What Are FMUs?
A Functional Mockup Unit (FMU) is an abstract representation of a dynamic system based on a tool independent standard interface called Functional Mockup Interface (FMI). An FMU enables the exchange of models from a very diverse range of domains and applications.
An FMU could be of the type Model Exchange (ME) or Co-simulation (CS) or both. An ME FMU contains the necessary states and variables that could be solved by the calling solver. A CS FMU can contain its own solver or calls another solver. In this case, two solvers co-simulate (one calling solver and other solving the FMU) to solve the entire model. An FMU may contain both modes ME and CS. In this case, the Type attribute in the FMU panel will be editable and you can select the mode in which the FMU is solved.
See the following for additional information:
MV-7012: Functional Mockup Unit (FMU) in MotionView and MotionSolve
Add an FMU in Inspire Motion
Add an FMU entity to the model.
-
On the Motion ribbon, under Profile, select Analyst.

-
Under Control, select the FMUs tool.

Tip: To find and open a tool, press Ctrl+F. For more information, see Find and Search for Tools.The guide panel is displayed.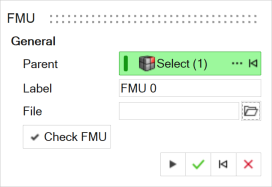
- Optional: To select a Parent system, click ....
- Optional:
Edit the Label.
Note: By default, variables names of entities follow a certain convention. For example, all FMU entities have a variable name starting with “FMU_”. This is the recommended convention to follow when building models since it has many advantages in identifying the entity during model editing and model manipulation.
-
Use the File browser to locate the FMU file and select
it.
An FMU file (
.fmu) is a zipped package that could contain the binaries and resources needed to solve the model that it represents along with a model description (.xml) file. -
To run the FMU compliance checker to provide more information and verify the
validity of the FMU, click the Check FMU button, and then
click the Details button to open the log file.
Note: Check FMU will run the FMU through the FMU compliance checker as provided by the FMI standard. Along with the information about the contents of the FMU, the checker verifies the validity of the information and try to execute the FMU. Warnings or errors are posted in the resulting log file.
The application runs the Check FMU on the model containing an FMU during a Check Model|Export Solver Deck|Run simulation and may flag an error or warning.
FMU Compliance Check Log from Check FMU 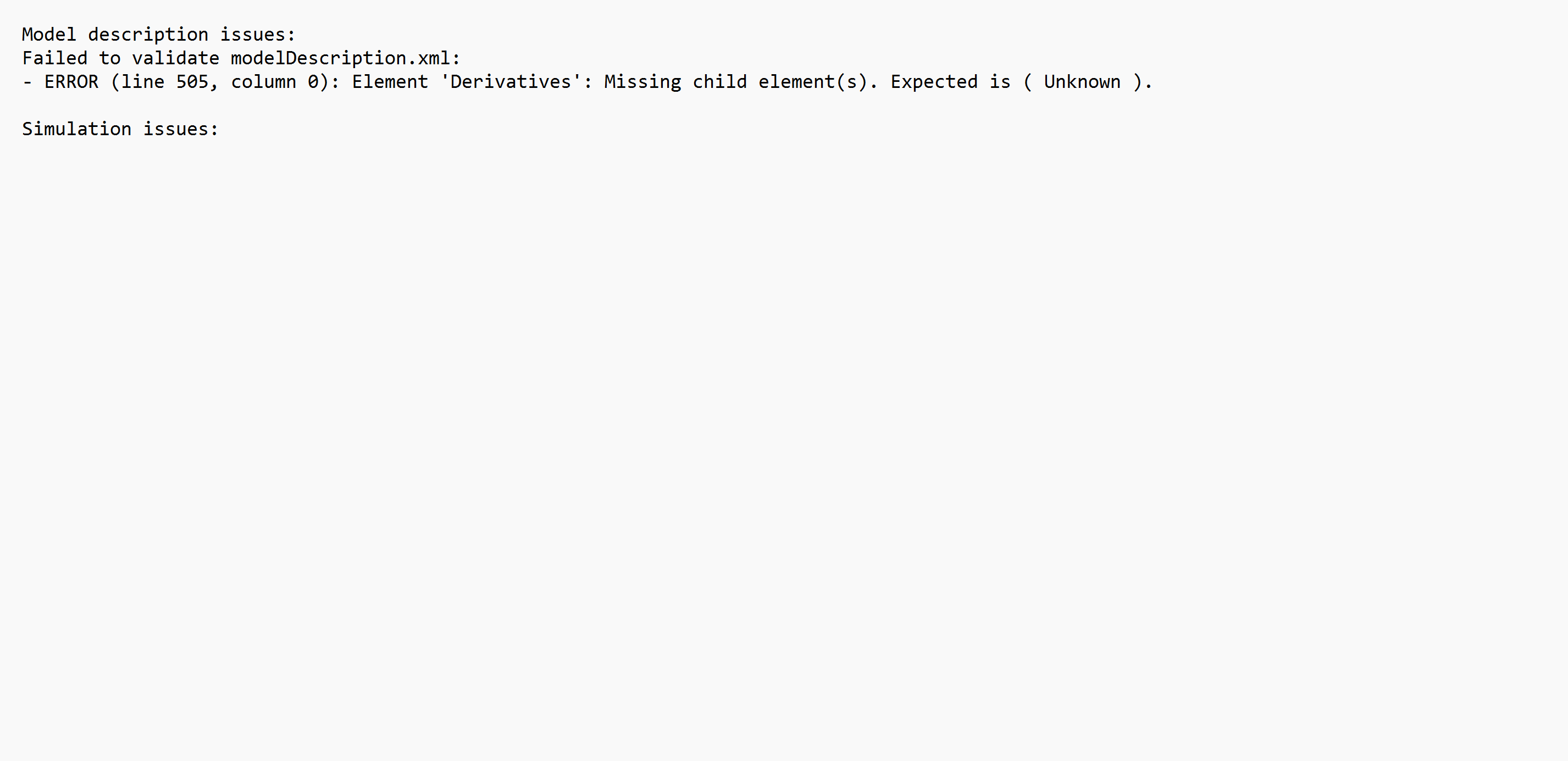
-
Click Apply
 .
The entity appears in the Model Browser and its properties appear in the Property Editor.
.
The entity appears in the Model Browser and its properties appear in the Property Editor. - Right-click and mouse through the check mark to exit, or double-right-click.
Connect an FMU to the Model in Inspire Motion
Import a Functional Mock-up Unit and connect it to the model.
- In the Property Editor, select Edit to open the FMU Editor by.
- Open the FMU Editor by clicking on Edit... within the Property Editor
- Provide solver expressions for each of the channels under the Value column of the Input tab.
-
Define the FMU Outputs. These are referenced by Force or Motion entities in the
Model.
The expression for the Forces/Motions in the Model use the ARYVAL function to reference the FMU outputs. The FMU outputs are available as attributes to the
y_arraydata member of the FMU entity. For instance,{fmu_1.y_array.output_3}, will contain the third output of the FMU.Figure 1. Force expression referring to an output of an FMU 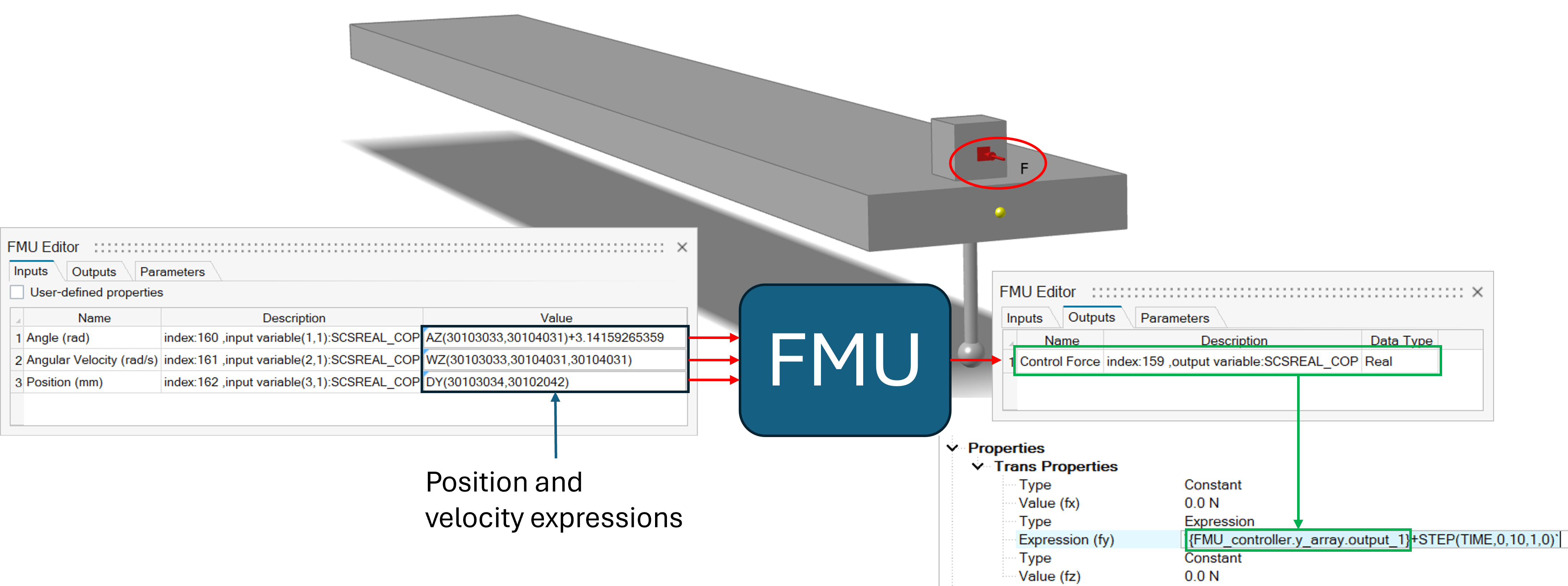
In the above model of a swing-up pendulum, the cart position and velocities captured by the solver expressions AZ(), WZ(), and DY() are provided as inputs to the FMU. The output from the FMU is tapped using the output attributes of the
y_arraydata member of the FMU that was resolved to the solver expression ARYVAL. In the demonstrated case, the force on the cart uses the first output. The expression{FMU_controller.y_array.output_1}returns the first output from the FMU’s (FMU_controller) output array (y_array).
Edit an FMU in Inspire Motion
Edit an FMU using the Property Editor.
-
Do one of the following:
- From the View menu, select Property Editor.
- Press F3.
- The selected FMU's properties are listed in the Property Editor and can be edited. Refer to FMU Properties.
FMU Properties in Inspire Motion
Descriptions of FMU properties in the Property Editor.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| General | |
| Name | Name of the entity |
| Variable Name | The variable name, a unique identifier string of the entity |
| ID | A unique identifying integer |
| Properties | |
| File | FMU file name with path |
| Type | Type of FMU
If an FMU contains both types, this option is available for selection. |
| Number of inputs | Number of input channels the FMU is seeking |
| Number of outputs | Number of output channels from the FMU |
| Number of states | Number of states within the FMU |
| Number of parameters | Number of parameters in the FMU |
| Model name | The name assigned to the model within the FMU. This is typically defined by the exporting tool and may be used for identification in simulation environments, logs, or user interfaces. |
| GUID | A globally unique identifier assigned to the FMU when it is generated. The GUID ensures that the FMU can be uniquely identified, which is important for version control, tool integration, and consistency checks during simulation. It follows a standardized format and should not be changed manually. |
| FMI version | The version of the Functional Mock-up Interface (FMI) standard that the FMU complies with. This determines compatibility with simulation tools and the supported features such as model exchange, co-simulation, and event handling. Currently, Inspire supports FMI 2.0 only. |
| Generation tool | Indicates the name and version of the software used to generate the FMU. This information can help identify the source of the model, assist with troubleshooting, and ensure compatibility between tools. |
| Values | An FMU represents a dynamic system which is characterized by arrays
of inputs (U), dynamic states (X), and outputs (Y). In addition, an
FMU can contain parameters that can be changed to vary the initial
state of the model that the FMU represents. Click on Edit to view and edit Input, Output, Parameters and Settings. The FMU Editor dialog box
appears. 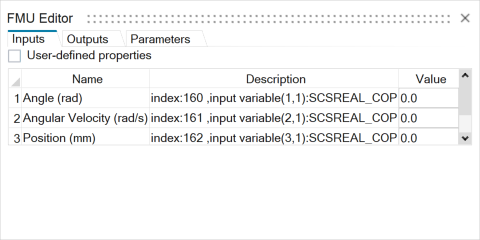 This dialog has the following tabs: Inputs The inputs tab lists all the input channels in the input array with their name and description. Provide a solver expression under the Value column to each of the channels as input to the FMU. The value of this solver expression is computed by MotionSolve during simulation and communicated to the FMU at every time-step of the simulation. To define how the input value is generated
during simulation using a custom expression or external
function, turn on User-defined
properties.
Outputs This tab lists all the output channels in the output array from the FMU with their names, descriptions, and data types. Parameters The parameters tab lists the parameters and initial conditions along with their default values in the FMU. Parameters are variables that are exposed by the FMU and can take a different value at the beginning of the simulation. Parameters can be of the type Real, Integer, Boolean, or String. |
| Settings | |
| Static hold | Applicable for FMU of type Model Exchange only. Flag to hold the value of the FMU’s dynamic states constant during a static or quasi-static simulation. Default: False |
| Communication interval | Time interval that MotionSolve uses to
communicate with the FMU. Value > 0, Default: Maximum integration step size |
| Error tolerance factor | Applicable for FMU of type Model Exchange only. A scale factor that
is multiplied to the displacement integration error tolerance define the
integration error tolerance for the continuous states of the
FMU. Value > 0, Default: 1.0 |
| Use address | Turn this option ON if the FMU is run on a different machine. Default: OFF (FMU is executed on the same machine as MotionSolve). |
| IP address | If Use Address is ON, provide the IP address of the machine where the FMU is executed. |