Since version 2026, Flux 3D and Flux PEEC are no longer available.
Please use SimLab to create a new 3D project or to import an existing Flux 3D project.
Please use SimLab to create a new PEEC project (not possible to import an existing Flux PEEC project).
/!\ Documentation updates are in progress – some mentions of 3D may still appear.
Thermal conductivity: definitions
Definition
The thermal conductivity k is a thermo-physical material property, which characterizes the quantity of heat transferred through a unit surface area in a time unit when the heat transfer is generated by a temperature gradient.
This quantity appears in Fourier's law:
![]()
where:
-
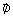 is the flux density
of the heat (W/m2)
is the flux density
of the heat (W/m2) - k is the tensor of the thermal conductivity (W/m/degree)
- T is the temperature (in degrees)
The thermal conductivity characterizes the ability of the material to transfer heat.
Dependence on temperature
The thermal conductivity can depend on the temperature: k=f(T). It increases or decreases when the temperature increases.