: Set Vref to 1/2 of Waveform swing amplitude.
- Check: Use Vref declared in IBIS file as Threshold Voltage.
- Bi-Directional(Option): This option specifies the signaling direction of the signal.
- Uncheck: Check only the direction in which the Start Component is the Driver.
- Check: Check the direction of Start Component as Driver and Receiver.
- Analyze Options: You can assign driver/receiver buffer simulation model, driving strength of driver and other simulation parameters.
- Use pre-defined buffer model: The buffer model set in the electrical pin part of UPE is used as default. The user cannot change the buffer model here.
- Use user defined buffer model: You can assign simulation buffer model.
The default buffer model is initially assigned to the buffer model field which can be changed.
Click the Model field to view the device models selected for the output and input pins. You can change the device model selection when multiple models are available for the pin.
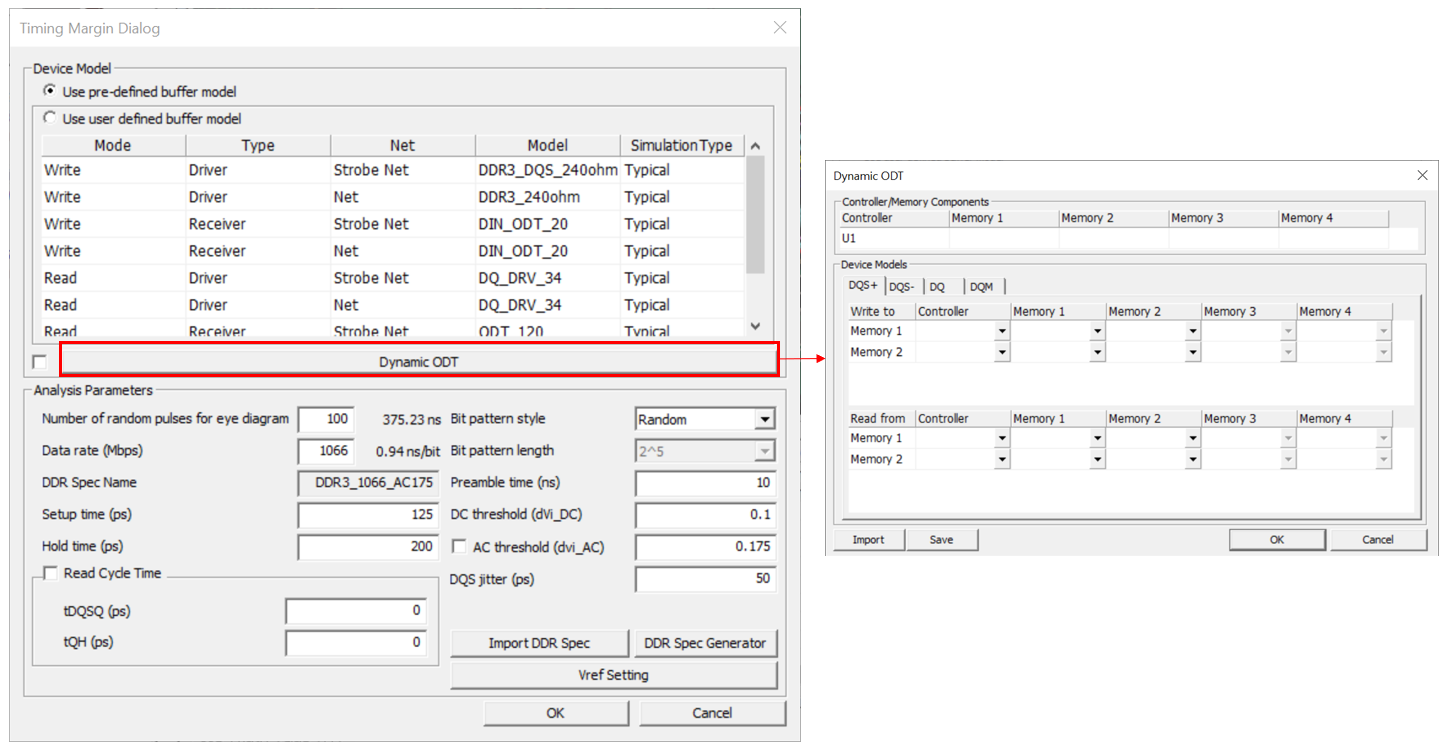
Figure 2.
- Model: The default buffer model is initially assigned to the buffer model field which can be changed by users. For the selected active driver, actual driver model can be selectable among many different models in IBIS or Linear device model types. User can use one of available models considering the output impedance, driving capability measured by output current level and operating frequencies. These driver’s characteristics lead huge impact on the simulated waveforms.
- Simulation Type: You can select the simulation type also among Typical, Fast, and Slow. The simulation type is applied to all device models used for the analysis.
- Dynamic ODT: This function allows for the individual configuration of On-Die Termination (ODT) for each memory when multiple memories are connected to a single controller on a PCB.
- Number of random pulses for eye diagram: Means the number of random pulses excited to the simulating net during the eye diagram analysis.
- Clock speed (Mbps): Enter DDR BUS operating speed. This value is automatically filled if user use Import DDR Spec option.
- DDR Spec Name: Shows DDR specification name. This value is automatically filled if user use Import DDR Spec option.
- Setup time(pS): Enter required setup time. This value is automatically filled if you use Import DDR Spec option.
- Hold time(pS): Enter required hold time. This value is automatically filled if you use Import DDR Spec option.
- Bit pattern style: Select the numerical method among random, ABS (Artificial Bit Stream) and PRBS (Pseudo Random Bit Stream) for generating the bit sequences. ABS (Artificial Bit Stream) is a method designed to provide a large pattern of bits to show worst case signal transmission quality of the net that would quickly converge the eye diagram. PRBS (Pseudo Random Bit Stream) is the mostly common method deemed as an industry standard.
- Bit pattern length: If bit pattern style is ABS or PRBS, choose the bit pattern length here.
- Preamble time(pS): Enter this value. Simulation start after this time to wait until status of internal circuit becomes stable.
- DC threshold (dvi_DC): Enter threshold voltage value for hold time measurement. This value is automatically filled if you use Import DDR Spec option.
- AC threshold (dvi_AC): Enter threshold voltage value for setup time measurement. This value is automatically filled if you use Import DDR Spec option.
- Clock jitter(pS): Enter system DDR bus jitter value.
- Read Cycle Time: Enter Read Cycle Time(tDQSQ, tQH) value for DQS time measurement when the memory operates as read cycle. This value is automatically filled if user use Import DDR Spec option.
- Import DDR Spec: In order to analyze DDR timing, enter every timing
parameter manually. Click Import DDR Spec to
automatically bring in a DDR timing specification to use among available DDR
timing tables.
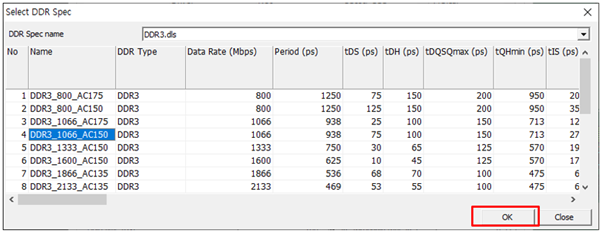
Figure 3.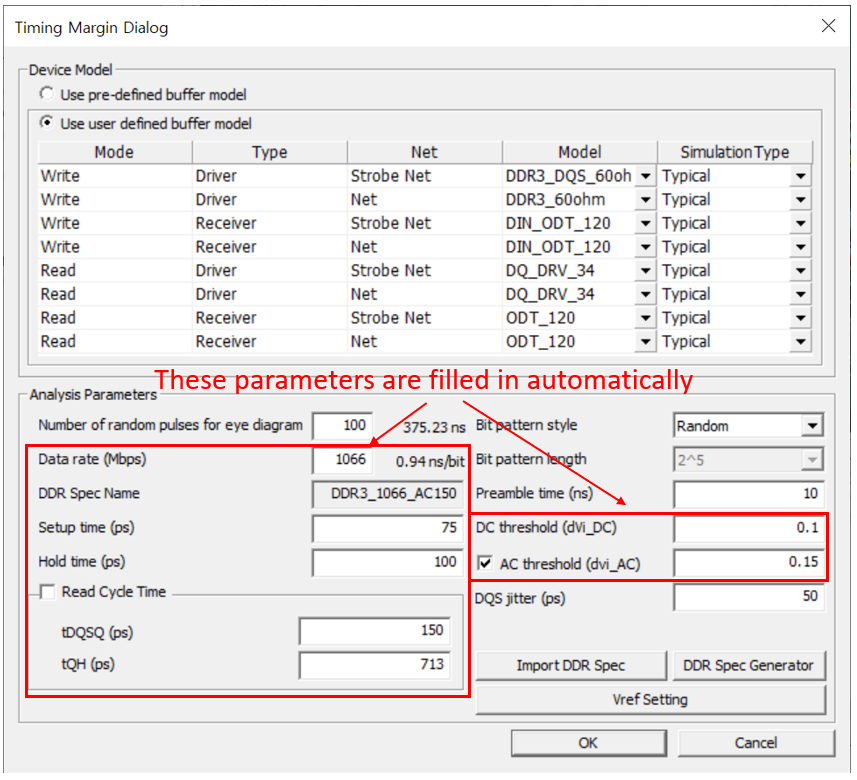
Figure 4. - DDR Spec Generator: You can also generate a new DDR timing specification into the exist DDR timing tables.
- Vref_DQ Setting: Normally the voltage level of Vref_DQ for timing check is defined by specification. But some technology memories, such as DDR4, require setting Vref_DQ value. Using this option, you assign Vref_DQ voltage level.
- Extract Vref_DQ using analysis result: Using this option, the DFE+ tool find the appropriate Vref_DQ value during analysis.
- Vref_DQ training result: You can assign Vref_DQ value for each memory component manually.