Lamination
Here are the properties needed to define a new lamination:
Description
| Label | Unit |
| Author | * |
| Manufacturer | * |
| Price | USD/kg |
| Reminder | * |
Mechanic
| Label | Unit |
| Sheet thickness | mm |
| Stacking factor | 1 |
| Mass density | kg/m3 |
| Young modulus | N/m2 |
| Poisson ratio | 1 |
Magnetic
| Label | Unit |
| Relative permeability | 1 |
| Magnetic polarization at saturation Js | T |
| Relative permeability | 1 |
| Knee coefficient | 1 |
Iron losses
| Label | Unit |
| Hysteresis loss coefficient (kh) | 1 |
| Exponent of B for the hysteresis losses (αh) | 1 |
| Exponent of f for the hysteresis losses (βh) | 1 |
| Classical loss coefficient - Sine wave (kc x kαc) | 1 |
| Classical loss coefficient - Any wave (kc) | 1 |
| Exponent for the classical losses (αc) | 1 |
| Excess loss coefficient - Sine wave (ke x kαe) | 1 |
| Excess loss coefficient - Any wave (ke) | 1 |
| Exponent of B for the excess losses (αe) | 1 |
Thermic
| Label | Unit |
| Reference temperature - Tref | °C |
| Thermal conductivity in the lamination direction at Tref | W/K/m |
| Thermal conductivity in the lamination insulation at Tref | W/K/m |
| Equivalent thermal conductivity in the lamination depth at Tref | W/K/m |
| Specific heat at Tref | J/K/kg |
Operating conditions
| Label | Unit |
| Frequency | Hz |
Note: The B(H) curve is defined with an analytical model given in
the Advanced section: Create a B(H) curve.
Note: A default stacking factor is considered to define the B(H)
curve to analyze the behavior of the magnetic circuit of the machine.
The user must define the magnetic characteristics of the solid material, while the magnetic characteristics of the lamination stack are automatically deduced considering the value of the default stacking factor.
Note: This default stacking factor must be set as the
maximum value allowed by the supplier of lamination. The stacking factor that
considers the assembly of the actual magnetic circuit is defined in Motor Factory –
Design area – Assembly – Material section.
See Advanced section: Create a B(H) curve.
Note: Electric properties are defined via an iron loss
model.
Note: Iron losses are defined with an analytical model given in
Advanced section: Define iron loss parameters.
Note: The thermal conductivity “in depth” along the stacking
direction: Kd is computed as follows:
| Sr | Stacking factor |
| Kins | Thermal conductivity of the lamination insulation |
| Kam | Thermal conductivity in the lamination |
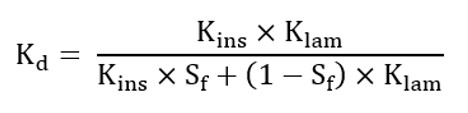
Note: The thermal conductivity of laminated regions is constant,
whatever the temperature of the region is.